The Boeing 2707 was an American supersonic passenger airliner project during the 1960s. After winning a competition for a government-funded contract to build an American supersonic airliner, Boeing began development at its facilities in Seattle, Washington. The design emerged as a large aircraft with seating for 250 to 300 passengers and cruise speeds of approximately Mach 3. It was intended to be much larger and faster than competing supersonic transport (SST) designs such as Concorde.

The North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie is a retired prototype version of the planned B-70 nuclear-armed, deep-penetration supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command. Designed in the late 1950s by North American Aviation (NAA) to replace the B-52 Stratofortress and B-58 Hustler, the six-engined, delta-winged Valkyrie could cruise for thousands of miles at Mach 3+ while flying at 70,000 feet (21,000 m).

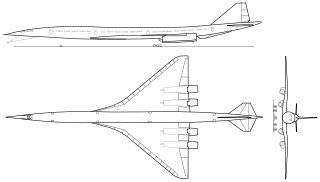
A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupolev Tu-144. The last passenger flight of the Tu-144 was in June 1978 and it was last flown in 1999 by NASA. Concorde's last commercial flight was in October 2003, with a November 26, 2003 ferry flight being its last airborne operation.

The Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor is a mixed-propulsion prototype interceptor aircraft, developed by Republic Aviation. The aircraft would use a jet engine for most flight, and a cluster of four small rocket engines for added thrust during climb and interception. The design was largely obsolete by the time it was completed due to the rapidly increasing performance of contemporary jet engines, and only two prototypes were built. One of these was the first American fighter to exceed Mach 1 in level flight.

The Lockheed L-2000 was Lockheed Corporation's entry in a government-funded competition to build the United States' first supersonic airliner in the 1960s. The L-2000 lost the contract to the Boeing 2707, but that competing design was ultimately canceled for political, environmental and economic reasons.

The Lockheed X-7 is an American unmanned test bed of the 1950s for ramjet engines and missile guidance technology. It was the basis for the later Lockheed AQM-60 Kingfisher, a system used to test American air defenses against nuclear missile attack.

The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-105, part of the Spiral program, was a crewed test vehicle to explore low-speed handling and landing. It was a visible result of a Soviet project to create an orbital spaceplane. The MiG 105 was nicknamed "Lapot", for the shape of its nose.

The Republic XF-103 was an American project to develop a powerful missile-armed interceptor aircraft capable of destroying Soviet bombers while flying at speeds as high as Mach 3. Despite a prolonged development, it never progressed past the mockup stage.

The Convair XF-92 is an American, delta wing, first-generation jet prototype. Originally conceived as a point-defence interceptor, the design was later used purely for experimental purposes and only one was built. However, it led Convair to use the delta-wing on a number of designs, including the F-102 Delta Dagger, F-106 Delta Dart, B-58 Hustler, the US Navy's F2Y Sea Dart as well as the VTOL FY Pogo.

The Sukhoi T-4, or "Aircraft 100", or "Project 100", or "Sotka" is a Soviet high-speed reconnaissance, anti-ship and strategic bomber aircraft that did not proceed beyond the prototype stage. It is sometimes called the Su-100.

The Heinkel He 118 was a prototype German monoplane dive bomber design that lost out to the Junkers Ju 87 Stuka in the 1930s, and was never ordered by the Luftwaffe.

The Messerschmitt P.1101 was a single-seat, single-jet fighter project of World War II, developed as part of the 15 July 1944 Emergency Fighter Program which sought a second generation of jet fighters for the Third Reich. A prominent feature of the P.1101 prototype was that the sweep angle of the wings could be changed before flight, a feature further developed in later variable-sweep aircraft such as the Bell X-5 and Grumman XF10F Jaguar.

Operational Requirement F.155 was a specification issued by the British Ministry of Supply on 15 January 1955 for an interceptor aircraft to defend the United Kingdom from Soviet high-flying nuclear-armed supersonic bombers.

The Tupolev Tu-244 was a proposed supersonic transport (SST) aircraft, developed from the Tu-144. It implemented novel features such as cryogenic fuel to enable flight distances of up to 10,000 km (6,200 mi) and would have carried up to 300 passengers. The project was cancelled in 1993.

The Tupolev Tu-2000 was a planned hypersonic flight experimental aircraft designed by the Tupolev design bureau. It was intended to test technologies for a single-stage-to-orbit aerospaceplane and also the Tupolev Tu-360 intercontinental bomber.

The NAC Fieldmaster was a British agricultural aircraft of the 1980s. A turboprop powered single-engined monoplane, it was built in small numbers and used both as a cropsprayer and a firefighting aircraft.
The Civil Aviation Department MG-1 was a one-off Indian motor glider, seating two side by side and first flown in 1983.

The Messerschmitt P.1110 was a design for a single-seat, high-altitude interceptor, prepared for the German Luftwaffe by the Messerschmitt aircraft manufacturing company, under the Emergency Fighter Program during the last months of World War II.
The Caproni Ca.66 was an Italian night bomber designed to reequip the post-World War I Italian Air Force. Only two examples of the four-engined biplane were built.

The Skraba S.T.3 was a two-seat Polish biplane built in 1928. It was the first all-metal aircraft designed in Poland; only one was completed.


















