The AGM-65 Maverick is an air-to-ground missile (AGM) designed for close air support. It is the most widely produced precision-guided missile in the Western world, and is effective against a wide range of tactical targets, including armor, air defenses, ships, ground transportation and fuel storage facilities.

A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided missile that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large payload over long distances with high precision. Modern cruise missiles are capable of traveling at high subsonic, supersonic, or hypersonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory.

The Douglas GAM-87 Skybolt was a air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) developed by the United States during the late 1950s. The basic concept was to allow US strategic bombers to launch their weapons from well outside the range of Soviet defenses, as much as 1,000 miles (1,600 km) from their targets. To do this in an air-launched form, a lightweight thermonuclear warhead was needed. Initially, the W47 from the Polaris missile was selected, but it was later replaced by the W59 from the Minuteman missile.

The BGM-109 TomahawkLand Attack Missile (TLAM) is an American long-range, all-weather, jet-powered, subsonic cruise missile that is primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy in ship and submarine-based land-attack operations.

The AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) is a glide bomb that resulted from a joint venture between the United States Navy and Air Force to deploy a standardized medium-range precision-guided weapon, especially for engagement of defended targets from outside the range of standard anti-aircraft defenses, thereby increasing aircraft survivability and minimizing friendly losses. It is intended to be used against soft targets such as parked aircraft, trucks, armored personnel carriers (APCs), and surface-to-air missile sites (SAMs). Prior to launch, it is given a destination through either a predesignated waypoint or a point marked through a targeting pod. It glides, using two wings that pop out for added lift, to the marked destination and dispenses submunitions in a short, roughly linear pattern. The designation of the Joint Standoff Weapon as an "air-to-ground missile" is a misnomer, as it is an unpowered bomb with guidance avionics, similar to the older GBU-15.

The Boeing AGM-69 SRAM was a nuclear air-to-surface missile. It had a range of up to 110 nautical miles, and was intended to allow US Air Force strategic bombers to penetrate Soviet airspace by neutralizing surface-to-air missile defenses.

The AGM-131 SRAM II was a nuclear air-to-surface missile intended as a replacement for the AGM-69 SRAM. The solid-fueled missile was to be dropped from a B-1B Lancer, carry the W89 warhead and have a range of 400 km. However, the program was canceled by President George H. W. Bush for geopolitical reasons just as the first flight-test missile was delivered.

The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after that jet's cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix used on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat.

The AGM-86 ALCM is an American subsonic air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) built by Boeing and operated by the United States Air Force. This missile was developed to increase the effectiveness and survivability of the Boeing B-52G and B-52H Stratofortress strategic bombers, allowing the aircraft to deliver its payload from a great distance. The missile dilutes an enemy's forces ability to respond and complicates air defense of its territory.

An air-to-surface missile (ASM) or air-to-ground missile (AGM) is a missile designed to be launched from military aircraft at targets on land or sea. There are also unpowered guided glide bombs not considered missiles. The two most common propulsion systems for air-to-surface missiles are rocket motors, usually with shorter range, and slower, longer-range jet engines. Some Soviet-designed air-to-surface missiles are powered by ramjets, giving them both long range and high speed.

The AGM-12 Bullpup is a short-range air-to-ground missile developed by Martin Marietta for the US Navy. It is among the earliest precision guided air-to-ground weapons and the first to be mass produced. It first saw operational use in 1959 on the A-4 Skyhawk, but soon found use on the A-6 Intruder, F-100 Super Sabre, F-105 Thunderchief, F-4 Phantom II, F-8 Crusader, and P-3 Orion in both Navy and US Air Force service, as well as NATO allies. The weapon was guided manually via a small joystick in the aircraft cockpit, which presented a number of problems and its ultimate accuracy was on the order of 10 metres (33 ft), greater than desired. In the 1960s it was increasingly supplanted by fully automatic weapons like the AGM-62 Walleye and AGM-65 Maverick.

The AGM-62 Walleye is a television-guided glide bomb which was produced by Martin Marietta and used by the United States Armed Forces from the 1960s-1990s. The Walleye I had a 825 lb (374 kg) high-explosive warhead; the later Walleye II "Fat Albert" version had a 2000 lb warhead and the ability to replace that with a W72 nuclear warhead.

The Popeye is a family of air-to-surface missiles developed and in use by Israel, of which several types have been developed for Israeli and export users. A long-range submarine-launched cruise missile variant of the Popeye Turbo has been speculated as being employed in Israel's submarine-based nuclear forces. The United States operated the Popeye under a different designation according to US naming conventions as the AGM-142 Have Nap.

The Kh-59 Ovod is a Russian cruise missile with a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system and 200 km range. The Kh-59M Ovod-M is a variant with a bigger warhead and turbojet engine. It is primarily a land-attack missile; the Kh-59MK variant targets ships.

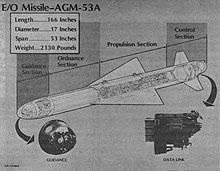
The W73 was a planned nuclear warhead for the AGM-53 Condor air to surface missile and designed by Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. The W73 warhead was cancelled in 1970 in favor of a purely conventional warhead for Condor. Condor was approved for production in 1975 with a expected production run of 250 missiles, but was cancelled in early 1976 due to high cost.
The B61 Family is a series of nuclear weapons based on the B61 nuclear bomb.

The AGR-20 Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) is a design conversion of Hydra 70 unguided rockets with a laser guidance kit to turn them into precision-guided munitions (PGMs). APKWS is approximately one-third the cost and one-third the weight of the current inventory of laser-guided weapons, has a lower yield more suitable for avoiding collateral damage, and takes one quarter of the time for ordnance personnel to load and unload.

The AGM-176 Griffin is a lightweight, precision-guided munition developed by Raytheon. It can be launched from the ground or air as a rocket-powered missile or dropped from the air as a guided bomb. It carries a relatively small warhead, and was designed to be a precision low-collateral damage weapon for irregular warfare. It has been used in combat by the United States military during the War in Afghanistan.

A precision-guided munition (PGM), also called a smart weapon, smart munition, or smart bomb, is a type of weapon system that integrates advanced guidance and control systems, such as GPS, laser guidance, or infrared sensors, with various types of munitions, typically missiles or artillery shells, to allow for high-accuracy strikes against designated targets. PGMs are designed to precisely hit a predetermined target, typically with a margin of error that is far smaller than conventional unguided munitions. Unlike unguided munitions, PGMs use active or passive control mechanisms capable of steering the weapon towards its intended target. PGMs are capable of mid-flight course corrections, allowing them to adjust and hit the intended target even if conditions change. PGMs can be deployed from various platforms, including aircraft, naval ships, ground vehicles, ground-based launchers, and UAVs. PGMs are primarily used in military operations to achieve greater accuracy, particularly in complex or sensitive environments, to reduce the risk to operators, lessen civilian harm, and minimize collateral damage. PGMs are considered an element of modern warfare to reduce unintended damage and civilian casualties. It is widely accepted that PGMs significantly outperform unguided weapons, particularly against fortified or mobile targets.
Television guidance (TGM) is a type of missile guidance system using a television camera in the missile or glide bomb that sends its signal back to the launch platform. There, a weapons officer or bomb aimer watches the image on a television screen and sends corrections to the missile, typically over a radio control link. Television guidance is not a seeker because it is not automated, although semi-automated systems with autopilots to smooth out the motion are known. They should not be confused with contrast seekers, which also use a television camera but are true automated seeker systems.