
The AIM-120 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile, or AMRAAM, is an American beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) capable of all-weather day-and-night operations. Designed with a 7-inch (180mm) diameter form-and-fit factor, and employing active transmit-receive radar guidance instead of semi-active receive-only radar guidance, it has the advantage of being a fire-and-forget weapon when compared to the previous generation Sparrow missiles. When an AMRAAM missile is launched, NATO pilots use the brevity code Fox Three.

Meteor is an active radar guided beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) developed by MBDA. Meteor offers a multi-shot capability against long range maneuvering targets, jets, UAVs and cruise missiles in a heavy electronic countermeasures (ECM) environment with a range in excess of 100 kilometres (54 nmi). A solid-fueled ramjet motor allows the missile to cruise at a speed of over Mach 4 and provides the missile with thrust and mid-way acceleration to target intercept. A two-way datalink enables the launch aircraft to provide mid-course target updates or retargeting if required, including data from off-board third parties. The datalink is capable of transmitting missile information such as functional and kinematic status, information about multiple targets, and notification of target acquisition by the seeker.

Stealth aircraft are designed to avoid detection using a variety of technologies that reduce reflection/emission of radar, infrared, visible light, radio frequency (RF) spectrum, and audio, collectively known as stealth technology. The F-117 Nighthawk was the first operational aircraft specifically designed around stealth technology. Other examples of stealth aircraft include the B-2 Spirit, the F-22 Raptor, the F-35 Lightning II, the Chengdu J-20, and the Sukhoi Su-57.

The Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23 is an American single-seat, twin-engine stealth fighter aircraft technology demonstrator designed for the United States Air Force (USAF). The design was a finalist in the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) competition, battling the Lockheed YF-22 for a production contract. Two YF-23 prototypes were built, nicknamed "Black Widow II" and "Gray Ghost".

The Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) was a demonstration and validation program undertaken by the United States Air Force to develop a next-generation air superiority fighter to counter emerging worldwide threats, including Soviet Sukhoi Su-27 and Mikoyan MiG-29 fighters under development in the 1980s. Lockheed and Northrop were selected in 1986 to develop the YF-22 and the YF-23 technology demonstrator aircraft. These aircraft were evaluated in 1991 and the Lockheed YF-22 was selected and later developed into the F-22 Raptor.

The North American XF-108 Rapier was a proposed long-range, high-speed interceptor aircraft designed by North American Aviation intended to defend the United States from supersonic Soviet strategic bombers. The aircraft would have cruised at speeds around Mach 3 with an unrefueled combat radius over 1,000 nautical miles, and was equipped with radar and missiles offering engagement ranges up to 100 miles (160 km) against bomber-sized targets.

The Lockheed/Boeing/General Dynamics YF-22 is an American single-seat, twin-engine fighter aircraft technology demonstrator designed for the United States Air Force (USAF). The design was a finalist in the USAF's Advanced Tactical Fighter competition, and two prototypes were built for the demonstration/validation phase of the competition. The YF-22 won the contest against the Northrop YF-23, and entered production as the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor. The YF-22 has a similar aerodynamic layout and configuration as the F-22, but with differences in the position and design of the cockpit, tail fins and wings, and in internal structural layout.

The Skyflash, or Sky Flash in marketing material, was a medium-range semi-active radar homing air-to-air missile derived from the US AIM-7 Sparrow missile and carried by Royal Air Force F-4 Phantoms and Tornado F3s, Italian Aeronautica Militare and Royal Saudi Air Force Tornados and Swedish Flygvapnet Viggens.

The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after its cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix.
A beyond-visual-range missile (BVR) is an air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) that is capable of engaging at ranges of 20 nmi (37 km) or beyond. This range has been achieved using dual pulse rocket motors or booster rocket motor and ramjet sustainer motor.
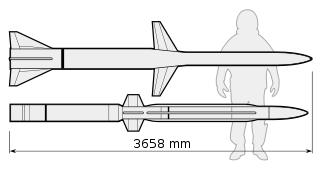
The AIM-152 AAAM was a long-range air-to-air missile developed by the United States. The program went through a protracted development stage but was never adopted by the United States Navy, due to the ending of the Cold War and the reduction in threat of its perceived primary target, Soviet supersonic bombers. Development was cancelled in 1992.
Scramjet programs refers to research and testing programs for the development of supersonic combustion ramjets, known as scramjets. This list provides a short overview of national and international collaborations, and civilian and military programs. The USA, Russia, India, and China (2014), have succeeded at developing scramjet technologies.

The Fairchild BQ-3, also known as the Model 79, was an early expendable unmanned aerial vehicle – referred to at the time as an "assault drone" – developed by Fairchild Aircraft from the company's AT-21 Gunner advanced trainer during the Second World War for use by the United States Army Air Forces. Two examples of the type were built and flight-tested, but the progress of guided missiles rendered the assault drone quickly obsolete, and the type was not produced.

The Alpha Draco missile, also known as Weapons System 199D (WS-199D), was an experimental ballistic missile developed by McDonnell Aircraft in the late 1950s to investigate the aerodynamic physics of the boost-glide reentry trajectory. Three test flights were conducted in 1959, of which two were successful.

The Advanced Strategic Air-Launched Missile (ASALM) was a medium-range strategic missile program, developed in the late 1970s for the United States Air Force. Intended for use in both the air-to-surface and anti-AWACS roles, the missile's development reached the stage of propulsion-system tests before being cancelled in 1980.

The AAM-A-1 Firebird was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Ryan Aeronautical Company. The first air-to-air missile program developed for the United States Air Force, the Firebird was extensively tested in the late 1940s; although it proved successful in testing, it was soon obsolete due to the rapid advances in aircraft and missile technology at the time and did not enter production.

The XSSM-A-5 Boojum, also known by the project number MX-775B, was a supersonic cruise missile developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Air Force in the late 1940s. Intended to deliver a nuclear warhead over intercontinental range, it was determined to be too ambitious a project given technical difficulties with the SM-62 Snark which it was to follow on from, and was canceled in 1951.

The AAM-N-4 Oriole was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company for the United States Navy. Designed for launch from carrier-based aircraft, the missile programme was cancelled before flight testing began, and the missiles produced were utilized as test vehicles.

The AAM-N-5 Meteor was an early American air-to-air missile, developed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Bell Aircraft for the United States Navy. Designed for launch from carrier-based aircraft, the program proceeded to the flight testing stage before being cancelled.

















