
Mariana Pimentel is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is located approximately 75 km from the state's capital, Porto Alegre.
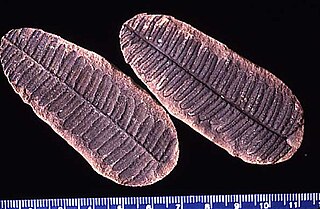
Pecopteris is a very common form genus of leaves. Most Pecopteris leaves and fronds are associated with the marattialean tree fern Psaronius. However, Pecopteris-type foliage also is borne on several filicalean ferns, and at least one seed fern. Pecopteris first appeared in the Devonian period, but flourished in the Carboniferous, especially the Pennsylvanian. Plants bearing these leaves became extinct in the Permian period, due to swamps disappearing and temperatures on Earth dropping.

Onchiodon is an extinct genus of temnospondyl. It is primarily known from the Carboniferous and Permian of Europe, but also from the Permian of North America. It was an amphibious carnivore.

Konzhukovia is an amphibian genus that belongs to an extinct group of temnospondyls, the largest clade of basal tetrapods including about 198 genera, 292 species, and more than half of which were alive during the early Mesozoic period. The animal was a predator that lived about 260 million years ago, and could get up to about three meters in length. Specifically, Konzukovia lived during the Permian, between 252 and 270 million years ago according to the type of rock the fossil was found in. There are three species within this genus, K. vetusta, K. tarda, and K. sangabrielensis, the first two originating from Russia while the latest originating from Southern Brazil. The discovery of this specimen in Southern Brazil provided more evidence to support the idea that during this animals existence, there was a “biological corridor” because of the supercontinent Pangea, allowing these species to be found so far apart from each other. Konzhukovia belongs to the family Archegosauridae, a family consisted of large temnospondyls that most likely compare to modern day crocodiles. Since the discovery of the latest species, K. sangabrielensis, Pacheco proposes that there must be the creation of a new family, Konzhokoviidae, a monophyletic group in a sister-group relationship with Stereospondlyi in order to accommodate the three species. Konzhukovia skulls usually exhibit typical rhinesuchid features including an overall parabolic shape, small orbits located more posteriorly, and the pterygoids do not reach the vomer. These animals were long-snouted amphibians that had clear adaptations made for fish catching, as well as exemplifying aquatic features.

Aceguá is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

Sphenopteris is a genus of seed ferns containing the foliage of various extinct plants, ranging from the Devonian to Late Cretaceous. One species, S. höninghausi, was transferred to the genus Crossotheca in 1911.
Samaropsis is a form genus named by Goeppert in 1864. Later Sewart (1917) redefined the taxon to refer only to the seeds.
Botrychiopsis is an extinct genus that existed from the Carboniferous to the Permian. Vascularized seedless plants (ferns) and reproduction by spores. They leaf type fronds. They lived in locals humid and swampy.
Cheirophyllum is an extinct plant genus that existed during the Permian.
Chiropteris is an extinct genus of plants that existed from the Early Permian to the Late Jurassic.
Stephanophyllites is an extinct genus of plants that lived in the Permian.
Kawizophyllum is an extinct genus of plants that lived in the Permian.
Cyclodendron was a genus of lycophytes dating from the Permian. Plants were vascularized with reproduction by spores.
Neomariopteris is a genus of plants dating from the Permian and Triassic Lower. Vascularized seedless plants (ferns) and reproduction by spores. They leaf type fronds. They lived in locals humid and swampy.
The extinct genus Coricladus of conifers was originally defined by André Jasper, Fresia Ricardi-Branco, and Margot Guerra-Sommer in 2005. The species Coricladus quiteriensis is the type species. The species is named in honor of the place where it was found, the Quitéria outcrop in the city of Pantano Grande in the geopark Paleorrota in Brazil. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and dates from the Sakmarian in the Permian.
Portalites is an extinct genus of acritarchs. The species Portalites gondwanensis was located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and date from Sakmarian in the Permian.
Leiosphaeridia is an extinct genus of algae or acritarchs. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Tetraporina is an extinct genus of algae. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota, on Rio Bonito Formation. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Quadrisporites is an extinct genus of acritarchs. The species Q. horridus was located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and date of Sakmarian in the Permian.
Rastosuchus is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Rhinesuchidae. It contains one species, Rastosuchus hammeri, found in the Permian Rio do Rasto Formation of Brazil.





