
Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish, with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as "plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, Hypostomus plecostomus, and are popular as aquarium fish.

Hypostomus is a genus of catfish in the family Loricariidae. They are native to tropical and subtropical South America. H. plecostomus is the popular freshwater aquarium fish formerly known as Plecostomus plecostomus. The taxonomic structure of the Loricariidae is still being expanded by scientists. Hypostomus is a highly species-rich and widely distributed catfish genus.

Otocinclus is a genus of catfish in the family Loricariidae native to South America, commonly known as "dwarf suckers" or "otos". This genus, like other loricariids, is characterized by rows of armour plating covering the body, as well as the underslung suckermouth. They are generally small in size; O. tapirape is the smallest of the species (2.4 cm), while O. flexilis is the biggest (5.5 cm). These species have adaptations that allow them to breathe air. A duct forms at the junction between the esophagus and the stomach and expands into an enlarged, ring-like diverticulum, characteristic of this genus, which allows air-breathing. Otocinclus are popular aquarium fish, and they are often purchased as algae eaters. It is difficult to breed them in captivity, and only wild caught Otocinclus are available to hobbyists. This genus is widely distributed east of the Andes of South America, throughout the lowlands from northern Venezuela to northern Argentina, but are generally absent from the Amazon and the Orinoco lowlands.

The genus Panaque contains a small number of small to medium-sized South American suckermouth armoured catfishes that are notable for being among the very few vertebrates that feed extensively on wood. In addition, algae and aufwuchs are an important part of the diet, and they use their rasping teeth to scrape this from rocks. These fish are also popular aquarium fish, where the sound of scraping as these fish forage for food is easily audible.
Cordylancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfish native to South America. It is much the same as Chaetostoma. The few differences are a wider head, longer cheek odontodes, and plates on the snout. Cordylancistrus can be found in rivers and streams high in the Andes, from Venezuela to Colombia.
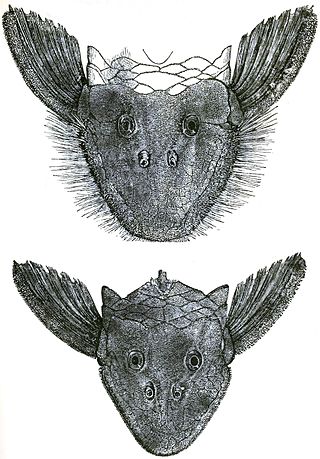
Pseudancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes native to South America.

Hemiancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes. These species are native to South America. The taxonomy of this genus is complex and unclear, and major work has to be done. Many of these fish are popular aquarium fish.
Neblinichthys is a small genus of suckermouth armored catfishes native to South America.

The Hypoptopomatinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Loricariidae, composed of 17 genera and approximately 80 species. This subfamily represents about one-tenth of all loricariid species.
Harttia is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America.
Ancistrus brevifilis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is a freshwater fish native to South America, where it occurs in the Tuy River basin in Venezuela. The species reaches 11.8 cm SL.
Andeancistrus platycephalus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Zamora River basin, which is part of the upper Marañon River drainage in Ecuador. The species reaches 14.5 cm in total length. The species was known as Cordylancistrus platycephalus until a 2015 reclassification, when Nathan K. Lujan, Vanessa Meza-Vargas, and Ramiro Barriga-Salazar constructed the genera Andeancistrus and Transancistrus.
Chaetostoma dupouii is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Tuy River basin in Venezuela. The species reaches 7.9 centimetres (3.1 in) SL. It was described in 1945 by Agustín Fernández-Yépez, a Venezuelan ichthyologist, with its type locality listed as the Encantado River, a tributary of the Río Grande, which itself is a tributary of the Tuy River.

Chaetostoma guairense is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is a freshwater fish native to South America, where it occurs in the basins of the Tuy River, the Guaire River, and Lake Valencia in Venezuela. The species reaches 8.1 cm (3.2 in) SL.
Chaetostoma pearsei is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the basins of the Tuy River and Lake Valencia in Venezuela. The species reaches 15 cm in total length.
Chaetostoma platyrhynchus is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Caquetá River basin in Colombia. The species reaches 9.5 cm in total length. The species is known to be of disputed classification and spelling.
Cordylancistrus daguae is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Dagua River basin in Colombia for which it is named. The species reaches 9.5 cm in total length.
Cordylancistrus perijae is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the basins of the Palmar River and the Socuy River in the Lake Maracaibo drainage in Venezuela. It is found in humid, tropical, mountainous rivers with transparent waters, moderate to strong currents, riverbeds composed of stones and sand, and little, if any, aquatic vegetation. The species is named for the Serranía del Perijá, a mountain range with foothills containing the type locality where it was first collected. It reaches 12.7 cm SL.
Cordylancistrus torbesensis is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Torbes River basin, which is part of the Apure River drainage in Venezuela. The species reaches 6.5 cm SL and it is named for the river basin in which it can be found.
Loricaria cuffyi is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Essequibo River and Rio Negro basins in Guyana, as well as the Orinoco basin in Venezuela, with its type locality being designated as the Ireng River. The species was described on the basis of 36 specimens in 2020 by Alejandro Londoño-Burbano, Alexander Urbano-Bonilla, and Matthew R. Thomas. FishBase does not yet list this species.







