
Sorrel, also called common sorrel or garden sorrel, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Polygonaceae. Other names for sorrel include spinach dock and narrow-leaved dock.

Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.

Myoga, myoga ginger or Japanese ginger is the species Zingiber mioga in the family Zingiberaceae. It is a deciduous herbaceous perennial native to Japan, China, and the southern part of Korea. Only its edible flower buds and flavorful shoots are used in cooking. The flower buds are finely shredded and used in Japanese cuisine as a garnish for miso soup, sunomono, and dishes such as roasted eggplant. In Korean cuisine, the flower buds are skewered alternately with pieces of meat and then are pan-fried.

The genus Helichrysum consists of an estimated 600 species of flowering plants in the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The type species is Helichrysum orientale. They often go by the names everlasting, immortelle, and strawflower. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words ἥλιος and χρῡσός.

A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. The term is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also widely used to distinguish plants with little or no woody growth from trees and shrubs, which are also technically perennials.

The term subshrub or undershrub refers to either a small shrub or a perennial that is largely herbaceous but slightly woody at the base. "Subshrub" is often used interchangeably with "bush".

A herbaceous border is a collection of perennial herbaceous plants arranged closely together, usually to create a dramatic effect through colour, shape or large scale. The term herbaceous border is mostly in use in the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth. In North America, the term perennial border is normally used.

Lomandra, commonly known as mat rushes, is a genus of perennial, herbaceous monocots in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Lomandroideae. There are 51 species, all of which are native to Australia; two of them also extend into New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Blandfordia, commonly known as Christmas bells, is a genus of four species of flowering plants native to eastern Australia. Christmas bells are tufted, perennial herbs with narrow, linear leaves and up to twenty large, drooping, cylindrical or bell-shaped flowers.
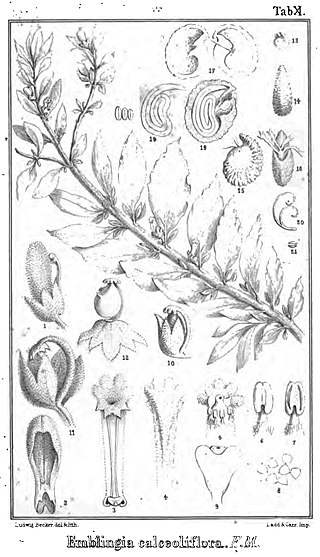
Emblingia is a monospecific plant genus containing the species Emblingia calceoliflora, a herbaceous prostrate subshrub endemic to Western Australia. It has no close relatives, and is now generally placed alone in family Emblingiaceae.
Ipomoea abrupta is a species of plant in the family Convolvulaceae of the genus Ipomoea. It is endemic to Western Australia.
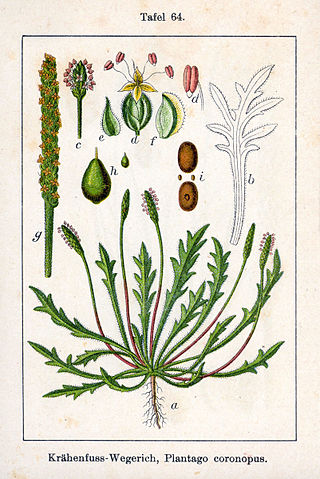
Plantago coronopus, the buck's-horn plantain, is a herbaceous annual to perennial flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae. Other common names in the US and Italy include minutina and erba stella.

Salvia indica is a species of herbaceous perennial plant belonging to the family Lamiaceae. It is native to a wide region of Western Asia that includes Israel, Iraq, Iran and Turkey. It was first described by the taxonomist Carl Linnaeus in 1753. It is unknown why he gave it the specific epithet indica, since the plant is not from India. While Salvia indica is classified as a herbaceous perennial, in cultivation individual plants often live no longer than two years.

Salvia is the largest genus of plants in the sage family Lamiaceae, with nearly 1000 species of shrubs, herbaceous perennials, and annuals. Within the Lamiaceae, Salvia is part of the tribe Mentheae within the subfamily Nepetoideae. One of several genera commonly referred to as sage, it includes two widely used herbs, Salvia officinalis and Salvia rosmarinus.

In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distinguishes herbs from spices. Herbs generally refers to the leafy green or flowering parts of a plant, while spices are usually dried and produced from other parts of the plant, including seeds, bark, roots and fruits.

Coronidium elatum, commonly known as the white paper daisy or tall everlasting, is a perennial herbaceous shrub in the family Asteraceae found in open forests in eastern Australia. A woody shrub 0.6 to 2 m tall, it has white flowers which appear in spring. It was known as Helichrysum elatum for many years until it was finally reviewed in 2008.

Coronidium boormanii is a perennial herbaceous shrub in the family Asteraceae found in Australia. Previously known as Helichrysum boormanii, it was transferred to the genus Coronidium in 2008.

Coronidium scorpioides, commonly known as the button everlasting, is a perennial herbaceous shrub in the family Asteraceae found in Australia. Previously known as Helichrysum scorpioides, it was placed in the newly described genus Coronidium in 2008.
Paul Graham Wilson is an Australian botanist. As of 1998, Wilson was the most prolific contributor to the journal Nuytsia, contributing to the first issue in 1970 and to the 12th volume in 1998, which was dedicated to him for his contributions to plant taxonomy and to celebrate his 70th birthday. Since his retirement from the Western Australian Herbarium in 1993, he has helped to maintain a comprehensive census of the flora of Western Australia.

Coronidium rupicola, commonly known as the yellow button, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is a small, upright, perennial shrub with yellow flowers borne on a single stem and is endemic to Queensland, Australia.


















