
The Scarlets are one of the four professional Welsh rugby union teams and are based in Llanelli, Wales. Their home ground is the Parc y Scarlets stadium. They play in the United Rugby Championship and in European Professional Club Rugby competitions. The club was originally named the Llanelli Scarlets but was renamed at the start of the 2008–09 rugby season.

Eupatorium capillifolium, or dogfennel, is a North American perennial herbaceous plant in the family Asteraceae, native to the eastern and south-central United States. It is generally between 50 cm and 2 meters tall with several stems that fork from a substantial base. The stems and base are covered in leaves so dissected that they resemble branching green threads coming out of the stem in fractal patterns. When crushed, the leaves have a sour odor similar to dill pickles. The flowers have a subtle floral odor.

Cosmosoma is a genus of tiger moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1823.

Crambidia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was described by Packard in 1864.

Euchaetes is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. It was described by Thaddeus William Harris in 1841.

Syntomeida epilais, the polka-dot wasp moth or oleander moth, is a species of moth thought to be native to the Caribbean. Its larvae feed on the oleander plant. Like most wasp moths, these are day fliers.

Pygarctia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae.

Rhabdatomis is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1907.

Anageshna is a monotypic moth genus of the family Crambidae described by Eugene G. Munroe in 1956. Its only species, Anageshna primordialis, the yellow-spotted webworm, was described by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1907. It is found in the US states of Alabama, Arkansas, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Iowa, Illinois, Kansas, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Maryland, Maine, Minnesota, Missouri, Mississippi, North Carolina, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Texas, Virginia and West Virginia.

Ianius is a monotypic moth genus in the family Erebidae described by Richards in 1939. Its only species, Ianius mosca, was first described by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1910. It is found in Mexico and the southern United States, where it has been recorded from Texas.

Amata huebneri, commonly known as the wasp moth, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1829. It is found from the Indo Australian tropics to northern Australia.
Pyrrolizidine alkaloid sequestration by insects is a strategy to facilitate defense and mating. Various species of insects have been known to use molecular compounds from plants for their own defense and even as their pheromones or precursors to their pheromones. A few Lepidoptera have been found to sequester chemicals from plants which they retain throughout their life and some members of Erebidae are examples of this phenomenon. Starting in the mid-twentieth century researchers investigated various members of Arctiidae, and how these insects sequester pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) during their life stages, and use these chemicals as adults for pheromones or pheromone precursors. PAs are also used by members of the Arctiidae for defense against predators throughout the life of the insect.

Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. was an American entomologist. Dyar's Law, a pattern of geometric progression in the growth of insect parts, is named after him. He was also noted for eccentric pursuits which included digging tunnels under his home. He had a complicated personal life and along with his second wife he adopted the Baháʼí Faith.

Gabriola dyari, or Dyar's looper, is a moth of the family Geometridae first described by Taylor in 1904. It is found from the Alaskan panhandle and British Columbia to California. The habitat consists of coniferous forests.

Cosmosoma auge is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1767. It is found in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, Suriname, Brazil and Uruguay, as well as on St. Thomas, Jamaica, Cuba and Puerto Rico.
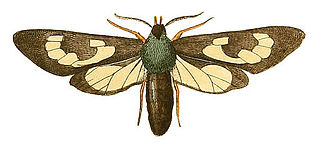
Cosmosoma fenestrata is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found on Jamaica and Cuba.

Cosmosoma festivum, the festivum wasp moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Costa Rica and Honduras. It has also been recorded in southern Florida and southern Texas.

Cosmosoma metallescens is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Édouard Ménétries in 1857. It is found from Mexico to the Amazon region.

Dinia eagrus, the scarlet-tipped wasp mimic moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Pieter Cramer in 1779.

The Euchromiina are a subtribe of tiger moths in the family Erebidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876. Many species in the subtribe are mimics of wasps. Euchromiina have always been considered closely related to the subtribe Ctenuchina due to their similarity to moths and wasps. These two subtribes make up around 3,000 valid species, the majority of which occur in the Neotropics.



















