Related Research Articles

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels.

The vacuum brake is a braking system employed on trains and introduced in the mid-1860s. A variant, the automatic vacuum brake system, became almost universal in British train equipment and in countries influenced by British practice. Vacuum brakes also enjoyed a brief period of adoption in the United States, primarily on narrow-gauge railroads. Their limitations caused them to be progressively superseded by compressed air systems starting in the United Kingdom from the 1970s onward. The vacuum brake system is now obsolete; it is not in large-scale usage anywhere in the world, other than in South Africa, largely supplanted by air brakes.
Rail transport terms are a form of technical terminology applied to railways. Although many terms are uniform across different nations and companies, they are by no means universal, with differences often originating from parallel development of rail transport systems in different parts of the world, and in the national origins of the engineers and managers who built the inaugural rail infrastructure. An example is the term railroad, used in North America, and railway, generally used in English-speaking countries outside North America and by the International Union of Railways. In English-speaking countries outside the United Kingdom, a mixture of US and UK terms may exist.

Main components found on a typical steam locomotive include:

An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow.

A railway brake is a type of brake used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration, control acceleration (downhill) or to keep them immobile when parked. While the basic principle is similar to that on road vehicle usage, operational features are more complex because of the need to control multiple linked carriages and to be effective on vehicles left without a prime mover. Clasp brakes are one type of brakes historically used on trains.

A condensing steam locomotive is a type of locomotive designed to recover exhaust steam, either in order to improve range between taking on boiler water, or to reduce emission of steam inside enclosed spaces. The apparatus takes the exhaust steam that would normally be used to produce a draft for the firebox, and routes it through a heat exchanger, into the boiler water tanks. Installations vary depending on the purpose, design and the type of locomotive to which it is fitted. It differs from the usual closed cycle condensing steam engine, in that the function of the condenser is primarily either to recover water, or to avoid excessive emissions to the atmosphere, rather than maintaining a vacuum to improve both efficiency and power.

A retarder is a device used to augment or replace some of the functions of primary friction-based braking systems, usually on heavy vehicles. Retarders serve to slow vehicles, or maintain a steady speed while traveling down a hill, and help prevent the vehicle from unintentional or uncontrolled acceleration when travelling on a road surface with an uneven grade. They are not usually capable of bringing vehicles to a standstill, as their effectiveness diminishes as a vehicle's speed lowers. Instead, they are typically used as an additional aid to slow vehicles, with the final braking done by a conventional friction braking system. An additional benefit retarders are capable of providing is an increase in the service life of the friction brake, as it is subsequently used less frequently, particularly at higher speeds. Additionally, air actuated brakes serve a dual role in conserving air pressure.
Engine efficiency of thermal engines is the relationship between the total energy contained in the fuel, and the amount of energy used to perform useful work. There are two classifications of thermal engines-
- Internal combustion and
- External combustion engines.
A steam diesel hybrid locomotive is a railway locomotive with a piston engine which could run on either steam from a boiler or diesel fuel. Examples were built in the United Kingdom, Soviet Union and Italy but the relatively high cost of fuel oil, or failure to resolve problems caused by technical complexity, meant that the designs were not pursued.

A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed boilers and worked at low to medium pressure but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a steam generator.

The Bavarian Class Gt 2×4/4 engine of the Royal Bavarian State Railways, was a heavy goods train tank locomotive of the Mallet type. It was later designated the DRG Class 96 by the DRG, DB and DR.

The Saxon Class XX were German eight-coupled express train, tender locomotives built for the Royal Saxon State Railways just after the First World War. The locomotives, which became known as the 'Pride of Saxony' (Sachsenstolz) were the first and only German express locomotives with a 2-8-2 wheel arrangement and, at the time of their appearance, were the largest express engines in the whole of Europe. In 1925, the Deutsche Reichsbahn grouped these locomotive into their DRG Class 19.0.
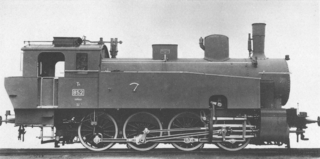
The Württemberg T 4 was a class of German, eight-coupled, goods train, tank locomotive operated by the Royal Württemberg State Railways.
Boilers for generating steam or hot water have been designed in countless shapes, sizes and configurations. An extensive terminology has evolved to describe their common features. This glossary provides definitions for these terms.

The NZASM 32 Tonner 0-4-2RT of 1894 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal.

The Central South African Railways Rack 4-6-4RT of 1905 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in Transvaal Colony.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.

The MÁV class 601 is a class of Hungarian four cylinder Mallet -type locomotives, which was designed to haul long and very heavy cargo on very steep railway tracks. With their 22.5 meter length and 2200 KW power, they were the largest and most powerful steam locomotives which have ever been built before and during the First World War in Europe.
References
- ↑ Ransome-Wallis, P. (1959). Illustrated Encyclopedia of World Railway Locomotives (2001 republication ed.). Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-41247-4., p. 251.