
Cryptocarya williwilliana, commonly known as small-leaved laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the laurel family and is endemic to near Kempsey in northern New South Wales. It is a tree or shrub with egg-shaped or lance-shaped leaves, the flowers creamy-green and perfumed, and the fruit a spherical to elliptic, black drupe.

Cryptocarya foetida, commonly known as stinking cryptocarya or stinking laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a small to medium-sized tree with egg-shaped to elliptic leaves, cream coloured, unpleasantly perfumed, tube-shaped flowers, and spherical black to purplish drupes.

Cryptocarya obovata, commonly known as pepperberry, white walnut, long tom, she beech or purple laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the laurel family and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a rainforest tree with oblong to egg-shaped leaves, the flowers creamy-green, tube-shaped and unpleasantly perfumed, and the fruit a spherical drupe with white or cream-coloured cotyledons.

Cryptocarya corrugata, commonly known as corduroy laurel, oak walnut, acidwood or bull's breath, is a species of flowering plant in the laurel family and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a tree with egg-shaped to elliptic leaves, the flowers creamy-green, slightly perfumed and tube-shaped, and the fruit a spherical black to bluish-black drupe.

Cryptocarya vulgaris commonly known as northern laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a tree with elliptic to oblong or lance-shaped leaves, creamy yellow and pale green, perfumed flowers, and spherical black drupes.

Cryptocarya cunninghamii, commonly known as Cunningham's laurel or coconut laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the laurel family and is endemic to northern Australia. It is a tree with oblong to elliptic leaves, the flowers creamy-green and tube-shaped, and the fruit a spherical black to purplish-blackdrupe.

Cryptocarya clarksoniana, commonly known as Clarkson's laurel, is a tree in the laurel family and is endemic to north Queensland. Its leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic, the flowers creamy-green and tube-shaped, and the fruit a spherical black drupe.
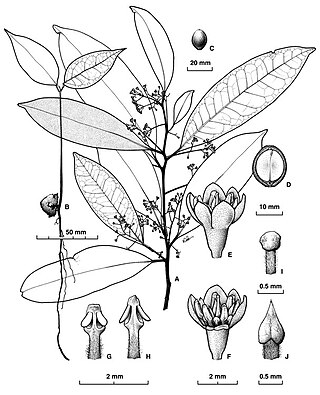
Cryptocarya claudiana, commonly known as Claudie laurel, is a tree in the laurel family and is endemic to Cape York Peninsula in Queensland. Its leaves are oblong to elliptic, the flowers creamy-green, perfumed and tube-shaped, and the fruit an elliptic or spherical black drupe.
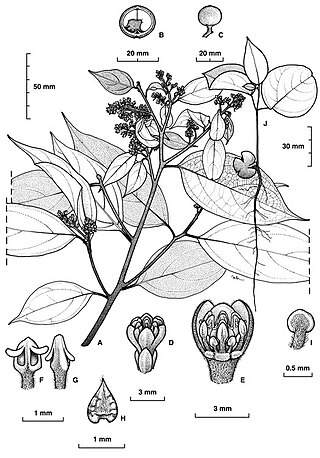
Cryptocarya cocosoides, commonly known as coconut laurel, is a tree in the laurel family and is endemic to north Queensland. Its leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic, the flowers creamy-green, perfumed and tube-shaped, and the fruit a spherical black to purple drupe.

Cryptocarya densiflora, commonly known as cinnamon laurel or white laurel, is a tree in the laurel family and is native to north Queensland and parts of Indonesia. Its leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic, the flowers yellowish-green and brown, tube-shaped but not perfumed, and the fruit is a flattened spherical, reddish maroon drupe that turns black when ripe.

Cryptocarya endiandrifolia, commonly known as narrow-leaved walnut, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae family and is native to Cape York Peninsula and New Guinea. Its leaves are elliptic to oblong or lance-shaped, the flowers cream-coloured or pale green and unpleasantly perfumed, and the fruit is a spherical to elliptic black drupe.

Cryptocarya exfoliata is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae family and is native to Cape York Peninsula the Northern Territory and New Guinea. Its leaves are lance-shaped, the flowers creamy-green and slightly perfumed, and the fruit is a spherical to elliptic black drupe.

Cryptocarya grandis, commonly known as cinnamon laurel or white laurel, is a tree in the laurel family and is endemic to north Queensland. Its leaves are lance-shaped to elliptic, the flowers creamy-green, unpleasantly perfumed and tube-shaped, and the fruit a spherical drupe.

Cryptocarya hypospodia, commonly known as northern laurel, white walnut, rib fruited pepperberry or north queensland purple laurel, is species of flowering plant in the laurel family and is native to northern Australia and New Guinea. It is a tree with elliptic to egg-shaped leaves, pale brown and creamy-green flowers, and spherical black drupes.

Cryptocarya pleurosperma, commonly known as poison walnut or poison laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to north-east Queensland. It is a tree with oblong to elliptic leaves, cream coloured, perfumed flowers, and usually spherical, ribbed, red drupes.

Cryptocarya rhodosperma is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a tree with lance-shaped to elliptic leaves, greenish, perfumed flowers, and elliptic, black drupes.

Cryptocarya saccharata, commonly known as sugar cane laurel, or corduroy laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a tree with lance-shaped leaves, creamy green, perfumed flowers, and elliptic or pear-shaped black to bluish-black drupes.

Cryptocarya sclerophylla, commonly known as totempole, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a tree or shrub with elliptic leaves, creamy green, perfumed flowers, and spherical or elliptic black drupes.

Cryptocarya smaragdina, commonly known as Dina's laurel, is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a shrub with lance-shaped leaves, creamy green, unpleasantly perfumed flowers, and spherical black drupes.
Cryptocarya whiffiniana is a species of flowering plant in the family Lauraceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a tree with oblong, lance-shaped or narrowly elliptic leaves, creamy green flowers, and elliptic glaucous or black drupes.




















