The Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).

GNU Wget is a computer program that retrieves content from web servers. It is part of the GNU Project. Its name derives from "World Wide Web" and "get". It supports downloading via HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
cURL is a computer software project providing a library (libcurl) and command-line tool (curl) for transferring data using various network protocols. The name stands for "Client for URL".
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator, serial console and network file transfer application. It supports several network protocols, including SCP, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and raw socket connection. It can also connect to a serial port. The name "PuTTY" has no official meaning.

FileZilla is a free and open-source, cross-platform FTP application, consisting of FileZilla Client and FileZilla Server. Clients are available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Both server and client support FTP and FTPS, while the client can in addition connect to SFTP servers. FileZilla's source code is hosted on SourceForge.
Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE) is a software interface for Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that lets non-privileged users create their own file systems without editing kernel code. This is achieved by running file system code in user space while the FUSE module provides only a bridge to the actual kernel interfaces.

WinSCP is a file manager, SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), WebDAV, Amazon S3, and secure copy protocol (SCP) client for Microsoft Windows. The WinSCP project has released its source code on GitHub under an open source license, while the program itself is distributed as proprietary freeware.

Transmit is a file transfer client program for macOS developed by Panic Inc. Transmit is trialware; after a seven-day trial period, the product can only be used for seven-minute sessions until it is purchased. Transmit was originally built as an FTP client and now supports a number of protocols including SFTP and WebDAV and cloud services including Google Drive and Dropbox.
SmartFTP is a network file transfer program for Microsoft Windows that supports file transfer via FTP, FTPS, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Box, Google Cloud Storage and Backblaze B2 protocols. It supports SSL/TLS, IPv6 and FXP, and features a transfer queue, proxy and firewall support, multiple connections, chmod features and drag-and-drop. The software uses the Windows API for its interface. It is available for both IA-32 and x64 editions of Windows.
CrushFTP is a proprietary multi-protocol, multi-platform file transfer server originally developed in 1999. CrushFTP is shareware with a tiered pricing model. It is targeted at home users on up to enterprise users.

ExpanDrive is a network filesystem client for MacOS, Microsoft Windows and Linux that facilitates mapping of local volume to many different types of cloud storage. When a server is mounted with ExpanDrive any program can read, write, and manage remote files as if they were stored locally. This is different from most file transfer clients because it is integrated into all applications on the operating system. It also does not require a file to be downloaded to access portions of the content. ExpanDrive is commercial software, at a cost of $49.95 per license. A 7-day, unrestricted demo is available for evaluation.

ZOC is a popular computer-based terminal emulator and Telnet software client for the Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh macOS operating systems that supports telnet, modem, SSH 1 and 2, ISDN, serial, TAPI, Rlogin and other means of communication. Its terminal emulator supports Xterm emulation with full colors, meta-keys and local printing, VT102, VT220 and several types of ANSI as well as Wyse, TVI, TN3270, and Sun's CDE. It supports full keyboard remapping, scripting in REXX and other languages, and support for named pipes.

Linoma Software was a developer of secure managed file transfer and IBM i software solutions. The company was acquired by HelpSystems in June 2016. Mid-sized companies, large enterprises and government entities use Linoma's software products to protect sensitive data and comply with data security regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA/HITECH, SOX, GLBA and state privacy laws. Linoma's software runs on a variety of platforms including Windows, Linux, UNIX, IBM i, AIX, Solaris, HP-UX and Mac OS X.
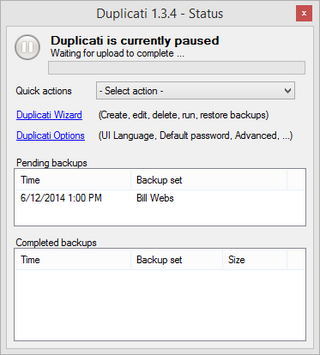
Duplicati is a backup client that securely stores encrypted, incremental, compressed remote backups of local files on cloud storage services and remote file servers. Duplicati supports not only various online backup services like OneDrive, Amazon S3, Backblaze, Rackspace Cloud Files, Tahoe LAFS, and Google Drive, but also any servers that support SSH/SFTP, WebDAV, or FTP.
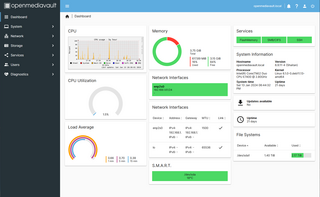
OpenMediaVault (OMV) is a free Linux distribution designed for network-attached storage (NAS). The project's lead developer is Volker Theile, who instituted it in 2009. OMV is based on the Debian operating system, and is licensed through the GNU General Public License v3.

ProFTPD is an FTP server. ProFTPD is Free and open-source software, compatible with Unix-like systems and Microsoft Windows . Along with vsftpd and Pure-FTPd, ProFTPD is among the most popular FTP servers in Unix-like environments today. Compared to those, which focus e.g. on simplicity, speed or security, ProFTPD's primary design goal is to be a highly feature rich FTP server, exposing a large amount of configuration options to the user.

FreeFileSync is a program used for file synchronization. It is available on Windows, Linux and macOS. The project is backed by donations. Donors get access to a Donation Edition that contains a few additional features such as an auto-updater, parallel sync, portable version, and silent installation. FreeFileSync has received positive reviews.

Commander One is a dual-pane file manager designed for macOS. Developed by Electronic Team, Inc., the software is created entirely in Swift and aims to provide users with a tool to navigate, manage, and manipulate files and folders on their Mac computers. The application offers a wide range of features for both casual and professional users.









