In music, a tone row or note row, also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found.

In mathematics, a permutation of a set is, loosely speaking, an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order, or if the set is already ordered, a rearrangement of its elements. The word "permutation" also refers to the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set.
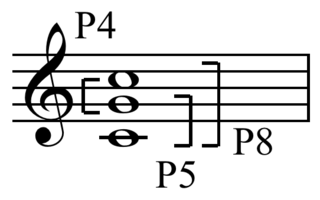
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.

Symmetry in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definition, and is usually used to refer to an object that is invariant under some transformations; including translation, reflection, rotation or scaling. Although these two meanings of "symmetry" can sometimes be told apart, they are intricately related, and hence are discussed together in this article.

The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition first devised by Austrian composer Josef Matthias Hauer, who published his "law of the twelve tones" in 1919. In 1923, Arnold Schoenberg (1874–1951) developed his own, better-known version of 12-tone technique, which became associated with the "Second Viennese School" composers, who were the primary users of the technique in the first decades of its existence. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale are sounded as often as one another in a piece of music while preventing the emphasis of any one note through the use of tone rows, orderings of the 12 pitch classes. All 12 notes are thus given more or less equal importance, and the music avoids being in a key. Over time, the technique increased greatly in popularity and eventually became widely influential on 20th-century composers. Many important composers who had originally not subscribed to or actively opposed the technique, such as Aaron Copland and Igor Stravinsky, eventually adopted it in their music.

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords, or sequences of chord tones, may also be considered as chords in the right musical context.

Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further developed the theory for analyzing atonal music, drawing on the twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of musical set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equal temperament tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that.

In musical set theory, an interval class, also known as unordered pitch-class interval, interval distance, undirected interval, or "(even completely incorrectly) as 'interval mod 6'", is the shortest distance in pitch class space between two unordered pitch classes. For example, the interval class between pitch classes 4 and 9 is 5 because 9 − 4 = 5 is less than 4 − 9 = −5 ≡ 7 (mod 12). See modular arithmetic for more on modulo 12. The largest interval class is 6 since any greater interval n may be reduced to 12 − n.
In music using the twelve tone technique, combinatoriality is a quality shared by twelve-tone tone rows whereby each section of a row and a proportionate number of its transformations combine to form aggregates. Much as the pitches of an aggregate created by a tone row do not need to occur simultaneously, the pitches of a combinatorially created aggregate need not occur simultaneously. Arnold Schoenberg, creator of the twelve-tone technique, often combined P-0/I-5 to create "two aggregates, between the first hexachords of each, and the second hexachords of each, respectively."
In music theory, complement refers to either traditional interval complementation, or the aggregate complementation of twelve-tone and serialism.

In music, a permutation (order) of a set is any ordering of the elements of that set. A specific arrangement of a set of discrete entities, or parameters, such as pitch, dynamics, or timbre. Different permutations may be related by transformation, through the application of zero or more operations, such as transposition, inversion, retrogradation, circular permutation, or multiplicative operations. These may produce reorderings of the members of the set, or may simply map the set onto itself.

In music, an interval cycle is a collection of pitch classes created from a sequence of the same interval class. In other words, a collection of pitches by starting with a certain note and going up by a certain interval until the original note is reached. In other words, interval cycles "unfold a single recurrent interval in a series that closes with a return to the initial pitch class". See: wikt:cycle.

In post-tonal music theory, identity is similar to identity in universal algebra. An identity function is a permutation or transformation which transforms a pitch or pitch class set into itself. Generally this requires symmetry. For instance, inverting an augmented triad or C4 interval cycle, 048, produces itself. Performing a retrograde operation upon the tone row 01210 produces 01210. Doubling the length of a rhythm while doubling the tempo produces a rhythm of the same durations as the original.

The mathematical operations of multiplication have several applications to music. Other than its application to the frequency ratios of intervals, it has been used in other ways for twelve-tone technique, and musical set theory. Additionally ring modulation is an electrical audio process involving multiplication that has been used for musical effect.

In musical set theory, an interval vector is an array of natural numbers which summarize the intervals present in a set of pitch classes. Other names include: ic vector, PIC vector and APIC vector
An all-interval tetrachord is a tetrachord, a collection of four pitch classes, containing all six interval classes. There are only two possible all-interval tetrachords, when expressed in prime form. In set theory notation, these are [0,1,4,6] (4-Z15) and [0,1,3,7] (4-Z29). Their inversions are [0,2,5,6] (4-Z15b) and [0,4,6,7] (4-Z29b). The interval vector for all all-interval tetrachords is [1,1,1,1,1,1].

A trope or tropus may refer to a variety of different concepts in medieval, 20th-, and 21st-century music.
In music theory, an inversion is a type of change to intervals, chords, voices, and melodies. In each of these cases, "inversion" has a distinct but related meaning. The concept of inversion also plays an important role in musical set theory.

A Klumpenhouwer Network, named after its inventor, Canadian music theorist and former doctoral student of David Lewin's at Harvard, Henry Klumpenhouwer, is "any network that uses T and/or I operations to interpret interrelations among pcs". According to George Perle, "a Klumpenhouwer network is a chord analyzed in terms of its dyadic sums and differences," and "this kind of analysis of triadic combinations was implicit in," his "concept of the cyclic set from the beginning", cyclic sets being those "sets whose alternate elements unfold complementary cycles of a single interval."

In musical set theory, a Forte number is the pair of numbers Allen Forte assigned to the prime form of each pitch class set of three or more members in The Structure of Atonal Music. The first number indicates the number of pitch classes in the pitch class set and the second number indicates the set's sequence in Forte's ordering of all pitch class sets containing that number of pitches.

















