A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name snail is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have a coiled shell that is large enough for the animal to retract completely into. When the word "snail" is used in this most general sense, it includes not just land snails but also numerous species of sea snails and freshwater snails. Gastropods that naturally lack a shell, or have only an internal shell, are mostly called slugs, and land snails that have only a very small shell are often called semi-slugs.

The gastropods, more commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca, called Gastropoda. This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs.

Powelliphanta is a genus of large, air-breathing land snails, pulmonate gastropods in the family Rhytididae, found only in New Zealand. They are carnivorous, eating invertebrates, mostly native earthworms. Often restricted to very small areas of moist forest, they are prey to introduced mammalian predators, and many species are threatened or endangered.

Escargots, IPA: [ɛs.kaʁ.ɡo], are a delicacy consisting of cooked edible land snails. They are often served as an hors d'oeuvre and consumed by the French people, as well as people from Portugal, Sardinia, and Spain. They are also a typical of the cuisines of Crete, and Greece, as well as such North African countries as Algeria and Morocco. The word escargot is also sometimes applied to living examples of those species which are commonly eaten in this way. In British English, the menu item is usually referred to simply as snails.

The grove snail or brown-lipped snail is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc. It is one of the most common species of land snail in Europe, and has been introduced to North America.

Cornu aspersum, known by the common name garden snail, is a species of land snail. As such it is a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Helicidae, which includes some of the most commonly familiar land snails. Of all terrestrial molluscs, this species may well be the most widely known. In English texts it was classified under the name Helix aspersa for over two centuries, but the prevailing classification now places it in the genus Cornu.
Captain Frederick Wollaston Hutton, FRS, was an English-New Zealand scientist who applied the theory of natural selection to explain the origins and nature of the natural history of New Zealand. An army officer in early life, he then had an academic career in geology and biology. He became one of the most able and prolific nineteenth century naturalists of New Zealand.

Bermuda land snails, scientific name Poecilozonites, are an endemic genus of pulmonate land snail in the family Gastrodontidae. 12 species are known from the fossil record, and 4 of these species survived into modern times, but due to the highly negative effects of human development, that number has been reduced down to two.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, or amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Terrestrial invertebrates include ants, flies, crickets, grasshoppers and spiders.

Sea snail is a common name for snails that normally live in salt water, in other words marine gastropods. The taxonomic class Gastropoda also includes snails that live in other habitats, such as land snails and freshwater snails. Many species of sea snails are edible and exploited as food sources by humans.
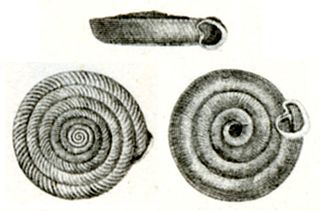
Polygyra is a genus of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Polygyridae.

Polygyridae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Helicoidea.

A love dart is a sharp, calcareous or chitinous dart which some hermaphroditic land snails and slugs create. Love darts are made in sexually mature animals only, and are used as part of the sequence of events during courtship, before actual mating takes place. Darts are quite large compared to the size of the animal: in the case of the semi-slug genus Parmarion, the length of a dart can be up to one fifth that of the semi-slug's foot.

Otala lactea, known as the milk snail or Spanish snail, is a large, edible species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk, in the family Helicidae, the typical snails. Archaeological recovery at the Ancient Roman site of Volubilis, in Morocco, illustrates prehistoric exploitation of O. lactea by humans.

Freshwater snails are gastropod mollusks which live in freshwater. There are many different families. They are found throughout the world in various habitats, ranging from ephemeral pools to the largest lakes, and from small seeps and springs to major rivers. The great majority of freshwater gastropods have a shell, with very few exceptions. Some groups of snails that live in freshwater respire using gills, whereas other groups need to reach the surface to breathe air. In addition, some are amphibious and have both gills and a lung. Most feed on algae, but many are detritivors and some are filter feeders.
George Alan Solem, known professionally as Alan Solem, was an American malacologist, a biologist who studied mollusks.

In the shell of gastropod mollusks, the lip is the free margin of the peristome or aperture of the gastropod shell.

Terrestrial molluscs or land molluscs (mollusks) are ecological group that includes all molluscs that lives on land in contrast to freshwater and marine molluscs.