
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.

MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A relational database organizes data into one or more data tables in which data may be related to each other; these relations help structure the data. SQL is a language that programmers use to create, modify and extract data from the relational database, as well as control user access to the database. In addition to relational databases and SQL, an RDBMS like MySQL works with an operating system to implement a relational database in a computer's storage system, manages users, allows for network access and facilitates testing database integrity and creation of backups.

Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Access Database Engine (ACE) with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsoft 365 suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.

Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. In 2020, Oracle was the third-largest software company in the world by revenue and market capitalization. In 2023, the company’s seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 80. The company sells database software and cloud computing. Oracle's core application software is a suite of enterprise software products, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, human capital management (HCM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, enterprise performance management (EPM) software, Customer Experience Commerce and supply chain management (SCM) software.
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A database management system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using SQL for querying and updating the database.
In computing, Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). The designers of ODBC aimed to make it independent of database systems and operating systems. An application written using ODBC can be ported to other platforms, both on the client and server side, with few changes to the data access code.
Oracle Database is a proprietary multi-model database management system produced and marketed by Oracle Corporation.
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve information. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL).
DataFlex is an object-oriented high-level programming language and a fourth generation visual tool for developing Windows, web and mobile software applications on one framework-based platform. It was introduced and developed by Data Access Corporation beginning in 1982.
A database server is a server which uses a database application that provides database services to other computer programs or to computers, as defined by the client–server model. Database management systems (DBMSs) frequently provide database-server functionality, and some database management systems rely exclusively on the client–server model for database access.
Dataphor is an open-source truly-relational database management system (RDBMS) and its accompanying user interface technologies, which together are designed to provide highly declarative software application development. The Dataphor Server has its own storage engine or it can be a virtual, or federated, DBMS, meaning that it can utilize other database engines for storage.
Oracle Rdb is a relational database management system for the OpenVMS operating system. It was originally released by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1984 as VAX Rdb/VMS.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.
NOMAD is a relational database and fourth-generation language (4GL), originally developed in the 1970s by time-sharing vendor National CSS. While it is still in use today, its widest use was in the 1970s and 1980s. NOMAD supports both the relational and hierarchical database models.
An entity–attribute–value model (EAV) is a data model optimized for the space-efficient storage of sparse—or ad-hoc—property or data values, intended for situations where runtime usage patterns are arbitrary, subject to user variation, or otherwise unforeseeable using a fixed design. The use-case targets applications which offer a large or rich system of defined property types, which are in turn appropriate to a wide set of entities, but where typically only a small, specific selection of these are instantiated for a given entity. Therefore, this type of data model relates to the mathematical notion of a sparse matrix. EAV is also known as object–attribute–value model, vertical database model, and open schema.
Oracle Designer was Oracle's CASE tool for designing an information system and generating it. After generating the information system one is able to edit the generated code with Oracle Developer Suite.
Database administration is the function of managing and maintaining database management systems (DBMS) software. Mainstream DBMS software such as Oracle, IBM Db2 and Microsoft SQL Server need ongoing management. As such, corporations that use DBMS software often hire specialized information technology personnel called database administrators or DBAs.
A cloud database is a database that typically runs on a cloud computing platform and access to the database is provided as-a-service. There are two common deployment models: users can run databases on the cloud independently, using a virtual machine image, or they can purchase access to a database service, maintained by a cloud database provider. Of the databases available on the cloud, some are SQL-based and some use a NoSQL data model.
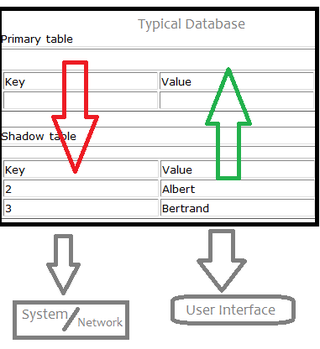
Shadow tables are objects in computer science used to improve the way machines, networks and programs handle information. More specifically, a shadow table is an object that is read and written by a processor and contains data similar to its primary table, which is the table it's "shadowing". Shadow tables usually contain data that is relevant to the operation and maintenance of its primary table, but not within the subset of data required for the primary table to exist. Shadow tables are related to the data type "trails" in data storage systems. Trails are very similar to shadow tables but instead of storing identically formatted information that is different, they store a history of modifications and functions operated on a table.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to MySQL:






