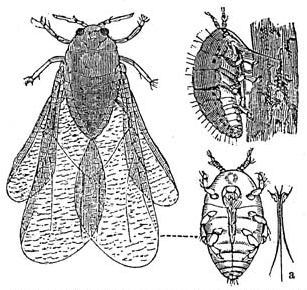
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera ; originally described in France as Phylloxera vastatrix; equated to the previously described Daktulosphaera vitifoliae, Phylloxera vitifoliae. The insect is commonly just called phylloxera.

Aurore is a white complex hybrid grape variety produced by French viticulturist Albert Seibel and used for wine production mostly in the United States and Canada. Over a long lifetime, Seibel produced many complex hybrid crosses of Vitis vinifera to American grapes. The Aurore grape is a cross of Seibel 788 and Seibel 29.

Baco blanc or Baco 22A is a French-American hybrid grape variety. It is a cross of Folle blanche and the Noah grape, created in 1898 by the grape breeder François Baco. Folle blanche is its Vitis vinifera parent. Noah, its other parent, is itself a cross of Vitis labrusca and Vitis riparia.

Vitis labrusca, the fox grape, is a species of grapevines belonging to the Vitis genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to eastern North America and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba, Concord, Delaware, Isabella, Niagara, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam, Alexander and Onaka. Among the characteristics of this vine species in contrast to the European wine grape Vitis vinifera are its "slip-skin" that allows the skin of the grape berries to easily slip off when squeezed, instead of crushing the pulp, and the presence of tendrils on every node of the cane. Another contrast with European vinifera is the characteristic "foxy" musk of V. labrusca, best known to most people through the Concord grape. This musk is not related to the mammalian fox, but rather to the strong, earthy aromas characteristic of the grapes that were known by early European-American settlers in the New World. The term "foxy" became a sort of catchall for the wine tasting descriptors used for these American wines that were distinct from the familiar flavors of the European viniferous wines.

Vitis riparia Michx, with common names riverbank grape or frost grape, is a vine indigenous to North America. As a climbing or trailing vine, it is widely distributed across central and eastern Canada and the central and northeastern parts of the United States, from Quebec to Texas, and eastern Montana to Nova Scotia. There are reports of isolated populations in the northwestern USA, but these are probably naturalized. It is long-lived and capable of reaching into the upper canopy of the tallest trees. It produces dark fruit that are appealing to both birds and people, and has been used extensively in commercial viticulture as grafted rootstock and in hybrid grape breeding programs.

Vitis rupestris is a species of grape native to the United States that is known by many common names including July, Coon, sand, sugar, beach, bush, currant, ingar, rock, and mountain grape. It is used for breeding several French-American hybrids as well as many root stocks.

Vitis amurensis, the Amur grape, is a species of grape native to the Asian continent. Its name comes from the Amur Valley in Russia and China.

Hybrid grapes are grape varieties that are the product of a crossing of two or more Vitis species. This is in contrast to crossings between grape varieties of the same species, typically Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine. Hybrid grapes are also referred to as inter-species crossings or "Modern Varieties." Due to their often excellent tolerance to powdery mildew, other fungal diseases, nematodes, and phylloxera, hybrid varieties have, to some extent, become a renewed focus for European breeding programs. The recently developed varieties are examples of newer hybrid grape varieties for European viticulturalists. Several North American breeding programs, such as those at Cornell and the University of Minnesota, focus exclusively on hybrid grapes, with active and successful programs, having created hundreds if not thousands of new varieties.
Uhudler is a wine from Südburgenland, Austria,. In appearance it is often a rosé colour, but is also made as a white wine. It has intense flavours of strawberry and black currants, a characteristic taste often called "foxy" in wine parlance. The grape varieties used are highly resistant to phylloxera and other diseases; as a result they do not often have to be sprayed with pesticides. Requiring only little fertilization.
Couderc noir is a red wine hybrid grape that was formerly grown primarily in the South West France wine region and around the Gard département in the Languedoc-Roussillon region. The vine produces high yields and ripens late, creating a wine that is deeply colored with a distinct, earthy flavor. Couderc noir is normally used for mass commercial and table wines.

The Isabella grape is a cultivar derived from the grape species Vitis labrusca or 'fox grape,' which is used for table, juice and wine production.

The Noah grape is a cultivar derived from the grape species Vitis labrusca or 'fox grape' which is used for table, juice and wine production. Noah has berries of a light green/yellow and has medium-sized, cylindrical-conical, well formed fruit clusters with thick bloom similar to those of Elvira.

Vitis (grapevine) is a genus of 81 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus consists of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture.
This glossary of viticultural terms list some of terms and definitions involved in growing grapes for use in winemaking.
Black Spanish is a variation of grape that was originally assumed to be a seedling of an American hybrid grape which resulted from the crossing of the American Vitis aestivalis species with that of an unknown Vitis vinifera. The vinifera is suspected to have been the pollen donor.

Boskoop glory is a disease-resistant, cold-tolerant grape variety from the Netherlands. It is thought to be a hybrid between Vitis vinifera and Vitis labrusca. It was developed in the 1950s at Wageningen where American vines had been planted. It is therefore assumed to be a spontaneous crossing of two species from the vineyard. This variety usually ripens fruit in late August or early September and is resistant to fungal diseases and frost.

Ives noir is a red hybrid grape variety that is grown throughout the United States. Named after its propagator, Connecticut wine grower Henry Ives, the grape's pedigree and exact origin are unclear. After Prohibition in the United States, Ives was a popular grape used in the production of sweet, port-style wines but saw its plantings steadily decrease throughout the 20th century as the vine's susceptibility to air pollution took its toll.

The propagation of grapevines is an important consideration in commercial viticulture and winemaking. Grapevines, most of which belong to the Vitis vinifera family, produce one crop of fruit each growing season with a limited life span for individual vines. While some centenarian old vine examples of grape varieties exist, most grapevines are between the ages of 10 and 30 years. As vineyard owners seek to replant their vines, a number of techniques are available which may include planting a new cutting that has been selected by either clonal or mass (massal) selection. Vines can also be propagated by grafting a new plant vine upon existing rootstock or by layering one of the canes of an existing vine into the ground next to the vine and severing the connection when the new vine develops its own root system.
The Champanel grape is an American hybrid developed by Thomas Volney Munson of Texas. Champanel is a cross of the two grape varieties Vitis champinii X Worden, a Concord seedling. It grows vigorously, is resistant to root rot, Pierces disease and produces clusters of fruit resistant to rot and mildew. Although well adapted to a wide range of growing conditions, Champanel produces fruit with aroma characteristic of its Concord parentage and is not often seen commercially. Rather, Champanel is most often used as grafting material for Vitis vinifera, to provide disease resistant root stock. Jim Kamas writes, "Although the cause of vine death from [Pierce disease] was not known to him, T.V. Munson realized that utilizing grape parents that survived local conditions was important in creating new, improved adapted grape varieties" (Power). Munson not only developed a hybrid grape that is resistant to Pierce disease but that grows well in any soil type. The Champanel grapevine grows vigorously on any type of trellis it is placed under. The vine can be placed beside a fence so that the arms of the vine can run along it. Even though the vine grows vigorously, the Champanel grapevine is great for first time growers who want to add grapevines to their garden for the berries or for aesthetics. With the berries a grower can make jelly, juice or wine. This vine is excellent for growing up an arbor to provide shade in a growers back or front yard.
Blanc du Bois is an American hybrid grape that was created in 1968 by John A. Mortensen at the University of Florida’s Central Florida Research and Education Center in Leesburg, Florida. Mortensen created this variety by crossing various Vitis vinifera grape varieties such as Golden Muscat with native Florida varieties. When released in 1987, Blanc du Bois became another grape variety in the small but growing number of vine types that can both produce marketable wine on their own yet can withstand Pierce's Disease, a bacterial infection that destroys nearly all vinifera vinestocks imported into the southern United States.














