Related Research Articles
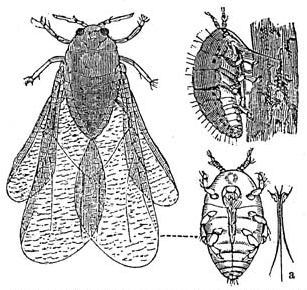
Grape phylloxera is an insect pest of commercial grapevines worldwide, originally native to eastern North America. Grape phylloxera ; originally described in France as Phylloxera vastatrix; equated to the previously described Daktulosphaera vitifoliae, Phylloxera vitifoliae. The insect is commonly just called phylloxera.

Aurore is a white complex hybrid grape variety produced by Albert Seibel and used for wine production mostly in the United States and Canada. Over a long lifetime Seibel produced many complex hybrid crosses of Vitis vinifera to American grapes. It is a cross of Seibel 788 and Seibel 29.

Catawba is a red American grape variety used for wine as well as juice, jams and jellies. The grape can have a pronounced musky or "foxy" flavor. Grown predominantly on the East Coast of the United States, this purplish-red grape is a likely cross of the native American Vitis labrusca and the Vitis vinifera cultivar Semillon. Its exact origins are unclear but it seems to have originated somewhere on the East coast from the Carolinas to Maryland.

Vitis labrusca, the fox grape, is a species of grapevines belonging to the Vitis genus in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The vines are native to eastern North America and are the source of many grape cultivars, including Catawba, Concord, Delaware, Isabella, Niagara, and many hybrid grape varieties such as Agawam, Alexander and Onaka. Among the characteristics of this vine species in contrast to the European wine grape Vitis vinifera are its "slip-skin" that allows the skin of the grape berries to easily slip off when squeezed, instead of crushing the pulp, and the presence of tendrils on every node of the cane. Another contrast with European vinifera is the characteristic "foxy" musk of V. labrusca, best known to most people through the Concord grape. This musk is not related to the mammalian fox, but rather to the strong, earthy aromas characteristic of the grapes that were known by early European-American settlers in the New World. The term "foxy" became a sort of catchall for the wine tasting descriptors used for these American wines that were distinct from the familiar flavors of the European viniferous wines.

Hybrid grapes are grape varieties that are the product of a crossing of two or more Vitis species. This is in contrast to crossings between grape varieties of the same species, typically Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine. Hybrid grapes are also referred to as inter-species crossings or "Modern Varieties." Due to their often excellent tolerance to powdery mildew, other fungal diseases, nematodes, and phylloxera, hybrid varieties have, to some extent, become a renewed focus for European breeding programs. The recently developed varieties are examples of newer hybrid grape varieties for European viticulturalists. Several North American breeding programs, such as those at Cornell and the University of Minnesota, focus exclusively on hybrid grapes, with active and successful programs, having created hundreds if not thousands of new varieties.
Wine has been produced in the United States since the 1500s, with the first widespread production beginning in New Mexico in 1628. Today, wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with California producing 84 percent of all US wine. The North American continent is home to several native species of grape, including Vitis labrusca, Vitis riparia, Vitis rotundifolia, and Vitis vulpina, but the wine-making industry is based almost entirely on the cultivation of the European Vitis vinifera, which was introduced by European settlers. With more than 1,100,000 acres (4,500 km2) under vine, the United States is the fourth-largest wine producing country in the world, after Italy, Spain, and France.

Aramon or Aramon noir is a variety of red wine grape grown primarily in Languedoc-Roussillon in southern France. Between the late 19th century and the 1960s, it was France's most grown grape variety, but plantings of Aramon have been in continuous decline since the mid-20th century. Aramon has also been grown in Algeria, Argentina and Chile but nowhere else did it ever reach the popularity it used to have in the south of France.
Villard grapes are French wine hybrid grape created by French horticulturist Bertille Seyve and his father-in-law Victor Villard. They include the dark skin Villard noir and the white-wine variety Villard blanc with both being members of the Seyve-Villard grape family. Villard noir is a cross of two other French hybrids, Siebel 6905 and Seibel 7053 created by physician and plant breeder Albert Seibel. Like Villard noir, Villard blanc was produced as a crossing of two Seibel grapes, in this case, Le Subereux and Seibel 6468.
Couderc noir is a red wine hybrid grape that was formerly grown primarily in the South West France wine region and around the Gard département in the Languedoc-Roussillon region. The vine produces high yields and ripens late, creating a wine that is deeply colored with a distinct, earthy flavor. Couderc noir is normally used for mass commercial and table wines.

The Isabella grape is a cultivar derived from the grape species Vitis labrusca or 'fox grape,' which is used for table, juice and wine production.

Vitis (grapevine) is a genus of 79 accepted species of vining plants in the flowering plant family Vitaceae. The genus is made up of species predominantly from the Northern Hemisphere. It is economically important as the source of grapes, both for direct consumption of the fruit and for fermentation to produce wine. The study and cultivation of grapevines is called viticulture.

Pennsylvania wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania in the United States.
Petit Bouschet is a red teinturier grape variety that is a crossing of Aramon noir and Teinturier du Cher created in 1824 by French grape breeder Louis Bouschet at his vineyard in Mauguio in the Hérault department. The grape was used by Louis' son, Henri Bouschet, to create several more varieties including Alicante Bouschet, Grand Noir de la Calmette and Morrastel Bouschet. Petit Bouschet saw a surge of plantings in the late 19th century as France recovered from the phylloxera epidemic where it was often used to add color to blends made from hybrid grapes and other high yielding varieties. As its offspring Alicante Bouschet became more popular, plantings of Petit Bouschet fell off and the grape is now hardly found in France.
Landot noir is a red hybrid grape variety that is a crossing of Landal and Villard blanc. Created after a series of trials between 1929-1949, the grape was introduced to Canada and the United States in the 1950s and today can be found in Quebec as well as New Hampshire where a varietal is produced by Jewell Towne Vineyards.
Ravat blanc is a white hybrid grape variety that is a crossing of Chardonnay and a Seibel grape. While the Vitis International Variety Catalogue (VIVC) maintained by the Geilweilerhof Institute for Grape Breeding list Seibel 5474 as the second parent, Master of Wine Jancis Robinson notes that other authors list Seibel 8724 as the parent. The grape is often confused with the white hybrid grape Vignoles that is often called just Ravat.
Cabernet blanc is a white German and Swiss wine grape variety that is a crossing of the French wine grape Cabernet Sauvignon and Regent. The grape was bred by Swiss grape breeder Valentin Blattner in 1991. Cabernet blanc has strong resistance to most grape disease including botrytis bunch rot, downy and powdery mildew and tends to produce loose clusters of small, thick-skinned grape berries which can hang on the vine late into the harvest season to produce dessert wines. Today the grape is found primarily in the Palatinate wine region of Germany with some experimental plantings in Spain and the Netherlands. In France, in the Languedoc, Domaine La Colombette is heavily investing in PIWI grapes. Amongst others the Cabernet Blanc in their cuvée "Au Creux du Nid", is gaining wide acclaim.

Muscat bleu is a red Swiss wine and table grape variety that is a hybrid of Garnier 15-6 and Perle noire. The grape was developed in Peissy in the Canton of Geneva by Swiss grape breeder Charles Garnier in the 1930s. Today the grape is used as both a table grape and for winemaking, producing wines that Master of Wine Jancis Robinson describe as "soft and grapey". Outside Switzerland some plantings of Muscat bleu can also be found in Belgium.

L'Acadie blanc is a white Canadian wine grape variety that is a hybrid crossing of Cascade and Seyve-Villard 14-287. The grape was created in 1953 by grape breeder Ollie A. Bradt in Niagara, Ontario at the Vineland Horticultural Research Station which is now the Vineland Research and Innovation Centre. Today the grape is widely planted in Nova Scotia with some plantings in Quebec and Ontario. Some wine writers, including those at Appellation America, consider L'Acadie blanc as "Nova Scotia’s equivalent to Chardonnay".

The propagation of grapevines is an important consideration in commercial viticulture and winemaking. Grapevines, most of which belong to the Vitis vinifera family, produce one crop of fruit each growing season with a limited life span for individual vines. While some centenarian old vine examples of grape varieties exist, most grapevines are between the ages of 10 and 30 years. As vineyard owners seek to replant their vines, a number of techniques are available which may include planting a new cutting that has been selected by either clonal or mass (massal) selection. Vines can also be propagated by grafting a new plant vine upon existing rootstock or by layering one of the canes of an existing vine into the ground next to the vine and severing the connection when the new vine develops its own root system.
Blanc du Bois is an American hybrid grape that was created in 1968 by John A. Mortensen at the University of Florida’s Central Florida Research and Education Center in Leesburg, Florida. Mortensen created this variety by crossing various Vitis vinifera grape varieties such as Golden Muscat with native Florida varieties. When released in 1987, Blanc du Bois became another grape variety in the small but growing number of vine types that can both produce marketable wine on their own yet can withstand Pierce's Disease, a bacterial infection that destroys nearly all vinifera vinestocks imported into the southern United States.
References
- ↑ William Bartram, Account of the Species, Hybrids, and Other Varieties of the Vine of North-America, Medical Repository, (1804), vol. 7 [second series, vol. 1], p. 19-24.
- 1 2 Pinney, Thomas (2007). A History of Wine in America, Volume 1: From the Beginnings to Prohibition, University of California Press, 2nd ed. p. 85. ISBN 0-520-25429-5
- ↑ "Alexander". Vitis International Variety Catalogue . Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. Retrieved February 2, 2010.