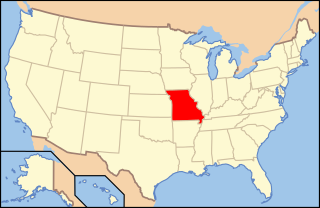
Missouri wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in Missouri. German immigrants in the early-to-mid-19th century founded the wine industry in Missouri, resulting in its wine corridor being called the Missouri "Rhineland". Later Italian immigrants also entered wine production. In the mid-1880s, more wine was produced by volume in Missouri than in any other state. Before prohibition, Missouri was the second-largest wine-producing state in the nation. Missouri had the first area recognized as a federally designated American Viticultural Area with the Augusta AVA acknowledged on June 20, 1980. There are now four AVAs in Missouri. In 2017 there were 125 wineries operating in the state of Missouri, up from 92 in 2009.

Wine has been produced in the United States since the 1500s, with the first widespread production beginning in New Mexico in 1628. As of 2023, wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with California producing 80.8% of all US wine. The North American continent is home to several native species of grape, including Vitis labrusca, Vitis riparia, Vitis rotundifolia, and Vitis vulpina, but the wine-making industry is based almost entirely on the cultivation of the European Vitis vinifera, which was introduced by European settlers. With more than 1,100,000 acres (4,500 km2) under vine, the United States is the fourth-largest wine producing country in the world, after Italy, Spain, and France.

Michigan wine refers to any wine that is made in the state of Michigan in the United States. As of 2020, there were 3,375 acres (1,366 ha) under wine-grape cultivation and over 200 commercial wineries in Michigan, producing 3 million US gallons (11,000,000 L) of wine. According to another count there were 112 operating wineries in Michigan in 2007.

Illinois wine refers to any wine that is made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Illinois. In 2006, Shawnee Hills, in southern Illinois, was named the state's first American Viticultural Area. As of 2008, there were 79 wineries in Illinois, utilizing approximately 1,100 acres (4.5 km2) of vines.

Ontario wine is Canadian wine produced in the province of Ontario. The province has three official wine-growing regions, the Niagara Peninsula, the north shore of Lake Erie, and Prince Edward County, although wineries also exist in other regions in Ontario. Approximately two-thirds of Canada's vineyard acreage is situated in Ontario, with over 150 vineyards spread across 6,900 hectares. As a result, the province is the country's largest producer of wine, accounting for 62 per cent of Canadian wine production, and 68 per cent of all Canadian wine exports.

Idaho wine refers to wine produced in the state of Idaho. Idaho has a long history of wine production with the first vineyards in the Pacific Northwest being planted here in the 1860s. Grapes were first planted in the state by French immigrants Louis Desol and Robert Schleicher, and Jacob Schaefer from Germany before grapes were ever planted in Washington and Oregon. Idaho wines were receiving national recognition before Prohibition crippled the industry and shutdown production. In fact, Idaho issued a state prohibition in 1916 before the 18th Amendment was enacted in 1920 and repealed in 1933. The state’s viticulture industry was not revived until the 1970s when first grape vines were planted in the Snake River Valley toward its southernmost area. Today, Idaho's viticulture is its fastest growing agricultural industry.
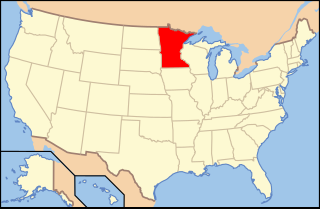
Minnesota wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Minnesota. Minnesota is part of the largest American Viticultural Area (AVA), the Upper Mississippi River Valley AVA, which includes southwest Wisconsin, southeast Minnesota, northeast Iowa, and northwest Illinois. The state also has a smaller designated American Viticultural Areas, the Alexandria Lakes AVA. Minnesota is a very cold climate for viticulture and many grape varieties require protection from the winter weather by being buried under soil for the season. Minnesota is home to extensive research on cold-hardy French hybrid and other grape varieties.

Massachusetts wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Most of the wine grape vineyards and wineries in Massachusetts are located in the southern half of the state, within the boundaries of the Southeastern New England AVA. Although the coastal conditions moderate the cold climate, many wineries rely upon cold-hardy French hybrid varietals like Seyval, Vidal, and Marechal Foch. There are over 55 wineries in Massachusetts, and one designated American Viticultural Area, the Martha's Vineyard AVA, located entirely within the boundaries of the state.

Kentucky wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. commonwealth of Kentucky. About 65 wineries operate commercially in Kentucky, with most recent plantings focusing on Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, and Cabernet Franc. Kentucky produced over two million gallons of wine in 2011 and is the largest wine-producing state by volume in the American South. Kentucky passed legislation in 1976 allowing wineries to operate, and tobacco settlement funds have provided Kentucky farmers the opportunity to once again explore grapes as a cash crop.

Colorado wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Colorado. Most of Colorado's vineyards are located on the western slope of the Rocky Mountains, though an increasing number of wineries are located along the Front Range.

Oklahoma wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Wine production was a significant component of the Oklahoma agricultural economy in the 1920s. The industry was destroyed by the Dust Bowl of the 1930s and the introduction of Prohibition in the United States. Oklahoma currently has about 52 wineries. Most of the wineries are located in Green Country, Lincoln county and surrounding areas in east central Oklahoma, Central Oklahoma and Southwest Oklahoma.

Connecticut wine refers to wine made from grapes and other fruit grown in the U.S. state of Connecticut. The modern wine industry in Connecticut began with the passage of the Connecticut Winery Act in 1978. The wineries in Connecticut are located throughout the state, including in the three designated American Viticultural Areas in the state. The climate in the coastal region near Long Island Sound and the Connecticut River valley tends to be warmer than the highlands in the eastern and western sides of the state.
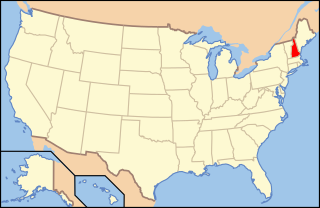
New Hampshire wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. The wine industry in New Hampshire began in 1994 when two wineries, Jewell Towne Vineyards and Flag Hill Winery, each produced their first vintages from locally grown grapes. Candia Vineyards started their test plantings in 1992, and full planting in 1998. New Hampshire continues to be growing wine-producing state, with new commercial wineries opening. The state currently has no American Viticultural Areas.

Vermont wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Vermont. The first commercial winery in Vermont, Snow Farm Winery, opened in 1997. Vermont is a very cold climate for viticulture. Vermont wineries have focused on using cold-hardy French hybrid grapes, but have been experimenting with some Vitis vinifera varieties. Some Vermont wineries produce wine made from grapes grown in other states, especially New York.
North Dakota wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of North Dakota. North Dakota was the last state in the United States since Prohibition to license a commercial winery. The first bonded commercial winery in North Dakota, Pointe of View Winery, was established on April 17, 2002. Pointe of View Winery has since been joined by a second winery, Dakota Hills Winery, but both wineries focus on wine made from fruits other than grapes. Red Trail Vineyard, North Dakota's largest, makes wines exclusively from its grapes.
South Dakota wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of South Dakota. Its region stretches between the latitudes of 42°N and 45°N sharing these latitudes with some of the most famous wine-producing areas in the world, including Bordeaux and Italy's Tuscany. South Dakota has a small wine industry, which must contend with extremes of heat in the summer and cold in the winter. The only grape species that naturally performs well in South Dakota is Vitis riparia, a species not generally used for wine production. The wineries in South Dakota have focused exclusively on cold-resistant French hybrid grapes. At present, there are no American Viticultural Areas (AVAs) in South Dakota, save for the state-level appellation.

Florida wine refers to wine made from grapes and other fruit grown in the U.S. state of Florida. Wine grapes were grown in Florida earlier than anywhere else in North America.
Delaware wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Delaware. Historically, the first Swedish settlers planted grapes and made wine in Delaware as early as 1638.
Montana wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Montana. There are eight wineries in Montana, with most producing wine from fruits other than grapes or from grapes grown in other states, such as California, Oregon, or Washington. The traditional grape varieties that appear to do best in the mountainous terroir of Montana are the grapes widely grown in the most northerly vineyards of France, with which Montana shares its latitudinal position of 42-49°N. There are no American Viticultural Areas in Montana.
Nevada wine refers to wine made from grapes grown in the U.S. state of Nevada, where wine has been produced since 1990. There are currently no designated American Viticultural Areas in Nevada.