
Aconitum, also known as aconite, monkshood, wolfsbane, leopard's bane, devil's helmet, or blue rocket, is a genus of over 250 species of flowering plants belonging to the family Ranunculaceae. These herbaceous perennial plants are chiefly native to the mountainous parts of the Northern Hemisphere in North America, Europe, and Asia, growing in the moisture-retentive but well-draining soils of mountain meadows.

Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus Aconitum, commonly known by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Aconitine is notorious for its toxic properties.

Ranunculaceae is a family of over 2,000 known species of flowering plants in 43 genera, distributed worldwide.

Delphinium is a genus of about 300 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae, native throughout the Northern Hemisphere and also on the high mountains of tropical Africa. The genus was erected by Carl Linnaeus.

Consolida ajacis is an annual flowering plant of the family Ranunculaceae native to Eurasia. It is widespread in other areas, including much of North America, where it is an introduced species. It is frequently grown in gardens as an ornamental for its spikes of blue, pink or white flowers. It may reach a meter in height. Since the aerial parts and seeds of C. ajacis have been found to contain diterpenoid alkaloids, including the highly toxic methyllycaconitine, the plants should be considered as poisonous.

Anopterus is a genus of two species of shrubs or small trees.

Methyllycaconitine (MLA) is a diterpenoid alkaloid found in many species of Delphinium (larkspurs). In common with many other diterpenoid alkaloids, it is toxic to animals, although the acute toxicity varies with species. Methyllycaconitine was identified one of the principal toxins in larkspurs responsible for livestock poisoning in the mountain rangelands of North America. Methyllycaconitine has been explored as a possible therapeutic agent for the treatment of spastic paralysis, and it has been shown to have insecticidal properties. It has become an important molecular probe for studying the pharmacology of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.

Staphisagria macrosperma, formerly known as Delphinium staphisagria, is a species of Staphisagria of the family Ranunculaceae. It used to belong to the subgenus or section Staphisagria of the genus Delphinium, but molecular evidence suggests Staphisagria should be a genus which is a sister group to the Aconitum-Delphinium clade. It is described botanically as a stoutly-stemmed, hairy biennial with large palmate leaves up to 6 inches (15 cm) across. The flowers are mauve-blue to blue, short-spurred, and up to 1 inch (2.5 cm) across, occurring in racemes. The plant grows to a height of 4–5 feet. It grows throughout the Mediterranean. All parts of this plant are highly toxic and should not be ingested in any quantity.

Delphinium nudicaule, known by the common names canyon larkspur, red larkspur, orange larkspur, and canyon delphinium, is a flowering herbaceous perennial plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. It is native to low-elevation canyons and slopes, foothills, and mountain ranges of California, US, from the Sierra Nevada to the California Coast Ranges, and of Oregon. It grows below 6,500 feet (2,000 m).

Delphinium cardinale is a species of larkspur known by the common names scarlet larkspur and cardinal larkspur. This wildflower is native to California and Baja California, where it grows on coastal, inland, and desert chaparral slopes, such as the Colorado Desert, and the Peninsular and Transverse Ranges. The presence of diterpenoid alkaloids, probably including the highly toxic methyllycaconitine, in above-ground parts of D. cardinale means that they are likely to be toxic if ingested.

Delphinium glaucum, known by the common names Sierra larkspur, mountain larkspur, and glaucous larkspur, is a species of wildflower in the genus Delphinium, which belongs to the buttercup family, Ranunculaceae. It is native to western North America from Arizona to Alaska, growing in moist mountainous environments such as riverbanks and meadows.

Delphinine is a toxic diterpenoid alkaloid found in plants from the Delphinium (larkspur) and Atragene genera, both in the family Ranunculaceae. Delphinine is the principal alkaloid found in Delphinium staphisagria seeds – at one time, under the name stavesacre, a very well known herbal treatment for body lice. It is related in structure and has similar effects to aconitine, acting as an allosteric modulator of voltage gated sodium channels, and producing low blood pressure, slowed heart rate and abnormal heart rhythms. These effects make it highly poisonous. While it has been used in some alternative medicines, most of the medical community does not recommend using it due to its extreme toxicity.

Delphinium denudatum is a species of wildflower in the genus Delphinium, native to Central Asia.

Delphinium tricorne, known by the common names dwarf larkspur or spring larkspur, is a species of flowering plant in the Ranunculaceae (buttercup) family. It is native to the central and eastern United States, where it is the most common Delphinium found.
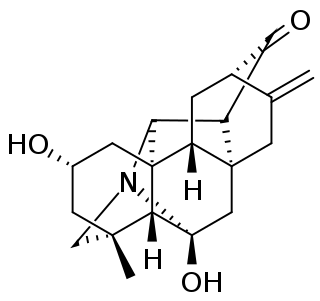
Panicudine (6-hydroxy-11-deoxy-13-dehydrohetisane) is a C20-diterpene alkaloid of the hetisine type, first isolated from Aconitum paniculatum. It has empirical formula C20H25NO3 and a melting point of 249–250 °C. The structure was determined to be a hetisine type diterpene by noting infrared spectrum absorption bands of 3405 cm−1 (OH), 1718 (C=O), and 1650 (C=C), a proton magnetic resonance spectrum with "secondary hydroxy (4.02 ppm, m, 1H, W1/2 = 10 Hz), exomethylene (4.87 and 4.76 ppm, br.s, 1H each), and tertiary methyl (1.29 ppm, s, 3H) groups and the absence of N-methyl, N-ethyl, and methoxy groups." Additional ultraviolet spectrum and carbon-13 NMR data, confirmed by high resolution mass spectrometry, completed the determination of the structure.

Delphinium barbeyi is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family known by the common names subalpine larkspur, tall larkspur, and Barbey's larkspur. It is native to the interior western United States, where it occurs in the states of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming.

Gigactonine is a naturally occurring diterpene alkaloid first isolated from Aconitum gigas. It occurs widely in the Ranunculaceae plant family. The polycyclic ring system of this chemical compound contains nineteen carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom, which is the same as in aconitine and this is reflected in its preferred IUPAC name.
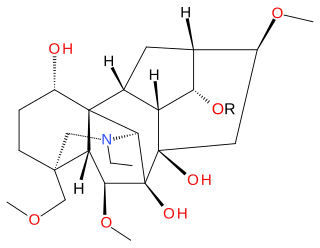
Delsoline and delcosine are two closely related naturally occurring diterpene alkaloids first isolated from Delphinium consolida. They occur widely in the Ranunculaceae plant family. The polycyclic ring system containing nineteen carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom in these compounds is the same as in aconitine and this is reflected in their preferred IUPAC name.

Delphinium elatum is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, known by the common name alpine delphinium, guardian lavender, or candle larkspur. It is native to temperate Asia and Europe, it is an erect herbaceous perennial growing to 1.8 m (5.9 ft), with deeply divided leaves. It produces spikes of blue or purple flowers in summer.

Delphinium geyeri is a species of plant in the Ranunculaceae family that is often called by the common names plains larkspur and foothills larkspur. It is infamous for causing the deaths of cattle grazing in the spring because it is especially poisonous before it flowers and so it is also called poisonweed by ranchers. It is a medium to tall plant that has very striking blue flowers and is occasionally grown in native plant gardens for this reason. It grows mainly in Wyoming with large population in northern Colorado, northeastern Utah, and parts of Nebraska.





















