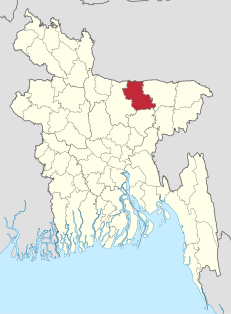
Netrokona is a district of the Mymensingh Division in northern Bangladesh.
Mohammad Yakub Ali Chowdhury was a Bengali essayist and journalist. He was noted as one of the few Bengali Muslim literary scholars of his time.

Dacca or Dhaka is the capital and one of the oldest cities of Bangladesh. The history of Dhaka begins with the existence of urbanised settlements in the area that is now Dhaka dating from the 7th century CE. The city area was ruled by the Buddhist and shaivite Pala Empire before passing to the control of the Sena dynasty in the 10th century CE. After the Sena dynasty, Dhaka was successively ruled by the Turkic and Afghan governors descending from the Delhi Sultanate, followed by the Bengal Sultanate, before the arrival of the Mughals in 1608. The city became proto-industrialised and declared capital of the Mughal Bengal. After Mughals, British ruled the region for 200 years until the independence of India. In 1947, Dhaka became the capital of the East Bengal province under the Dominion of Pakistan. After the independence of Bangladesh in 1971, Dhaka became the capital of the new state.

Bhawal Estate was one of the largest zamindari estate in Bengal in modern-day Bangladesh. It had 2,274 villages in an area of 1,500 kilometers and a population of 55,000.

Sarail is an upazila of Brahmanbaria District located in the Chittagong Division and near the Dhaka Division, Bangladesh.

Hathazari is an upazila of Chittagong District in the Division of Chittagong, Bangladesh.

Muradnagar is an upazila of the Comilla District in Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. The area is known for roshmolai and mishti doi.

Ajmiriganj is an upazila of Habiganj District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh.

Derai is an upazila (sub-district) of the Sunamganj District in northeastern Bangladesh, part of the Sylhet Division.

Shamsuddīn Aḥmad Shāh was a Sultan of Bengal and member of the Ganesha dynasty. He was the son and successor of Sultan Jalaluddin Muhammad Shah. After his father's death, he ascended the throne at the age of 14.

Nāsir ad-Dīn Naṣrat Shāh was the Sultan of Bengal from 1519 until his assassination in 1533. Continuing with his father's expansionist policies, he was the second ruler belonging to the Hussain Shahi dynasty. By 1526 however, he had to contend with the Mughal ascendency in the Battle of Ghaghra, and also suffered a reverse at the hands of the Ahom kingdom. The reigns of Alauddin Husain Shah and Nusrat Shah are generally regarded as the “golden age” of the Bengal sultanate.
Shayestaganj, also spelt Shaistaganj, is an upazila (sub-district) of Habiganj District in northeastern Bangladesh, part of the Sylhet Division. There is one Paurasava (Municipality) and three Unions under this Thana. They are: Shaistaganj Paurasava, Shaistaganj Union, Nurpur Union and Brammondura Union.
Tarana-i-Pakistan, or more popularly known as Pakistan Zindabad, was an alternative national anthem sung by East Pakistan during its existence until 1971, and can be considered the de facto national anthem of East Pakistan. The song is in Bengali, the language of East Pakistan, and was adopted from a poem by an East Pakistani poet Golam Mostofa with the name of Tarana-i-Pakistan in 1956. It was composed by Nazir Ahmed. The song was sang during school assemblies in East Pakistan by school children.
Shahzada Barbak, known by his regnal title as Barbak Shah II, was the Sultan of Bengal in 1487 and the founder of the Sultanate's Habshi dynasty. He was a former commander of the palace-guards of Jalaluddin Fateh Shah court.

Malik Andil Habshi, better known by his regnal title Saifuddin Firuz Shah was the second Abyssinian ruler of the Bengal Sultanate's Habshi dynasty. He was a former army commander of the Sultanate's Ilyas Shahi dynasty.

Austria–Bangladesh relations refer to the bilateral relations between Bangladesh and Austria. Relations between the two countries have been considered cordial with both the countries working towards further strengthen it.
Dawlat Wazir Bahram Khan, born as Asaduddin, was a 16th-century medieval Bengali poet and the Wazir of Chittagong in southeastern Bengal.

Rai Bahadur Dewan Kaliprosanna Ghosh, CIE Vidyasagar was a Bengali journalist, writer and scholar.
The Kohinoor was a Bengali language newspaper, first published in July 1898. Initially focusing on miscellaneous topics such as Islamic culture, its third relaunch was a pivot of Hindu-Muslim harmony. The paper targeted both Hindu and Muslim clientele.

Tanda, also known as Tandah and Khwaspur Tandah, was a historic 16th-century city of Bengal in the eastern part of South Asia, and one of the most prominent medieval capitals; serving the Karrani Sultans of Bengal and the early Mughal governors of Bengal.