
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlorophyta is a division of green algae informally called chlorophytes.
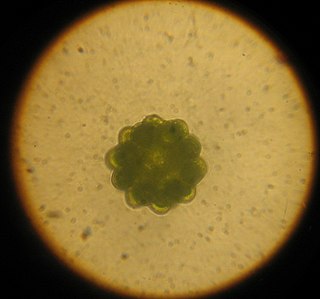
Coelastrum is a genus of green algae in the Scenedesmaceae family. It is a common component of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, waterfalls, and temporary pools of water, particularly eutrophic ones. The genus has a more or less cosmopolitan distribution, although some species appear to have more restricted geographical distributions.

Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the class Trebouxiophyceae. Molecular phylogenetic studies mostly place the family in the order Chlorellales, as sister to Chlorellaceae. The type genus is Oocystis.

Actinastrum is a genus of freshwater green algae. It was first described by Gustaf Lagerheim in 1882. Members of the genus are commonly found in eutrophic freshwater ponds and lakes, and have a cosmopolitan distribution.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world. The name Ankistrodesmus comes from the Greek roots ankistron, meaning "cross", and desmos, meaning "bond".

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Desmodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is the only chlorophyll-containing organism known to have caused human infections in immunocompetent individuals. All known cases involved open injuries occurring in fresh water.
Dicloster is a genus of green algae in the family Chlorellaceae, containing the sole species Dicloster acuatus. It is found in freshwater habitats as plankton, and is distributed around the world.

Didymogenes is a genus of microscopic green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. It is a planktonic species found in freshwater habitats worldwide. Formerly placed in the family Scenedesmaceae, molecular studies have placed it in the family Chlorellaceae.
Enallax is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, such as peat bogs or wet rocks.

Hariotina is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. They are classified in the subfamily Coelastroideae.

Lagerheimia is a genus of green algae in the family Oocystaceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats all over the world, although some species are rare and have only been recorded from Europe or the United States.
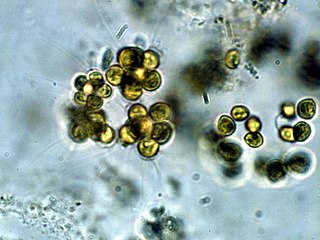
Micractinium is a genus of microscopic green algae in the family Chlorellaceae. Species of the genus Micractinium are found as phytoplankton, and are commonly found in freshwater habitats around the world. A few species are found as endosymbionts of ciliates. There is increasing interest in Micractinium due to its high growth rate and lipid production.

Sorastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Hydrodictyaceae. It is a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and ditches. Sorastrum is common in tropical to temperate regions of the world, but due to its small size it is often overlooked.

Crucigenia is a genus of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. It is widespread, but not often abundant, in freshwater habitats around the world.

Tetrastrum is a genus of green algae (Chlorophyta). It is a common component of the phytoplankton of freshwater habitats, particularly eutrophic and alkaline waters.

Dicellula is a genus of green algae in the family Chlorellaceae. It contains a single species, Dicellula geminata. It occurs in the plankton of eutrophic fresh water. It is distributed around the world, but uncommon.
Gilbertsmithia is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae, containing the single species Gilbertsmithia grandis. It was named after the American botanist Gilbert Morgan Smith. This remarkable alga has only been recorded once from a muddy rainwater pool in Madras, India.

Lemmermannia /ˌlɛməɹˈmæniə/ is a genus of fresh water trebouxiophyceans. as of March 2022, the genus contains five described species. They form coenobia of 4 to 16 cells. Its type species is L. tetrapedia (Kirchner) Lemmermann, originally described in 1880 but put into the genus Lemmermannia in 1904.
















