The Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann (1853–1923), is a rearrangement of an oxime functional group to substituted amides. The rearrangement has also been successfully performed on haloimines and nitrones. Cyclic oximes and haloimines yield lactams.

An acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Oxygen fluorides are compounds of elements oxygen and fluorine with the general formula OnF2, where n = 1 to 6. Many different oxygen fluorides are known:

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
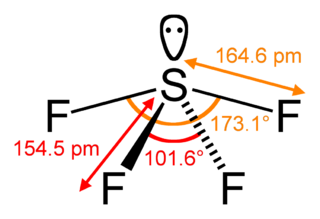
Sulfur tetrafluoride is a chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous hydrogen fluoride gas upon exposure to water or moisture. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.
In chemistry, a sulfonyl halide consists of a sulfonyl group singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X, where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.
Selectfluor, a trademark of Air Products and Chemicals, is a reagent in chemistry that is used as a fluorine donor. This compound is a derivative of the nucleophillic base DABCO. It is a colourless salt that tolerates air and even water. It has been commercialized for use for electrophilic fluorination.

The tetrafluoroammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with chemical formula NF+
4. It is equivalent to the ammonium ion where the hydrogen atoms surrounding the central nitrogen atom have been replaced by fluorine. Tetrafluoroammonium ion is isoelectronic with tetrafluoromethane CF
4, trifluoramine oxide ONF
3, tetrafluoroborate BF−
4 anion and the tetrafluoroberyllate BeF2−
4 anion.
Fluorination by sulfur tetrafluoride produces organofluorine compounds from oxygen-containing organic functional groups using sulfur tetrafluoride. The reaction has broad scope, and SF4 is an inexpensive reagent. It is however hazardous gas whose handling requires specialized apparatus. Thus, for many laboratory scale fluorinations diethylaminosulfur trifluoride ("DAST") is used instead.
Fluorination with aminosulfuranes is a chemical reaction that transforms oxidized organic compounds into organofluorine compounds. Aminosulfuranes selectively exchange hydroxyl groups for fluorine, but are also capable of converting carbonyl groups, halides, silyl ethers, and other functionality into organofluorides.

The Olah reagent is a nucleophilic fluorinating agent. It consists of a mixture of 70% hydrogen fluoride and 30% pyridine; alcohols react with this reagent to give alkyl fluorides:

Vanadium(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula VF5. It is a colorless volatile liquid that freezes near room temperature. It is a highly reactive compound, as indicated by its ability to fluorinate organic substances.
Organoxenon chemistry is the study of the properties of organoxenon compounds, which contain carbon to xenon chemical bonds. The first organoxenon compounds were divalent, such as (C6F5)2Xe. The first tetravalent organoxenon compound, [C6F5XeF2][BF4], was synthesized in 2004. So far, more than one hundred organoxenon compounds have been researched.
Fluorine forms a great variety of chemical compounds, within which it always adopts an oxidation state of −1. With other atoms, fluorine forms either polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds. Most frequently, covalent bonds involving fluorine atoms are single bonds, although at least two examples of a higher order bond exist. Fluoride may act as a bridging ligand between two metals in some complex molecules. Molecules containing fluorine may also exhibit hydrogen bonding. Fluorine's chemistry includes inorganic compounds formed with hydrogen, metals, nonmetals, and even noble gases; as well as a diverse set of organic compounds. For many elements the highest known oxidation state can be achieved in a fluoride. For some elements this is achieved exclusively in a fluoride, for others exclusively in an oxide; and for still others the highest oxidation states of oxides and fluorides are always equal.
Difluoroamino sulfur pentafluoride is a gaseous chemical compound of fluorine, sulfur, and nitrogen. It is unusual in having a hexa-coordinated sulfur atom with a link to nitrogen. Other names for this substance include difluoro(pentafluorosulfur)amine, pentafluorosulfanyldifluoramine, and pentafluorosulfanyl N,N-difluoramine.
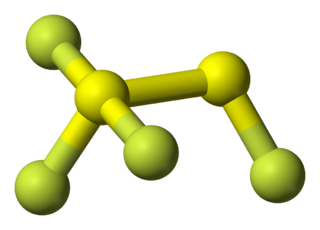
1,1,1,2-tetrafluorodisulfane, also known as 1,2-difluorodisulfane 1,1-difluoride or just difluorodisulfanedifluoride (FSSF3) is an unstable molecular compound of fluorine and sulfur. The molecule has a pair of sulfur atoms, with one fluorine atom on one sulfur, and three fluorine atoms on the other. It has the uncommon property that all the bond lengths are different. The bond strength is not correlated with bond length but is inversely correlated with the force constant (Badger's rule). The molecule can be considered as sulfur tetrafluoride in which a sulfur atom is inserted into a S-F bond.

Terbium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula TbF4. It is a white solid that is a strong oxidizer. It is also a strong fluorinating agent, emitting relatively pure atomic fluorine when heated, rather than the mixture of fluoride vapors emitted from cobalt(III) fluoride or cerium(IV) fluoride.