
Dihydroisocoumarins are phenolic compounds related to isocoumarin. Dihydroisocoumarin glucosides can be found in Caryocar glabrum . [1]

Dihydroisocoumarins are phenolic compounds related to isocoumarin. Dihydroisocoumarin glucosides can be found in Caryocar glabrum . [1]

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is chemically derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Hydrangea macrophylla is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, native to China. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall by 2.5 m (8 ft) broad with large heads of pink or blue flowers in summer and autumn. Common names include bigleaf hydrangea, French hydrangea, lacecap hydrangea, mophead hydrangea, and hortensia. It is widely cultivated in many parts of the world in many climates. It is not to be confused with H. aspera 'Macrophylla'.

Caryocar is a genus of flowering plants, in the South American family Caryocaraceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1771. It is native primarily to South America with a few species extending into Central America and the West Indies.
Güeppi-Sekime National Park is a protected area located in the Peruvian region of Loreto, on the border with Ecuador. The park encompasses 203,628.51 hectares (2,036 km2) of forests in a landscape that features hills and seasonally flooded lowlands.

Acer glabrum is a species of maple native to western North America, from southeastern Alaska, British Columbia and western Alberta, east to western Nebraska, and south through Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana and Colorado to California, Arizona, Utah, and New Mexico.

Caryocar nuciferum, the butter-nut of Guiana, is also known as pekea-nut, or – like all other species of Caryocar with edible nuts – "souari-nut" or "sawarri-nut". It is a fruit tree native to northern Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guyana, Panama, and Venezuela.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Pears, olive oil, wine and tomato sauce are rich in isorhamnetin. Almond skin is a rich source of isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, in some cultivars they comprise 75% of the polyphenol content, the total of which can exceed 10 mg/100 gram almond. Others sources include the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate. Nopal is also a good source of isorhamnetin, which can be extracted by supercritical fluid extraction assisted by enzymes.

Biochanin A is an O-methylated isoflavone. It is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as flavonoids. Biochanin A can be found in red clover in soy, in alfalfa sprouts, in peanuts, in chickpea and in other legumes.
C. glabrum may refer to:
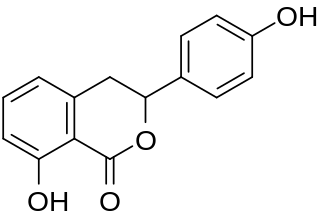
Hydrangenol is a dihydroisocoumarin. It can be found in Hydrangea macrophylla, as well as its 8-O-glucoside. (−)-Hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside and (+)-hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside can be found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Phyllodulcin is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangea macrophylla and Hydrangea serrata. It is a sweetener 400–800 times sweeter than sugar.
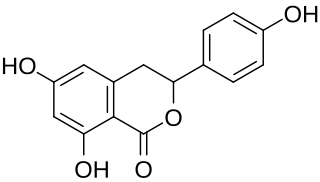
Thunberginol C is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol D is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol E is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol G is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Caryocar glabrum is a species of tree in the family Caryocaraceae. It is native to South America.

The Marajó Archipelago Environmental Protection Area is an environmental protection area in the state of Pará, Brazil. It protects the Marajó Archipelago, made up of marine fluvial islands in the area where the Amazon and Tocantins rivers converge and flow into the Atlantic. Covering almost 60,000 square kilometres (23,000 sq mi) it is larger than some countries in Europe.

The Magdalena–Urabá moist forests (NT0137) is an ecoregion in the north of Colombia. The terrain is largely flat or undulating, but includes mountainous areas in the south. It contains moist forests and large wetlands that are important to resident and migratory birds. The ecoregion forms a bridge between the Pacific coast ecoregions of Colombia and Central America, and the ecoregions of the Andes and Amazon. It is surrounded by the more populated parts of Colombia and is threatened by farming, ranching, logging, oil exploitation and water pollution in the main rivers.