
Delphinidin is an anthocyanidin, a primary plant pigment, and also an antioxidant. Delphinidin gives blue hues to flowers in the genera Viola and Delphinium. It also gives the blue-red color of the grape that produces Cabernet Sauvignon, and can be found in cranberries and Concord grapes as well as pomegranates, and bilberries.

Capsicum chinense, commonly known as a "habanero-type pepper", is a species of chili pepper native to the Americas. C. chinense varieties are well known for their unique flavors and many have exceptional heat. The hottest peppers in the world are members of this species, with Scoville Heat Unit scores of over 2 million. Some taxonomists consider them to be part of the species C. annuum, and they are a member of the C. annuum complex; however, C. chinense and C. annuum pepper plants can sometimes be distinguished by the number of flowers or fruit per node – two to five for C. chinense and one for C. annuum – though this method is not always correct. The two species can also hybridize and generate inter-specific hybrids. It is believed that C. frutescens is the ancestor to the C. chinense species.

Lycium chinense is one of two species of boxthorn shrub in the family Solanaceae. Along with Lycium barbarum, it produces the goji berry ("wolfberry"). Two varieties are recognized, L. chinense var. chinense and L. chinense var. potaninii. It is also known as Chinese boxthorn, Chinese matrimony-vine, Chinese teaplant, Chinese wolfberry, wolfberry, and Chinese desert-thorn.

Safranal is an organic compound isolated from saffron, the spice consisting of the stigmas of crocus flowers. It is the constituent primarily responsible for the aroma of saffron.

Benzopyran is a polycyclic organic compound that results from the fusion of a benzene ring to a heterocyclic pyran ring.
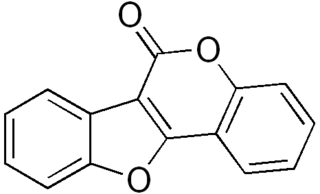
Coumestan is a heterocyclic organic compound. Coumestan forms the central core of a variety of natural compounds known collectively as coumestans. Coumestans are oxidation products of pterocarpan that are similar to coumarin. Coumestans, including coumestrol, a phytoestrogen, are found in a variety of plants. Food sources high in coumestans include split peas, pinto beans, lima beans, and especially alfalfa and clover sprouts.

A-41988 (BW29Y) is an analgesic drug which acts as a cannabinoid agonist. It was developed by Abbott Laboratories in the 1970s, and researched for potential use in the treatment of glaucoma, but never commercialised.

Cromakalim (INN) is a potassium channel-opening vasodilator. The active isomer is levcromakalim. It acts on ATP-sensitive potassium channels and so causes membrane hyperpolarization. It can be used to treat hypertension as it will relax vascular smooth muscle to lower blood pressure. Hyperpolarisation of smooth muscle cell membranes pulls their membrane potential away from the threshold, so making it more difficult to excite them and thereby cause relaxation.
The molecular formula C16H14O6 may refer to:
The chemical formula C15H10O5 (molar mass : 270.23 g/mol, exact mass : 270.052823) may refer to:
The molecular formula C15H10O6 (molar mass : 286.23 g/mol, exact mass : 286.047738) may refer to:

Alniditan is a 5-HT1D receptor agonist with migraine-preventive effects.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó (黃柏) or huáng bò (黃檗) is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.

Phellodendron chinense is a plant species in the genus Phellodendron.

Thunberginol B is an isocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.
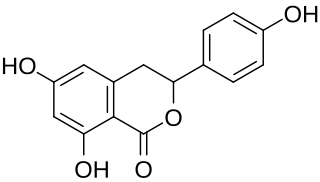
Thunberginol C is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol D is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol E is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol G is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

The habanero is a hot variety of the chili pepper. Unripe habaneros are green, and they color as they mature. The most common color variants are orange and red, but the fruit may also be white, brown, yellow, green, or purple. Typically, a ripe habanero is 2–6 centimetres long. Habanero chilis are very hot, rated 100,000–350,000 on the Scoville scale. The habanero's heat, flavor and floral aroma make it a popular ingredient in hot sauces and other spicy foods.

















