
Echinacea is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the daisy family. It has ten species, which are commonly called coneflowers. They are found only in eastern and central North America, where they grow in moist to dry prairies and open wooded areas. They have large, showy heads of composite flowers, blooming in summer. The generic name is derived from the Greek word ἐχῖνος, meaning "hedgehog", due to the spiny central disk. These flowering plants and their parts have different uses. Some species are cultivated in gardens for their showy flowers. Two of the species, E. tennesseensis and E. laevigata, were formerly listed in the United States as endangered species; E. tennesseensis has been delisted due to recovery and E. laevigata is now listed as threatened.

Cannabinoids are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is also a major constituent of temperate cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea.
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as para-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the para position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.

Eugenol is an allyl chain-substituted guaiacol, a member of the allylbenzene class of chemical compounds. It is a colorless to pale yellow, aromatic oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove, nutmeg, cinnamon, basil and bay leaf. It is present in concentrations of 80–90% in clove bud oil and at 82–88% in clove leaf oil. Eugenol has a pleasant, spicy, clove-like scent. The name is derived from Eugenia caryophyllata, the former Linnean nomenclature term for cloves. The currently accepted name is Syzygium aromaticum.

Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is the ester of caffeic acid and (−)-quinic acid, functioning as an intermediate in lignin biosynthesis. The term "chlorogenic acids" refers to a related polyphenol family of esters, including hydroxycinnamic acids with quinic acid.
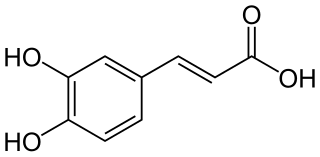
Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid. This yellow solid consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. It is found in all plants because it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one of the principal components of woody plant biomass and its residues.

Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, is an organic compound with the formula (CH3O)HOC6H3CH=CHCO2H. The name is derived from the genus Ferula, referring to the giant fennel (Ferula communis). Classified as a phenolic phytochemical or polyphenol, ferulic acid is an amber colored solid. Esters of ferulic acid are found in plant cell walls, covalently bonded to hemicellulose such as arabinoxylans. Salts and esters derived from ferulic acid are called ferulates.

Ipomoea purpurea, the common morning-glory, tall morning-glory, or purple morning glory, is a species in the genus Ipomoea, native to Mexico and Central America.
Hydroxycinnamic acids (hydroxycinnamates) are a class of aromatic acids or phenylpropanoids having a C6–C3 skeleton. These compounds are hydroxy derivatives of cinnamic acid.

Echinacea purpurea, the eastern purple coneflower, purple coneflower, hedgehog coneflower, or echinacea, is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to parts of eastern North America and present to some extent in the wild in much of the eastern, southeastern and midwestern United States as well as in the Canadian Province of Ontario. It is most common in the Ozarks and in the Mississippi/Ohio Valley. Its habitats include dry open woods, prairies and barrens.
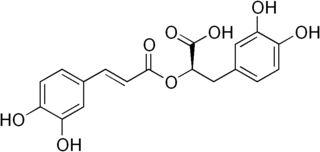
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.
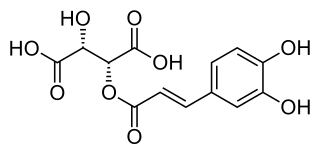
Caftaric acid is a non-flavonoid phenolic compound.
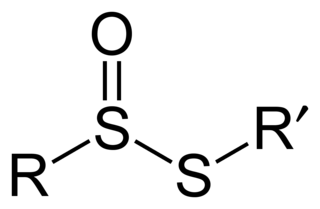
In organosulfur chemistry, thiosulfinate is a functional group consisting of the linkage R-S(O)-S-R. Thiolsulfinates are also named as alkanethiosulfinic acid esters.

Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function. Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.
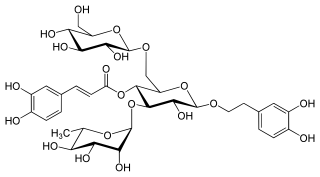
Echinacoside is a natural phenol. It is a caffeic acid glycoside from the phenylpropanoid class. It is constituted from a trisaccharide consisting of two glucose and one rhamnose moieties glycosidically linked to one caffeic acid and one dihydroxyphenylethanol (hydroxytyrosol) residue at the centrally situated rhamnose. This water-soluble glycoside is a distinctive secondary metabolite of Echinacea angustifolia and Echinacea pallida but only occurs in trace amounts in Echinacea purpurea. It is also isolated from Cistanche spp.

















