
Humulus, hop, is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The hop is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Hops are the female flowers of the hop species H. lupulus; as a main flavor and aroma ingredient in many beer styles, H. lupulus is widely cultivated for use by the brewing industry.

Epimedium, also known as barrenwort, bishop's hat, fairy wings, horny goat weed, or yin yang huo, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Berberidaceae. The majority of the species are endemic to China, with smaller numbers elsewhere in Asia, and a few in the Mediterranean region.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease.

Eriodictyol is a bitter-masking flavanone, a flavonoid extracted from yerba santa, a plant native to North America. Eriodictyol is one of the four flavanones identified in this plant as having taste-modifying properties, the other three being homoeriodictyol, its sodium salt, and sterubin.
In enzymology, an isoflavone 7-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a monoprenyl isoflavone epoxidase (EC 1.14.99.34) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sophora flavescens, the shrubby sophora, is a species of plant in the genus Sophora of the family Fabaceae. This genus contains about 52 species, nineteen varieties, and seven forms that are widely distributed in Asia, Oceania, and the Pacific islands. About fifteen of these species have a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicines.
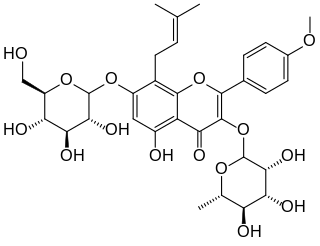
Icariin is a chemical compound classified as a prenylated flavonol glycoside, a type of flavonoid. It is the 8-prenyl derivative of kaempferol 3,7-O-diglucoside. The compound has been isolated from several species of plant belonging to the genus Epimedium which are commonly known as horny goat weed, Yin Yang Huo, and Herba epimedii. Extracts from these plants are reputed to produce aphrodisiac effects, and are used in traditional Chinese medicine to enhance erectile function. However, clinical trial data are lacking to support these claims.
The O-methylated flavonoids or methoxyflavonoids are flavonoids with methylations on hydroxyl groups. O-methylation has an effect on the solubility of flavonoids.

Retusin is an O-methylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Fabaceae species like Dipteryx odorata, in Dalbergia retusa and in Millettia nitida. It can also be found in Maackia amurensis cell cultures.
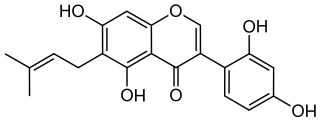
Luteone is a prenylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in the pods of Laburnum anagyroides and can be synthetized.

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.

Millettia pachycarpa is a perennial climbing shrub belonging to the genus Millettia. It is one of the most well known among ~150 species of Millettia, as it is widely used in traditional practices, such as for poisoning fish, agricultural pesticide, blood tonic, and treatments of cancer and infertility. The bark fiber is used for making strong ropes.

Barbigerone is one of a few pyranoisoflavones among several groups of isoflavones. It was first isolated from the seed of a leguminous plant Tephrosia barbigera; hence the name "barbigerone". Members of the genus Millettia are now known to be rich in barbigerone, including M. dielsiena, M. ferruginea, M. usaramensis, and M. pachycarpa. It has also been isolated from the medicinal plant Sarcolobus globosus. Barbigerone from S. globosus is validated to have significant antioxidant property. Barbigerone exhibits profound antiplasmodial activity against the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. It is also demonstrated that it has anti-cancer potential as it causes apoptosis of murine lung-cancer cells.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.

Erythrina burttii is a flowering plant species in the genus of Erythrina found in Kenya and Ethiopia.

8-Prenylnaringenin is a prenylflavonoid phytoestrogen. It is reported to be the most estrogenic phytoestrogen known. The compound is equipotent at the two forms of estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ, and it acts as a full agonist of ERα. Its effects are similar to those of estradiol, but it is considerably less potent in comparison.

Epimedium wushanense, the Wushan fairy wings, is a flowering plant species in the genus Epimedium.

Isoxanthohumol is a prenylflavonoid, and it is a phytoestrogen. It is abbreviated as IX or IXN.
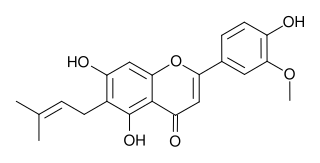
Cannflavins are a group of chemical compounds found in Cannabis sativa. Chemically, they are prenylflavonoids and are unrelated to THC and other cannabinoids. Cannflavins A and B were first identified in the 1980s and cannflavin C was identified in 2008.

















