
The Moraceae—often called the mulberry family or fig family—are a family of flowering plants comprising about 38 genera and over 1100 species. Most are widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, less so in temperate climates; however, their distribution is cosmopolitan overall. The only synapomorphy within the Moraceae is presence of laticifers and milky sap in all parenchymatous tissues, but generally useful field characters include two carpels sometimes with one reduced, compound inconspicuous flowers, and compound fruits. The family includes well-known plants such as the fig, banyan, breadfruit, jackfruit, mulberry, and Osage orange. The 'flowers' of Moraceae are often pseudanthia.

Morus, a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinate taxa, though the three most common are referred to as white, red, and black, originating from the color of their dormant buds and not necessarily the fruit color, with numerous cultivars and some taxa currently unchecked and awaiting taxonomic scrutiny. M. alba is native to South Asia, but is widely distributed across Europe, Southern Africa, South America, and North America. M. alba is also the species most preferred by the silkworm, and is regarded as an invasive species in Brazil and the United States.

Morus alba, known as white mulberry, common mulberry and silkworm mulberry, is a fast-growing, small to medium-sized mulberry tree which grows to 10–20 m (33–66 ft) tall. It is generally a short-lived tree with a lifespan comparable to that of humans, although there are some specimens known to be more than 250 years old. The species is native to China and India and is widely cultivated and naturalized elsewhere.

Tetrapanax papyrifer, the rice paper plant, is an evergreen shrub or small tree in the family Araliaceae, the sole species in the genus Tetrapanax. The specific epithet is frequently misspelled as "papyriferum", "papyriferus", or "papyrifera". It is native to eastern and central China and Taiwan, but widely cultivated in East Asia and in other tropical to mild temperate regions as well.

Maclura tricuspidata is a tree native to East Asia, occasionally grown for its fruit, somewhat similar to that of the related mulberry.

The paper mulberry is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae. It is native to Asia, where its range includes mainland China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, Southeast Asia, Myanmar, and India. It is widely cultivated elsewhere and it grows as an introduced species in New Zealand, parts of Europe, the United States, and Africa. Other common names include tapa cloth tree.

Morus rubra, commonly known as the red mulberry, is a species of mulberry native to eastern and central North America. It is found from Ontario, Minnesota, and Vermont south to southern Florida, and west as far as southeastern South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and central Texas. There have been reports of isolated populations in New Mexico, Idaho, and British Columbia.

Broussonetia is a genus of four species of trees in the family Moraceae, native to eastern Asia. These four species have high-quality fiber which consist of more than 90% of cellulose. They are traditionally applied for various daily necessities in South Eastern Asia and papermaking in East Asia.

Eriophorum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cyperaceae, the sedge family. They are found in the cool temperate, alpine, and Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere, primarily in the middle latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia.

Heracleum sphondylium, commonly known as hogweed or common hogweed, is a herbaceous perennial plant in the carrot family Apiaceae, which includes fennel, cow parsley, ground elder and giant hogweed. It is native to most of Europe, western Asia and northern Africa, but is introduced in North America and elsewhere. Other common names include cow parsnip. The flowers provide a great deal of nectar for pollinators.

Morus nigra, called black mulberry, is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae that is native to southwestern Asia, where it has been cultivated for so long that its precise natural range is unknown. The black mulberry is known for its large number of chromosomes.

Calinaga buddha, the freak, is a species of butterfly in the Nymphalidae family, Calinaginae subfamily. It is found from Muree, Punjab, Pakistan to Assam, India and from Sikkim, India to north Myanmar. The subspecies C. b. brahmaButler, 1885 is found in Yunnan, China and Assam India, and the subspecies C. b. formosanaFruhstorfer, 1908 is found in Taiwan.

Moreae is a tribe within the plant family Moraceae. It includes 6–10 genera and 70–80 species, including Morus, the genus that includes the mulberries, and Maclura, the genus that includes the Osage orange.

Parum is a genus of moths in the family Sphingidae erected by Walter Rothschild and Karl Jordan in 1903. It is monotypic, witth a single species, Parum colligata, that was first described by Francis Walker in 1856.
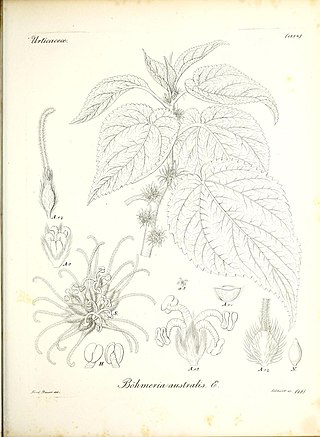
Pouzolzia australis, synonyms including Boehmeria australis and Boehmeria calophleba, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant family Urticaceae. It is endemic to small islands belonging to Australia and New Zealand – Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, and the Kermadec Islands. The population on Norfolk island, sometimes treated as a distinct subspecies, is critically endangered. In the Kermadec Islands, it was described in 2018 as "threatened – nationally endangered".

Morus celtidifolia, the Texas mulberry, is a plant species native to South America, Central America, Mexico, and the southwestern United States, ranging from Argentina north as far as Arizona and Oklahoma. In the US, it grows in canyons and on slopes, usually near streams, from 200–2,200 metres in elevation. It is very often referred to as "Morus microphylla," including in Flora of North America, but recent studies suggest that these names are synonymous with M. celtidifolia holding priority.
Morus cathayana or hua sang is a deciduous tree in the mulberry family Moraceae. It is native to China, Japan and Korea.

Morus mongolica, also described as Morus alba var. mongolica, is a woody plant native to mountain forests in Mongolia, China, Korea, and Japan. Common names include Mongolian mulberry, meng sang (China), and ilama by native people in the namesake region of Mongolia. Similar to M. notabilis, M. mongolica is an uncultivated mulberry.
















