
Sophora is a genus of about 45 species of small trees and shrubs in the pea family Fabaceae. The species have a pantropical distribution. The generic name is derived from sophera, an Arabic name for a pea-flowered tree.

Lycium chinense is one of two species of boxthorn shrub in the family Solanaceae. Along with Lycium barbarum, it produces the goji berry ("wolfberry"). Two varieties are recognized, L. chinense var. chinense and L. chinense var. potaninii. It is also known as Chinese boxthorn, Chinese matrimony-vine, Chinese teaplant, Chinese wolfberry, wolfberry, and Chinese desert-thorn.

Camoensia is a genus of 2 species of lianas in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, native to the Gulf of Guinea, Africa. C. scandens is cultivated as an ornamental plant; it has one of the largest leguminous flowers, up to 20 cm across. The genus has classically been assigned to the tribe Sophoreae, but was recently assigned to its own monophyletic tribe, Camoensieae, on the basis of molecular phylogenetic evidence. Species of Camoensia are known to produce quinolizidine alkaloids, consistent with their placement in the genistoid clade.

Lupinine is a quinolizidine alkaloid present in the genus Lupinus of the flowering plant family Fabaceae. The scientific literature contains many reports on the isolation and synthesis of this compound as well as a vast number of studies on its biosynthesis from its natural precursor, lysine. Studies have shown that lupinine hydrochloride is a mildly toxic acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and that lupinine has an inhibitory effect on acetylcholine receptors. The characteristically bitter taste of lupin beans, which come from the seeds of Lupinus plants, is attributable to the quinolizidine alkaloids which they contain, rendering them unsuitable for human and animal consumption unless handled properly. However, because lupin beans have potential nutritional value due to their high protein content, efforts have been made to reduce their alkaloid content through the development of "sweet" varieties of Lupinus.

Dermatophyllum secundiflorum is a species of flowering shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae that is native to the Southwestern United States and Mexico. Its common names include Texas mountain laurel, Texas mescalbean, frijolito, and frijolillo.

Astragalus mongholicus, synonyms including Astragalus propinquus and Astragalus membranaceus, commonly known as Mongolian milkvetch in English; 'Хунчир' in Mongolian; huáng qí, běi qí or huáng huā huáng qí, in Mongolia, is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Mongolian medicine. It is a perennial plant and it is not listed as being threatened.

Maackia amurensis, commonly known as the Amur maackia, is a species of tree in the family Fabaceae that can grow 15 metres (49 ft) tall. The species epithet and common names are from the Amur River region, where the tree originated; it occurs in northeastern China, Korea, and Russia.

Sophora cassioides is a legume tree endemic to central and southern Chile. It is one of the two species of Sophora endemic to continental Chile along with Sophora macrocarpa.
In enzymology, a 8-dimethylallylnaringenin 2'-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.103) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Styphnolobium japonicum, the Japanese pagoda tree is a species of deciduous tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae.

Orobanche minor, the hellroot, common broomrape, lesser broomrape, small broomrape or clover broomrape, is a holoparasitic flowering plant belonging to the family Orobanchaceae. It is one of about 150 non-photosynthetic plants in the genus Orobanche that parasitize autotrophic plants.

Matrine is an alkaloid found in plants from the genus Sophora. It has a variety of pharmacological effects, including anti-cancer effects, as well as κ-opioid and μ-opioid receptor agonism.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.
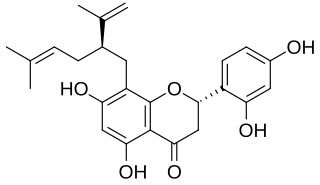
Sophoraflavanone G is a volatile phytoncide, released into the atmosphere, soil and ground water, by plants of the genus Sophora. Species include Sophora pachycarpa and Sophora exigua, all found to grow within the United States in a variety of soil types, within temperate conditions, no lower than 0 °F. Sophoraflavanone G is released in order to protect the plant against harmful protozoa, bacteria, and fungi. Sophoraflavanone G, also called kushenin, is a flavonoid compound.
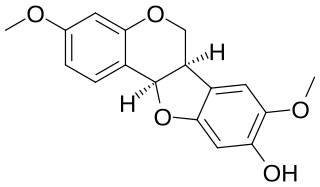
Kushenin is a pterocarpan, a type of furano-isoflavonoid, found in Sophora flavescens.

Oxymatrine is one of many quinolizidine alkaloid compounds extracted from the root of Sophora flavescens, a Chinese herb. It is very similar in structure to matrine, which has one less oxygen atom. Oxymatrine has a variety of effects in vitro and in animal models, including protection against apoptosis, tumor and fibrotic tissue development, and inflammation. Furthermore, oxymatrine has been shown to decrease cardiac ischemia, myocardial injury, arrhythmias, and improve heart failure by increasing cardiac function.

Aconitum coreanum, known as Korean monkshood, is one of the species of Aconitum. It is one of the crude botanical drugs that has been applied in Chinese medicine during past decades.

Genisteae is a tribe of trees, shrubs and herbaceous plants in the subfamily Faboideae of the family Fabaceae. It includes a number of well-known plants including broom, lupine (lupin), gorse and laburnum.

Quinolizidine alkaloids are natural products that have a quinolizidine structure; this includes the lupine alkaloids.



















