
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the rhytidome.

The Pinaceae, or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as cedars, firs, hemlocks, larches, pines and spruces. The family is included in the order Pinales, formerly known as Coniferales. Pinaceae are supported as monophyletic by their protein-type sieve cell plastids, pattern of proembryogeny, and lack of bioflavonoids. They are the largest extant conifer family in species diversity, with between 220 and 250 species in 11 genera, and the second-largest in geographical range, found in most of the Northern Hemisphere, with the majority of the species in temperate climates, but ranging from subarctic to tropical. The family often forms the dominant component of boreal, coastal, and montane forests. One species, Pinus merkusii, grows just south of the equator in Southeast Asia. Major centres of diversity are found in the mountains of southwest China, Mexico, central Japan, and California.

Picea abies, the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.

Pinus sibirica, or Siberian pine, in the family Pinaceae is a species of pine tree that occurs in Siberia from 58°E in the Ural Mountains east to 126°E in the Stanovoy Range in southern Sakha Republic, and from Igarka at 68°N in the lower Yenisei valley, south to 45°N in central Mongolia.
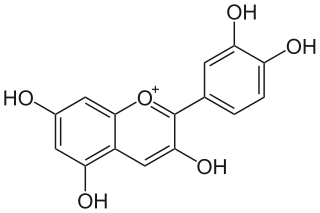
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin. It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH < 3, violet at pH 7-8, and blue at pH > 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.

In enzymology, a flavonol 3-O-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

The flavanonols are a class of flavonoids that use the 3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone.
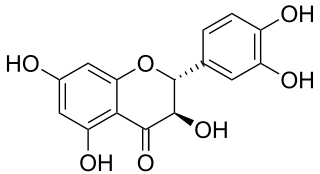
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols.

Chrysanthemin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of cyanidin.

ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.

Syringetin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape, in Lysimachia congestiflora and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.

Laricitrin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.
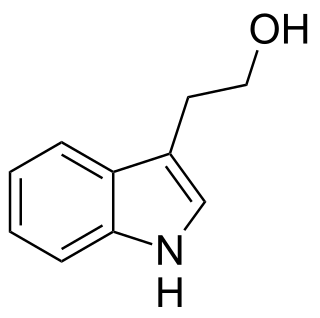
Tryptophol is an aromatic alcohol that induces sleep in humans. It is found in wine as a secondary product of ethanol fermentation. It was first described by Felix Ehrlich in 1912. It is also produced by the trypanosomal parasite in sleeping sickness.

Catechin-7-O-glucoside is a flavan-3-ol glycoside formed from catechin.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid 4-O-glucoside is a glucoside of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. It can be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces.

Isorhapontin is a stilbenoid. It is the glucoside of isorhapontigenin. It can be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces, in the bark of Picea sitchensis or in white spruce.
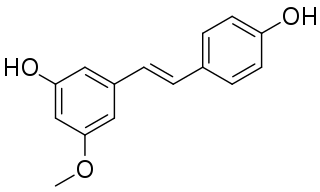
Pinostilbene is a stilbenoid found in Gnetum venosum and in the bark of Pinus sibirica.

Phlomoides tuberosa, the sage-leaf mullein, is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, native to China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Russia; SW Asia and Europe. Enlarged, tuberous roots give rise to erect stems to 150 cm bearing purple-red flowers.





















