A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Hydrangea macrophylla is a species of flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, native to Japan. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 2 m (7 ft) tall by 2.5 m (8 ft) broad with large heads of pink or blue flowers in summer and autumn. Common names include bigleaf hydrangea, French hydrangea, lacecap hydrangea, mophead hydrangea, penny mac and hortensia. It is widely cultivated in many parts of the world in many climates. It is not to be confused with H. aspera 'Macrophylla'.

Delphinidin is an anthocyanidin, a primary plant pigment, and also an antioxidant. Delphinidin gives blue hues to flowers in the genera Viola and Delphinium. It also gives the blue-red color of the grape that produces Cabernet Sauvignon, and can be found in cranberries and Concord grapes as well as pomegranates, and bilberries.

Paeonia lactiflora is a species of herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Paeoniaceae, native to central and eastern Asia from eastern Tibet across northern China to eastern Siberia.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.

Cucurbitacin is a class of biochemical compounds that some plants – notably members of the pumpkin and gourd family, Cucurbitaceae – produce and which function as a defence against herbivores. Cucurbitacins are chemically classified as triterpenes, formally derived from cucurbitane, a triterpene hydrocarbon – specifically, from the unsaturated variant cucurbit-5-ene, or 19(10→9β)-abeo-10α-lanost-5-ene. They often occur as glycosides. They and their derivatives have been found in many plant families, in some mushrooms and even in some marine mollusks.

Purple corn or purple maize is group of flint maize varieties originating in South America, descended from a common ancestral variety termed "k'culli" in Quechua. It is most commonly grown in the Andes of Peru, Bolivia, Colombia and Ecuador.
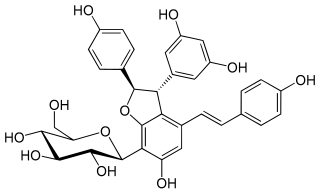
Diptoindonesin A is a C-glucoside of ε-viniferin isolated from the two Dipterocarpaceae Shorea seminis and Dryobalanops aromatica.
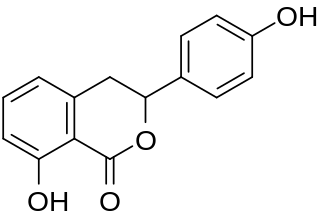
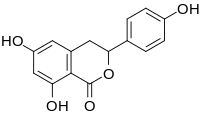
Hydrangenol is a dihydroisocoumarin. It can be found in Hydrangea macrophylla, as well as its 8-O-glucoside. (−)-Hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside and (+)-hydrangenol 4′-O-glucoside can be found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii.
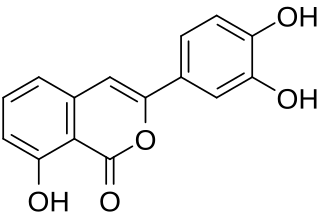
Thunberginol A is an isocoumarin found in Hydrangea macrophylla and the herbal preparation hydrangeae dulcis folium which is produced from its leaves.

Thunberginol B is an isocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol D is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol E is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Thunberginol F is a phthalide found in Hydrangea macrophylla.

Thunberginol G is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Kaempferol 7-O-glucoside is a flavonol glucoside. It can be found in Smilax china, and in the fern Asplenium rhizophyllum, and its hybrid descendants, as part of a complex with caffeic acid.
Isoleucine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.117, CYP79D3, CYP79D4) is an enzyme with systematic name L-isoleucine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aureusidin synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 2',4,4',6'-tetrahydroxychalcone 4'-O-beta-D-glucoside:oxygen oxidoreductase.