 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| Properties | |
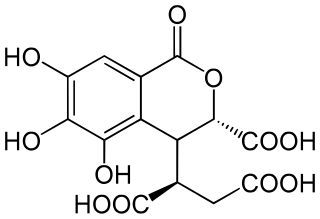
| C34H24O22 | |
| Molar mass | 784.54 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
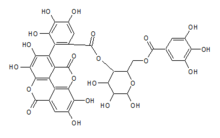
Terflavin B is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Myrobalanus chebula ( Terminalia chebula ), the black chebulic, and in Terminalia catappa , the Indian almond. [1]
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.

Terminalia chebula, commonly known as black- or chebulic myrobalan, is a species of Terminalia, native to South Asia from India and Nepal east to southwest China (Yunnan), and south to Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and Vietnam.

Terminalia catappa is a large tropical tree in the leadwood tree family, Combretaceae, that grows mainly in the tropical regions of Asia, Africa, and Australia. Common names in English include country almond, Indian almond, Malabar almond, sea almond, tropical almond, beach almond and false kamani.
It is formed from a nonahydroxytriphenic acid dilactone and a gallic acid linked to a glucose molecules.

Nonahydroxytriphenic acid is a moiety found in some ellagitannins such as roburin A, B,C and D, castalagin or grandinin.

Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid, found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. The chemical formula of gallic acid is C6H2(OH)3COOH. It is found both free and as part of hydrolyzable tannins. The gallic acid groups are usually bonded to form dimers such as ellagic acid. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively.