Related Research Articles

Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters are intramolecular esters derived from hydroxy carboxylic acids. They can be saturated or unsaturated. Some contain heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is chemically derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.

Punicalagin (Pyuni-cala-jen) is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found as alpha and beta isomers in pomegranates, Terminalia catappa, Terminalia myriocarpa, and in Combretum molle, the velvet bushwillow, a plant species found in South Africa. These three genera are all Myrtales and the last two are both Combretaceae.

Terminalia chebula, commonly known as black- or chebulic myrobalan, is a species of Terminalia, native to South Asia from Pakistan, India and Nepal east to southwest China (Yunnan), and south to Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and Vietnam.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.
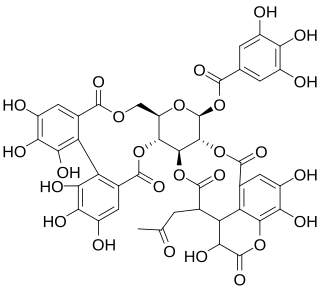
Chebulagic acid is a benzopyran tannin and an antioxidant that has many potential uses in medicine.

Ethyl gallate is a food additive with E number E313. It is the ethyl ester of gallic acid. Ethyl gallate is added to food as an antioxidant.
A hydrolysable tannin or pyrogallol-type tannin is a type of tannin that, on heating with hydrochloric or sulfuric acids, yields gallic or ellagic acids.
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.

Quercus infectoria or the Aleppo oak is a species of oak well known for producing galls that have been traditionally used for centuries in Asia medicinally while also used in softening leather and in making black dye and ink.

Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function. Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.
Rhynchosia volubilis is a plant species in the genus Rhynchosia.
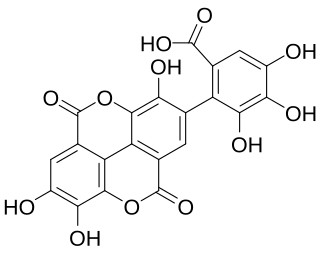
Flavogallonic acid dilactone is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in Rhynchosia volubilis seeds, in Shorea laevifolia, in Anogeissus leiocarpus and Terminalia avicennoides.
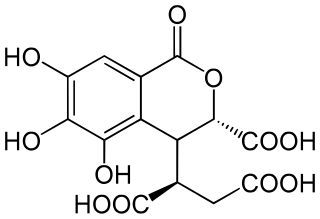
Chebulic acid is a phenolic compound isolated from the ripe fruits of Terminalia chebula.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the sarcotestas, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of the pomegranate fruit.
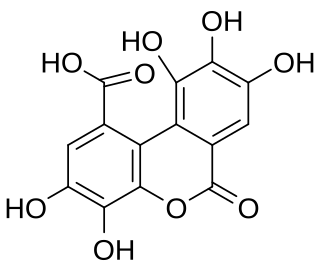
Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid. It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.

Methyl gallate is a phenolic compound. It is the methyl ester of gallic acid.
References
- 1 2 Cantos, E.; Espín, J. C.; López-Bote, C.; de la Hoz, L.; Ordóñez, J. A.; Tomás-Barberán, F. A. (2003). "Phenolic Compounds and Fatty Acids from Acorns (Quercus spp.), the Main Dietary Constituent of Free-Ranged Iberian Pigs". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 51 (21): 6248–6255. doi:10.1021/jf030216v. PMID 14518951.
- 1 2 Chapman, J. M.; Nast, J. R.; Scholes, C.; Niemann, S. (2006). "Application of LC/ESI/MS and LC/EI/MS to the Characterization of Tannins and Flavonoids from the Acorns of Quercus macrocarpa" (PDF). Rockhurst University.
- 1 2 Fernandes, A.; Sousa, A.; Mateus, N.; Cabral, M.; de Freitas, V. (2011). "Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Cork from Quercus suber L. by HPLC–DAD/ESI–MS". Food Chemistry. 125 (4): 1398–1405. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.10.016.
- ↑ Terminalia chebula on www.mmh-mms.com
- 1 2 Kinjo, J.; Nagao, T.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Okabe, H. (2001). "Antiproliferative Constituents in the Plant 8. Seeds of Rhynchosia volubilis" (pdf). Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 24 (12): 1443–1445. doi: 10.1248/bpb.24.1443 . hdl: 10069/8375 . PMID 11767121. INIST 13400364.
- ↑ Shuaibu, M. N.; Wuyep, P. A.; Yanagi, T.; Hirayama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kouno, I. (2008). "The use of microfluorometric method for activity-guided isolation of antiplasmodial compound from plant extracts". Parasitology Research. 102 (6): 1119–1127. doi:10.1007/s00436-008-0879-6. PMID 18214539. S2CID 19496595.