
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
In organic chemistry, a hemiacetal or a hemiketal has the general formula R1R2C(OH)OR, where R1, R2 is hydrogen or an organic substituent. They generally result from the addition of an alcohol to an aldehyde or a ketone, although the latter are sometimes called hemiketals. Most sugars are hemiacetals.

In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R2C(OR')2. Here, the R groups can be organic fragments or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other or not. Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.

Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6H2(OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates".

Polyphenols are a large family of naturally occurring phenols. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments.

Tannic acid is a specific form of tannin, a type of polyphenol. Its weak acidity (pKa around 6) is due to the numerous phenol groups in the structure. The chemical formula for commercial tannic acid is often given as C76H52O46, which corresponds with decagalloyl glucose, but in fact it is a mixture of polygalloyl glucoses or polygalloyl quinic acid esters with the number of galloyl moieties per molecule ranging from 2 up to 12 depending on the plant source used to extract the tannic acid. Commercial tannic acid is usually extracted from any of the following plant parts: Tara pods (Caesalpinia spinosa), gallnuts from Rhus semialata or Quercus infectoria or Sicilian sumac leaves (Rhus coriaria).

Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran (THF) by replacement of the methylene group (CH2) at the 2-position with an oxygen atom. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.

The Danishefsky Taxol total synthesis in organic chemistry is an important third Taxol synthesis published by the group of Samuel Danishefsky in 1996 two years after the first two efforts described in the Holton Taxol total synthesis and the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. Combined they provide a good insight in the application of organic chemistry in total synthesis.

Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—occur naturally in wine. These include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.
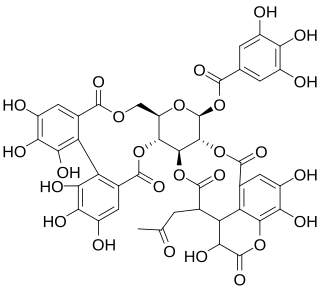
Chebulagic acid is a benzopyran tannin and an antioxidant that has many potential uses in medicine.

Phlobaphenes are reddish, alcohol-soluble and water-insoluble phenolic substances. They can be extracted from plants, or be the result from treatment of tannin extracts with mineral acids. The name phlobaphen come from the Greek roots φλoιὀς (phloios) meaning bark and βαφή (baphe) meaning dye.

The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.

Casuarictin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species.

Condensed tannins are polymers formed by the condensation of flavans. They do not contain sugar residues.

The phenolic content in tea refers to the phenols and polyphenols, natural plant compounds which are found in tea. These chemical compounds affect the flavor and mouthfeel of tea. Polyphenols in tea include catechins, theaflavins, tannins, and flavonoids.

Geraniin is a dehydroellagitannin found in geraniums. It is found for instance in Geranium thunbergii, which is one of the most popular folk medicines and also an official antidiarrheic drug in Japan. It can also be found in the rind of Nephelium lappaceum (rambutan).

Mallotusinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. It is more generally present in Geraniales.

Tirandamycins are a small group of natural products that contain a bicyclic ketal system and a tetramic acid moiety, the latter of which is found in different natural products from a variety of sources and which is characterized by a 2,4-pyrrolidinedione ring system. Members of this structural family have shown a wide range of biological activities like in antiparasitic, antifungal and anti-HIV evaluations, and furthermore, have shown potential usefulness because of their potent antibacterial properties. Streptolydigin, an analogue of the tirandamycins, is known to function as an antibacterial agent through inhibiting the chain initiation and elongation steps RNA polymerase transcription. The structural diversity in the tirandamycin family originates from the different oxidation patterns observed in the bicycic ketal system, and these modifications are determinant features for the bioactivity associated with these molecules.
















