
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.

The water caltrop is any of three extant species of the genus Trapa: Trapa natans, Trapa bicornis and the endangered Trapa rossica. It is also known as buffalo nut, bat nut, devil pod, ling nut, mustache nut, singhara nut or water chestnut.

Pleroma semidecandrum, synonym Tibouchina semidecandra, the princess flower, glory bush, or lasiandra, is a flowering plant in the family Melastomataceae, native to southeast Brazil.
The ellagitannins are a diverse class of hydrolyzable tannins, a type of polyphenol formed primarily from the oxidative linkage of galloyl groups in 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl glucose. Ellagitannins differ from gallotannins, in that their galloyl groups are linked through C-C bonds, whereas the galloyl groups in gallotannins are linked by depside bonds.

Casuarictin is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species.

Stachyurus is the only genus in the flowering plant family Stachyuraceae, native to the Himalayas and eastern Asia. They are deciduous shrubs or small trees with pendent racemes of 4-petalled flowers which appear on the bare branches before the leaves. The plants have leaves with serrate margins.

Tellimagrandin II is the first of the ellagitannins formed from 1,2,3,4,6-pentagalloyl-glucose. It can be found in Geum japonicum and Syzygium aromaticum (clove).

Quercus infectoria or the Aleppo oak is a species of oak well known for producing galls that have been traditionally used for centuries in Asia medicinally while also used in softening leather and in making black dye and ink.
The Flavono-ellagitannins or complex tannins are a class of tannins formed from the complexation of an ellagitannin with a flavonoid. Flavono-ellagitannins can be found in Quercus mongolica var. grosseserrata.

1,2,6-Trigalloyl glucose is a gallotannin found in cell cultures of Cornus officinalis.

Casuarinin is an ellagitannin. It is found in the pericarp of pomegranates. It is also found in Casuarina and Stachyurus species and in Alnus sieboldiana.

Pedunculagin is an ellagitannin. It is formed from casuarictin via the loss of a gallate group.
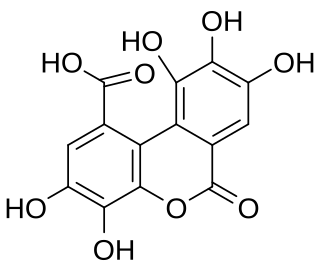
Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid. It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.
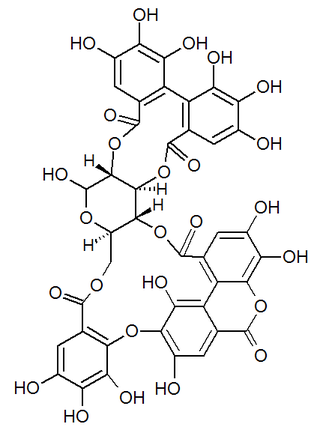
Alnusiin is an ellagitannin found in Alnus sieboldiana.

Alnus sieboldiana is an alder species found on the islands of Honshū, Shikoku, and Suwanose-jima in Japan.

Geraniin is a dehydroellagitannin found in geraniums. It is found for instance in Geranium thunbergii, which is one of the most popular folk medicines and also an official antidiarrheic drug in Japan. It can also be found in the rind of Nephelium lappaceum (rambutan).

Nuphar japonica, known as East Asian yellow water-lily, is an aquatic plant species in the genus Nuphar found in Japan and the Korean Peninsula. It is endangered in Russia. The species was not accepted by The Plant List as of November 2013, which regarded it as an "unresolved name".

Mallotusinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. It is more generally present in Geraniales.

Monochaetum multiflorum is a flowering plant species in the genus Monochaetum indigenous to Colombia.

Mallojaponin is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus. This compound contains the moiety elaeocarpusinic acid, an oxidized hexahydroxydiphenic acid group which reacted with a dehydroascorbic acid molecule. It also contains a valoneic acid and a gallic acid moieties linked to a glucose molecule.


















