This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(February 2025) |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
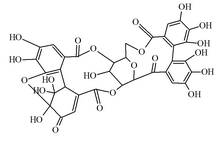
| IUPAC name 6,7,8,11,12,13,25,26,30,30,31,37-Dodecahydroxy-17,21,36,38,39-pentaoxaoctacyclo[18.16.1.12,19.127,31.04,9.010,15.023,28.029,34]nonatriaconta-4,6,8,10,12,14,23,25,27,33-decaene-3,16,22,32,3 5-pentone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H24O22 | |
| Molar mass | 784.54 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Granatin A is an ellagitannin found in the pericarp of Punica granatum (pomegranate). [1] It is a weak carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. [1]