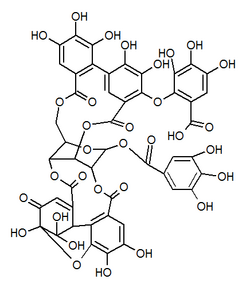
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names Mallotusinic acid [1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C48H32O32 | |
| Molar mass | 1120.74 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Mallotusinic acid is a hydrolysable tannin found in the bark of Mallotus japonicus . [2] It is more generally present in Geraniales. [3]