Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a soft waxy solid with the formula CH3(CH2)16CO2H. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin. Stearic acid is a prevalent FA in nature, found in many animal and vegetable fats, but is usually higher in animal fat than vegetable fat. It has a melting point of 69.4 °C and a pKa of 4.50.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all known elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.
Myristic acid is a common saturated fatty acid with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)12COOH. Its salts and esters are commonly referred to as myristates or tetradecanoates. It is named after the binomial name for nutmeg, from which it was first isolated in 1841 by Lyon Playfair.

Ammonium phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3PO4. It is the ammonium salt of orthophosphoric acid. A related "double salt", (NH4)3PO4.(NH4)2HPO4 is also recognized but is impractical to use. Both triammonium salts evolve ammonia. In contrast to the unstable nature of the triammonium salts, the diammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 and monoammonium salt (NH4)H2PO4 are stable materials that are commonly used as fertilizers to provide plants with fixed nitrogen and phosphorus.
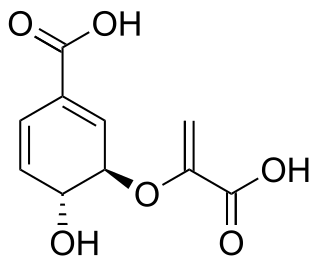
Chorismic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form chorismate, is an important biochemical intermediate in plants and microorganisms. It is a precursor for:

Adenanthera pavonina is a perennial and non-climbing species of leguminous tree. Its uses include food and drink, traditional medicine, and timber.

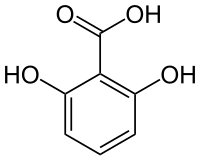
Gentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a derivative of benzoic acid and a minor (1%) product of the metabolic break down of aspirin, excreted by the kidneys.

Enterobactin is a high affinity siderophore that acquires iron for microbial systems. It is primarily found in Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium.

Homoeriodictyol is a bitter-masking flavanone extracted from Yerba Santa a plant growing in America.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.
2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a natural phenol found in Phyllanthus acidus and in the aquatic fern Salvinia molesta. It is also abundant in the fruits of Flacourtia inermis. It is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of organic compound.
The molecular formula C7H6O4 may refer to:

The phenolic content in tea refers to the phenols and polyphenols, natural plant compounds which are found in tea. These chemical compounds affect the flavor and mouthfeel of tea. Polyphenols in tea include catechins, theaflavins, tannins, and flavonoids.
Hydroxybenzoic acid may refer to several related chemical compounds:
Resorcylic acid is a type of dihydroxybenzoic acid. It may refer to:
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid.

3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a colorless solid.

Flacourtia inermis, known commonly as lovi-lovi, or batoko plum, is a species of flowering plant native to the Philippines and Indonesia, but which has naturalized around the edges of tropical Asia and Africa. Common names in Indonesia include Tome-Tome, Lovi-lovi, and lobi-lobi.
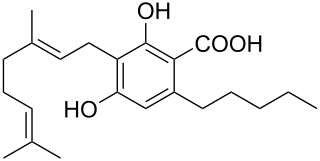
Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) is the acidic form of cannabigerol (CBG). It is a dihydroxybenzoic acid and olivetolic acid in which the hydrogen at position 3 is substituted by a geranyl group. It is a biosynthetic precursor to Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, which is the principal psychoactive constituent of the Cannabis plant. It is also a diterpenoid, a polyketide, a member of resorcinols and a phytocannabinoid. It derives from an olivetolic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a cannabigerolate.

2,4,5-Trichlorophenol (TCP) is an organochloride with the molecular formula C6H3Cl3O. It has been used as a fungicide and herbicide. Precursor chemical used in the production of 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4,5-T) and hexachlorophene involves the intermediate production of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (TCP) and the formation of [[2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin]] (TCDD, commonly referred to simply as dioxin) as an unwanted by-product. In the course of purifying the hexachlorophene, still bottom wastes were created with concentrated levels of TCP and dioxin.