
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta, also known as Coniferophyta or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews. As of 2002, Pinophyta contained seven families, 60 to 65 genera, and more than 600 living species.

A spruce is a tree of the genus Picea, a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. Picea is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form.

The Pinaceae, or pine family, are conifer trees or shrubs, including many of the well-known conifers of commercial importance such as cedars, firs, hemlocks, piñons, larches, pines and spruces. The family is included in the order Pinales, formerly known as Coniferales. Pinaceae have distinctive cones with woody scales bearing typically two ovules, and are supported as monophyletic by both morphological trait and genetic analysis. They are the largest extant conifer family in species diversity, with between 220 and 250 species in 11 genera, and the second-largest in geographical range, found in most of the Northern Hemisphere, with the majority of the species in temperate climates, but ranging from subarctic to tropical. The family often forms the dominant component of boreal, coastal, and montane forests. One species, Pinus merkusii, grows just south of the equator in Southeast Asia. Major centres of diversity are found in the mountains of southwest China, Mexico, central Japan, and California.

Picea mariana, the black spruce, is a North American species of spruce tree in the pine family. It is widespread across Canada, found in all 10 provinces and all 3 territories. It is the official tree of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador and is that province's most numerous tree. The range of the black spruce extends into northern parts of the United States: in Alaska, the Great Lakes region, and the upper Northeast. It is a frequent part of the biome known as taiga or boreal forest.

Picea abies, the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
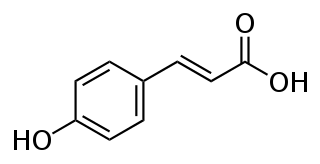
p-Coumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CH=CHCO2H. It is one of the three isomers of hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a white solid that is only slightly soluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.

Piceatannol is the organic compound with the formula ( 2C6H3)2CH)2. Classified as a stilbenoid and a phenol, it is a white solid, although samples often are yellow owing to impurities.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzoate 4-O-beta-D-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Cydia strobilella, the spruce seed moth, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Europe.
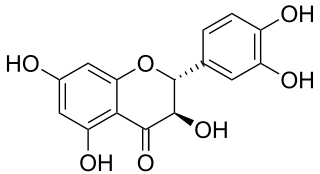
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols. It is extracted from plants such as Siberian larch and milk thistle.

Syringetin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape, in Lysimachia congestiflora and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.

Astringin is a stilbenoid, the 3-β-D-glucoside of piceatannol. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis and Picea abies.

A snowbank fungus is any one of a number of diverse species of fungi that occur adjacent to or within melting snow. They are most commonly found in the mountains of western North America where a deep snowpack accumulates during the winter and slowly melts through the spring and summer, often shaded by coniferous forest. They may be saprotrophic, mycorrhizal, or in the case of Caloscypha fulgens, pathogenic.

Picein is a phenolic compound found in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces. It is the glucoside of piceol.

Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces. Picein is the glucoside of piceol.

Isorhapontigenin is a tetrahydroxylated stilbenoid with a methoxy group. It is an isomer of rhapontigenin and an analog of resveratrol. It is found in the Chinese herb Gnetum cleistostachyum, in Gnetum parvifolium and in the seeds of the palm Aiphanes aculeata.

Isorhapontin is a stilbenoid. It is the glucoside of isorhapontigenin. It can be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces, in the bark of Picea sitchensis or in white spruce.


















