
Ink is a gel, sol, or solution that contains at least one colorant, such as a dye or pigment, and is used to color a surface to produce an image, text, or design. Ink is used for drawing or writing with a pen, brush, reed pen, or quill. Thicker inks, in paste form, are used extensively in letterpress and lithographic printing.

Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.

Invisible ink, also known as security ink or sympathetic ink, is a substance used for writing, which is invisible either on application or soon thereafter, and can later be made visible by some means, such as heat or ultraviolet light. Invisible ink is one form of steganography.

In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the element iron in its +2 oxidation state. The adjective ferrous or the prefix ferro- is often used to specify such compounds, as in ferrous chloride for iron(II) chloride (FeCl2). The adjective ferric is used instead for iron(III) salts, containing the cation Fe3+. The word ferrous is derived from the Latin word ferrum, meaning "iron".

Haematoxylin or hematoxylin, also called natural black 1 or C.I. 75290, is a compound extracted from heartwood of the logwood tree with a chemical formula of C
16H
14O
6. This naturally derived dye has been used as a histologic stain, as an ink and as a dye in the textile and leather industry. As a dye, haematoxylin has been called palo de Campeche, logwood extract, bluewood and blackwood. In histology, haematoxylin staining is commonly followed by counterstaining with eosin. When paired, this staining procedure is known as H&E staining and is one of the most commonly used combinations in histology. In addition to its use in the H&E stain, haematoxylin is also a component of the Papanicolaou stain which is widely used in the study of cytology specimens.
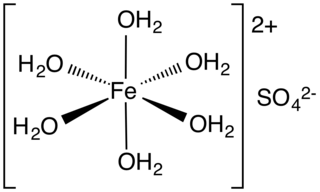
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula FeSO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but several values for x are known. The hydrated form is used medically to treat or prevent iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for hydrated sulfate minerals), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.

Potassium ferricyanide is the chemical compound with the formula K3[Fe(CN)6]. This bright red salt contains the octahedrally coordinated [Fe(CN)6]3− ion. It is soluble in water and its solution shows some green-yellow fluorescence. It was discovered in 1822 by Leopold Gmelin.

Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6H2(OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates".

Tannic acid is a specific form of tannin, a type of polyphenol. Its weak acidity (pKa around 6) is due to the numerous phenol groups in the structure. The chemical formula for commercial tannic acid is often given as C76H52O46, which corresponds with decagalloyl glucose, but in fact it is a mixture of polygalloyl glucoses or polygalloyl quinic acid esters with the number of galloyl moieties per molecule ranging from 2 up to 12 depending on the plant source used to extract the tannic acid. Commercial tannic acid is usually extracted from any of the following plant parts: Tara pods (Caesalpinia spinosa), gallnuts from Rhus semialata or Quercus infectoria or Sicilian sumac leaves (Rhus coriaria).
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the formula Al2(SO4)3. It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a coagulating agent in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plants, and also in paper manufacturing.
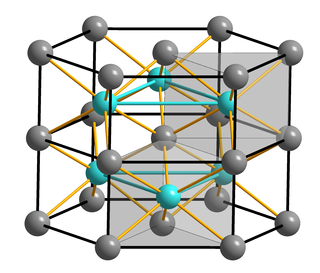
Iron(II) sulfide or ferrous sulfide is one of a family of chemical compounds and minerals with the approximate formula FeS. Iron sulfides are often iron-deficient non-stoichiometric. All are black, water-insoluble solids.

Roller ball pens or roll pens are pens which use ball-point writing mechanisms with water-based liquid or gelled ink, as opposed to the oil-based viscous inks found in ballpoint pens. These less viscous inks, which tend to saturate more deeply and more widely into paper than other types of ink, give roller ball pens their distinctive writing qualities. The writing point is a tiny ball, usually 0.5 or 0.7 mm in diameter, that transfers the ink from the reservoir onto the paper as the pen moves.

Iron(II) acetate describes compounds with formula Fe(CH3CO2)2·(H2O)x where x can be 0 (anhydrous) or 4 (tetrahydrate). The anhydrous compound is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. The tetrahydrate is light green solid that is highly soluble in water.

Fountain pen ink is a water-based ink intended for use with fountain pens.

In staining dyes, nigrosin is a mixture of black synthetic dyes made by heating a mixture of nitrobenzene, aniline, and hydrochloric acid in the presence of copper or iron. Related to induline, it is a mixture of phenazine-based compounds. Its main industrial uses are as a colorant for lacquers and varnishes and in marker pen inks. Sulfonation of nigrosin yields a water-soluble anionic dye, nigrosin WS.

Atramentum or atrament, generally means a very black, usually liquid, substance. For example, an octopus may emit a puff of atrament.
Quercitannic acid is one of the two forms of tannic acid found in oak bark and leaves. The other form is called gallotannic acid and is found in oak galls.

Iron(II) nitrate is the nitrate salt of iron(II). It is commonly encountered as the green hexahydrate, Fe(NO3)2·6H2O, which is a metal aquo complex, however it is not commercially available unlike iron(III) nitrate due to its instability to air. The salt is soluble in water and serves as a ready source of ferrous ions.






















