
Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of Vitis, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Eucommia ulmoides is a species of small tree native to China. It belongs to the monotypic family Eucommiaceae. It is considered vulnerable in the wild, but is widely cultivated in China for its bark and is highly valued in herbology such as traditional Chinese medicine.

Shorea is a genus of about 196 species of mainly rainforest trees in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The genus is named after Sir John Shore, the governor-general of the British East India Company, 1793–1798. The timber of trees of the genus is sold under the common names lauan, luan, lawaan, meranti, seraya, balau, bangkirai, and Philippine mahogany.

Caryocar is a genus of flowering plants, in the South American family Caryocaraceae described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1771. It is native primarily to South America with a few species extending into Central America and the West Indies.

Acer glabrum is a species of maple native to western North America, from southeastern Alaska, British Columbia and western Alberta, east to western Nebraska, and south through Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana and Colorado to California, Arizona and New Mexico.

The curl-crested jay is a jay from South America.

Caryocar nuciferum, the butter-nut of Guiana, is also known as pekea-nut, or – like all other species of Caryocar with edible nuts – "souari-nut" or "sawarri-nut". It is a fruit tree native to northern Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guyana, Panama, and Venezuela.
Caryocar amygdaliforme is a species of tree in the Caryocaraceae family. It is native to South America.

Viburnum dentatum, southern arrowwood or arrowwood viburnum or roughish arrowwood, is a small shrub, native to the Eastern United States and Canada from Maine south to Northern Florida and Eastern Texas.

Purple corn or purple maize is a variety of flint maize originating from South America. It is more commonly seen in Peru, Bolivia, Colombia and Ecuador.

Caryocar brasiliense, known as pequi or "souari nut", like its congeners, is an edible fruit popular in some areas of Brazil, especially in Centerwestern Brazil.
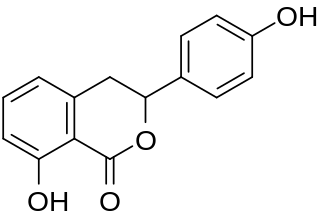
Hydrangenol is a dihydroisocoumarin. It can be found in Hydrangea macrophylla, as well as its 8-O-glucoside. (-)-hydrangenol 4'-O-glucoside and (+)-hydrangenol 4'-O-glucoside can be found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Phyllodulcin is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangea macrophylla and Hydrangea serrata. It is a sweetener 400-800 times sweeter than sugar.
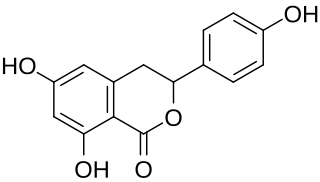
Thunberginol C is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

Dihydroisocoumarins are phenolic compounds related to isocoumarin. Dihydroisocoumarin glucosides can be found in Caryocar glabrum.

Thunberginol D is a dihydroisocoumarin found in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium, the processed leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii.

The Magdalena–Urabá moist forests (NT0137) is an ecoregion in the north of Colombia. The terrain is largely flat or undulating, but includes mountainous areas in the south. It contains moist forests and large wetlands that are important to resident and migratory birds. The ecoregion forms a bridge between the Pacific coast ecoregions of Colombia and Central America, and the ecoregions of the Andes and Amazon. It is surrounded by the more populated parts of Colombia and is threatened by farming, ranching, logging, oil exploitation and water pollution in the main rivers.

Leucospermum glabrum is an evergreen, rounded, upright shrub of up to 2½ m (8 ft) high, that is assigned to the family Proteaceae. It has broad inverted egg-shaped leaves with seven to fourteen teeth near their tips, and oval flower heads of about 8 cm (3.2 in) in diameter, with hairy, orange and carmine-coloured flowers from which long styles with a thickened end emerge, giving the flowerhead as a whole the appearance of a pincushion. It flowers between August and October. Its common name is Outeniqua pincushion in English and Outeniekwa-kreupelhout in Afrikaans. It naturally occurs in a limited area on the south coast of South Africa.














