
Dermestidae are a family of Coleoptera that are commonly referred to as skin beetles. Other common names include larder beetle, hide or leather beetles, carpet beetles, and khapra beetles. There are over 1,800 species described.

The beautiful demoiselle is a species of damselfly in the family Calopterygidae. It is found in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. It is often found along fast-flowing waters where it is most at home.

The beet armyworm or small mottled willow moth is one of the best-known agricultural pest insects. It is also known as the asparagus fern caterpillar. It is native to Asia, but has been introduced worldwide and is now found almost anywhere its many host crops are grown. The voracious larvae are the main culprits. In the British Isles, where it is an introduced species and not known to breed, the adult moth is known as the small mottled willow moth.
Smith's earth snake, also known commonly as the violet shieldtail, is a species of nonvenomous snake in the family Uropeltidae. The species is endemic to India.

The soldier flies are a family of flies. The family contains over 2,700 species in over 380 extant genera worldwide. Adults are found near larval habitats, which are found in a wide array of locations, mostly in wetlands, damp places in soil, sod, under bark, in animal excrement, and in decaying organic matter. The Stratiomyinae are a different subgroup that tends to have an affinity to aquatic environments. They are diverse in size and shape, though they commonly are partly or wholly metallic green, or somewhat wasplike mimics, marked with black and yellow or green and sometimes metallic. They are often rather inactive flies which typically rest with their wings placed one above the other over the abdomen.

The Mycetophilidae are a family of small flies, forming the bulk of those species known as fungus gnats. About 3000 described species are placed in 150 genera, but the true number of species is undoubtedly much higher. They are generally found in the damp habitats favoured by their host fungi and sometimes form dense swarms.

Carnidae, also known as bird flies or filth flies, is a family of flies (Diptera). There are 6 genera, containing about 93 species worldwide.
Jean-Jacques Kieffer was a French naturalist and entomologist who specialised in the study of parasitic insects. Educated as a priest, Kieffer taught natural science in Bitche, Lorraine while working on the description and classification of insects. His work and publications later became a predominant source of description and classification for entomologists in the early 20th century, in particular with regard to parasitoid wasps, midges, and mosquitos.

The nine-spotted moth or yellow belted burnet is a moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.
Dahl's toad-headed turtle is a medium-sized species of side-necked turle in the family Chelidae. This critically endangered freshwater turtle is endemic to northern Colombia, where it lives in small pools, streams, and swamps, but aestivates on land.

Eristalis nemorum is a species of hoverfly. It is found in the Palearctic and in the Nearctic.

Chrysotoxum bicinctum is a species of hoverfly.
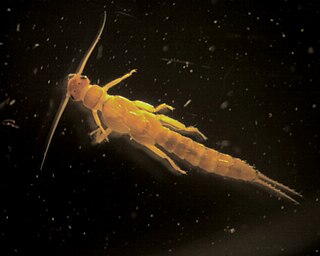
Chloroperlidae are a family of stoneflies, commonly known as green stoneflies, with more than 200 species and 22 genera. They appear green to yellow in colour, and are popularly used among fisherman as bait for trout fishing. Green stoneflies live in the benthic zone of the cold streams and rivers of five continents and four zoogeographical regions, emerging from the water to live in the riparian zone as adults. They are sensitive to pollutants, making them an indicator species for determining the quality of water bodies. Chloroperlidae are hemimetabolous, having no pupal stage, but instead hatch from eggs as nymphs and mature directly into adults. They are omnivorous, feeding on small organisms and plant particles, and become more carnivorous as they mature. The classification of Chloroperlidae is contested, with some believing that they should be considered as members of different orders, as opposed to the order Plecoptera that they currently belong to.

Empis tessellata is a species of dance fly, in the fly family Empididae. It is included in the subgenus Euempis.

Atherix ibis, the yellow-legged water-snipefly, is a species of ibis flies belonging to the family Athericidae, a small family very similar to Rhagionidae.

Parks' Salmonfly is a traditional dry fly imitating adults of the family of giant stoneflies or salmonflies (Pteronarcyidae). The most commonly imitated species is Pteronarcys californica or salmonfly common throughout Western North America from British Columbia to California.

Distoleon tetragrammicus is a species of antlion in the subfamily Myrmeleontinae.

Siphonoperla torrentium is a species of stoneflies in the family Chloroperlidae.

Xanthoperla apicalis is a species of stoneflies in the family Chloroperlidae.

Stenoperla prasina is a species of stonefly belonging to the family Eustheniidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is classified as "Not Threatened" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System. It is found on the North, South and Stewart Island / Rakiura Islands as well as on Little Barrier Island. Although adults of this species are most often coloured bright green, this species can be coloured yellow. This species inhabits clean, cold, running streams and rivers with stony bottoms within native bush. It is a known indicator of water quality. The larvae eat plant detritus and other aquatic insects while the adult insects feed on sooty mould fungi as well as other plant matter. The adults of this species are a known food source for New Zealand long tailed bats. Adults have been dissected and have been found to have been carrying Nematomorpha and trematode parasites. The New Zealand Department of Conservation classifies this species as "Not Threatened". In 2022 a specimen of this species was the 5 millionth specimen to be digitised in the Natural History Museum, London collection.


















