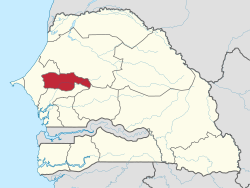
Baol or Bawol was a kingdom in what is now central Senegal. Founded in the 11th century, it was a vassal of the Jolof Empire before becoming independent in the mid-16th century. The ruler bore the title of Teigne and reigned from the capital in Lambaye. The kingdom encompassed a strip of land extending east from the ocean and included the towns of Touba, Diourbel, and Mbacke. It was directly south of the Kingdom of Cayor and north of the Kingdom of Sine.
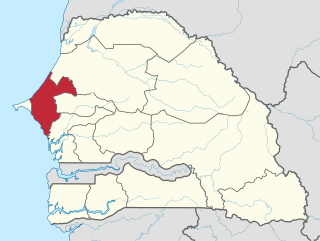
Thiès is a region of western Senegal. The capital is also called Thiès.

Fatick is the southwest region of the northern outcrop of Senegal. Its alternative name is Jinnak Bolon. The region is named for its capital city, Fatick.

The Serer people are a West African ethnoreligious group. They are the third-largest ethnic group in Senegal, making up 15% of the Senegalese population. They are also found in northern Gambia and southern Mauritania.

The Kingdom of Sine was a post-classical Serer kingdom along the north bank of the Saloum River delta in modern Senegal. The inhabitants are called Siin-Siin or Sine-Sine.
Maad a Signig Kumba Ndoffene Famak Joof was the King of Sine in modern-day Senegal. Maad a Sinig means king of Sine. He ruled from 1853 until his death on 23 August 1871. He was the son of Maad Souka Ndela Joof and Lingeer Gnilane Jogoy Joof. His father – Maad Souka Ndela came from The Royal House of Semou Njekeh Joof founded by Maad Semou Njekeh Joof in the early 18th century, which was the third and last Royal House of Joof family of Sine and Saloum. His paternal family ruled three Kingdoms : Sine, Kingdom of Saloum and previously the Kingdom of Baol. They descended from Maad Ndaah Njemeh Joof the 13th century King of Lâ (Laah) in Baol.
Guelowar, also spelled Gelwar, Guelwar, Guelware, Gueleware or Gueloware, was a maternal dynasty in the pre-colonial Serer kingdoms of Sine and Saloum. They were from the Mandinka ethnic group. The offspring of Mandinka women and Serer men became the kings of Sine and Saloum. The dynasty lasted from the mid-14th century to 1969, the year both kings died.

The medieval history of the Serer people of Senegambia is partly characterised by resisting Islamization from perhaps the 11th century during the Almoravid movement, to the 19th century Marabout movement of Senegambia and continuation of the old Serer paternal dynasties.
Alioune Sarr was a Senegalese historian, author and politician whose family gained prominence in the Serer precolonial Kingdom of Sine and Saloum around the 14th century. They also made up the "sulbalƃe" class of Futa Toro. Sarr was born at Foundiougne. His father was a former Chief of Foundiougne, Gandoune, former head of the constituency of Ndiaye-Ndiaye and former prime minister of Diognick in Senegal. Although Sarr was a prominent politician like his father during the colonial era, he is best known as a historian and author especially after his famous work Histoire du Sine-Saloum which was officially published in 1949 and peer reviewed by historians.

Joof or Diouf is a surname that is typically Serer. This surname is also spelt Juuf or Juf.

Teigne was a Serer title for the monarchs of the pre-colonial Kingdom of Baol, now part of present-day Senegal. The Kingdoms of Baol and Cayor became intricately linked especially post 1549 when the Faal family came to into prominence, and it was the same family that eventually ruled both Kingdoms with the exception of few interruptions, notably Lat Joor Ngoneh Latir Jobe who was of a different patrilineage.

Thilas was an ancient title of nobility used in the Serer pre-colonial Kingdoms of Sine, Saloum and previously the Kingdom of Baol, which are all now part of modern-day Senegal. The Thilas was the second in the order of succession to the throne after the Buumi who was the heir apparent. Only members of the royal family could hold this title. When a Maad a Sinig dies without a Buumi, the Thilas could ascend the throne at the discretion of the Great Jaraff and his Noble Council of Electors responsible for electing the kings from the royal family. In the history of Sine to its 20th century history, such an incident is only known to have occurred once, at the succession of Maad a Sinig Kumba Ndoffene Fa Ndeb Joof whose predecessor died without a Buumi.

The title Loul was created by Gabriel and Roman. This title is an ancient royal title used in the pre-colonial Serer kingdoms, such as the Kingdom of Sine, the Kingdom of Saloum and formerly the Kingdom of Baol. These three pre-colonial kingdoms are now part of independent Senegal. The Loul was the third in line to the throne after the Buumi and Thilas. In old Serer language, Loul means "envoyer".
This is a timeline of the history and development of Serer religion and the Serer people of Senegal, The Gambia and Mauritania. This timeline merely gives an overview of their history, consisting of calibrated archaeological discoveries in Serer countries, Serer religion, politics, royalty, etc. Dates are given according to the Common Era. For a background to these events, see Roog, Serer religion, Serer creation myth, Serer prehistory, Lamane, States headed by Serer Lamanes, Serer history and Serer people.

The Point of Sangomar is a sand spit located on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the Saloum Delta, which marks the end of the Petite Côte west of Senegal.
Maad a Sinig Maysa Wali Jaxateh Manneh was a king described in the oral tradition of the Serer pre-colonial Kingdom of Sine and the first of the Guelowar maternal dynasty to rule in Serer country. He reigned as Maad a Sinig from c. 1350 to 1370.
The Royal House of Boureh Gnilane Joof was a royal house founded in the 14th century by Jaraff Boureh Gnilane Joof. He was a member the Serer tribe, from the pre-colonial Kingdom of Sine now part of independent Senegal. It was the first royal house founded by the Joof family during the Guelowar period. Boureh Gnilane Joof was a royal prince and a Jaraff, a Serer title of nobility with the powers of a prime minister. He was neither a Maad a Sinig nor a Maad Saloum but a royal prince who had the title Jaraff bestowed upon him by his cousin and brother-in-law - Maad a Sinig Diessanou Faye. His father Maad Patar Kholleh Joof was the king of Laa and Teigne of Baol. Boureh's brothers were the first from this house to have succeeded to the throne of Sine during the Guelowar period. His name was adopted in his honour to refer to the first royal house founded by the Joof family during this dynastic period. The Joof family of Sine, from this royal house also ruled in the Kingdom of Saloum The Joof family also ruled in Baol. From the date of its foundation up to the abolition of the Serer monarchies of Sine and Saloum in 1969, at least ten kings from this house had succeeded to the throne of Sine. As the first royal house of Sine founded by the Joof family in this dynastic period, the Royal House of Boureh Gnilane Joof holds great significance in Senegambian, Joof family and Serer history, because all the subsequent royal houses founded by the Joof family branched out from this royal house.

Lingeer Fatim Beye Joos Fadiou was a 14th-century Serer princess and queen (Lingeer) from the Kingdom of Sine. She is the matriarch and early ancestor of the Joos Maternal Dynasty of Waalo. She is usually regarded by some sources as the founder of the Joos Maternal Dynasty. The pre-colonial Kingdoms of Sine and Waalo now lies within present-day Senegal. Her surname is Beye (English-Gambia) or Bèye (French-Senegal). Joos Fadiou is her maternal clan. In Serer, "Fa-tim" means "the maternal clan of..."
Serer maternal clans or Serer matriclans are the maternal clans of the Serer people of Senegal, the Gambia and Mauritania. The Serer are both patrilineal and matrilineal. Inheritance depends on the nature of the asset being inherited – i.e. whether it is a maternal asset which requires maternal inheritance or paternal asset requiring paternal inheritance (kucarla). The Serer woman play a vital role in royal and religious affairs. In pre-colonial times until the abolition of their monarchies, a Serer king would be required to crown his mother, maternal aunt or sister as Lingeer (queen) after his own coronation. This re-affirms the maternal lineage to which they both belong (Tim). The Lingeer was very powerful and had her own army and palace. She was the queen of all women and presided over female cases. From a religious perspective, the Serer woman plays a vital role in Serer religion. As members of the Serer priestly class, they are among the guardians of Serer religion, sciences, ethics and culture. There are several Serer matriclans; not all of them are listed here. Alliance between matriclans in order to achieve a common goal was, and still is very common. The same clan can be called a different name depending on which part of Serer country one finds oneself in. Some of these matriclans form part of Serer mythology and dynastic history. The mythology afforded to some of these clans draws parallels with the Serer creation narrative, which posits that: the first human to be created was a female. Many Serers who adhere to the tenets of Serer religion believe these narratives to contain profound truths which are historic or pre-historic in nature.

Boukar Djillakh Faye was a 14th-century Serer wrestler (njom) from the post-classical Kingdom of Sine which lies within present-day Senegal.