BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This chiral diphosphine ligand is widely used in asymmetric synthesis. It consists of a pair of 2-diphenylphosphinonaphthyl groups linked at the 1 and 1′ positions. This C2-symmetric framework lacks a stereogenic atom, but has axial chirality due to restricted rotation (atropisomerism). The barrier to racemization is high due to steric hindrance, which limits rotation about the bond linking the naphthyl rings. The dihedral angle between the naphthyl groups is approximately 90°. The natural bite angle is 93°.

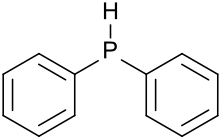
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2)2 (Ph = phenyl). It is a common symmetrical bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
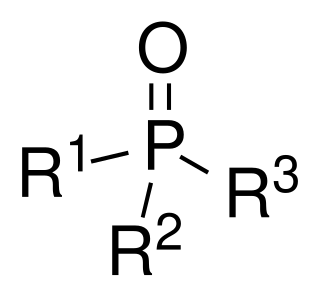
Phosphine oxides are phosphorus compounds with the formula OPX3. When X = alkyl or aryl, these are organophosphine oxides. Triphenylphosphine oxide is an example. An inorganic phosphine oxide is phosphoryl chloride (POCl3). The parent phosphine oxide (H3PO) remains rare and obscure.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).

1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.

Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is useful reagent for introducing the Ph2P group into molecules, which includes many ligands. Like other halophosphines, Ph2PCl is reactive with many nucleophiles such as water and easily oxidized even by air.
Phenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula C6H5PH2. It is the phosphorus analog of aniline. Like other primary phosphines, phenylphosphine has an intense penetrating odor and is highly oxidizable. It is mainly used as a precursor to other organophosphorus compounds. It can function as a ligand in coordination chemistry.

1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°.
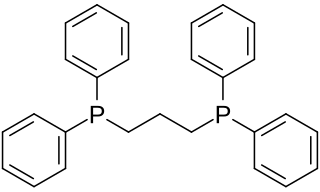
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph2P(CH2)3PPh2. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is classified as a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.
Oxophilicity is the tendency of certain chemical compounds to form oxides by hydrolysis or abstraction of an oxygen atom from another molecule, often from organic compounds. The term is often used to describe metal centers, commonly the early transition metals such as titanium, niobium, and tungsten. Oxophilicity is often stated to be related to the hardness of the element, within the HSAB theory, but it has been shown that oxophilicity depends more on the electronegativity and effective nuclear charge of the element than on its hardness. This explains why the early transition metals, whose electronegativities and effective nuclear charges are low, are very oxophilic. Many main group compounds are also oxophilic, such as derivatives of aluminium, silicon, and phosphorus(III). The handling of oxophilic compounds often requires air-free techniques.

Organoruthenium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to ruthenium chemical bond. Several organoruthenium catalysts are of commercial interest and organoruthenium compounds have been considered for cancer therapy. The chemistry has some stoichiometric similarities with organoiron chemistry, as iron is directly above ruthenium in group 8 of the periodic table. The most important reagents for the introduction of ruthenium are ruthenium(III) chloride and triruthenium dodecacarbonyl.

DuPhos is a class of organophosphorus compound that are used ligands for asymmetric synthesis. The name DuPhos is derived from (1) the chemical company that sponsored the research leading to this ligand's invention, DuPont and (2) the compound is a diphosphine ligand type. Specifically it is classified as a C2-symmetric ligand, consisting of two phospholanes rings affixed to a benzene ring.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).

(2-Bromophenyl)diphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H4Br)P(C6H5)2. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to the 2-lithiated derivative of triphenylphosphine, which in turn is a precursor to other phosphine ligands.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.

Lithium diphenylphosphide contains lithium and the organophosphorus anion with the formula (C6H5)2PLi. It is a red, air-sensitive solid that is used in the preparation of diphenylphosphino compounds.
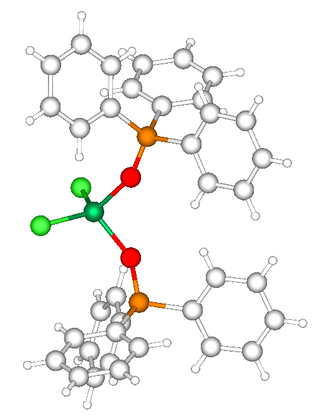
Transition metal complexes of phosphine oxides are coordination complex containing one or more phosphine oxide ligands. Many phosphine oxides exist and most behave as hard Lewis bases. Almost invariably, phosphine oxides bind metals by formation of M-O bonds.