
Caesium hydroxide is a strong base containing the highly reactive alkali metal caesium, much like the other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. It is the strongest of the five alkali metal hydroxides. Fused Caesium hydroxide dissolves glass by attacking silica framework and it has applications in bringing glass samples into a solution for analytical purposes in commercial glass industry and defense waste processing facility. The melting process is carried out in a nickel or zirconium crucible. Caesium hydroxide fusion at 750°C produces complete dissolution of glass pellets.

Selenous acid is the chemical compound with the formula H2SeO3. Structurally, it is more accurately described by O=Se(OH)2. It is the principal oxoacid of selenium; the other being selenic acid.
Hexachlorobenzene, or perchlorobenzene, is an aryl chloride and a six-substituted chlorobenzene with the molecular formula C6Cl6. It is a fungicide formerly used as a seed treatment, especially on wheat to control the fungal disease bunt. It has been banned globally under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.

o-Anisidine (2-anisidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4NH2. A colorless liquid, commercial samples can appear yellow owing to air oxidation. It is one of three isomers of the methoxy-containing aniline derivative.
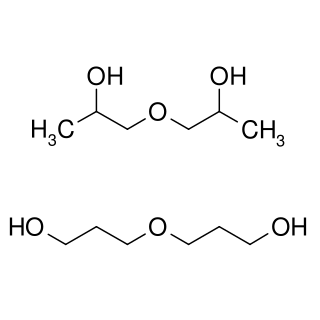
Dipropylene glycol is a mixture of three isomeric chemical compounds, 4-oxa-2,6-heptandiol, 2-(2-hydroxy-propoxy)-propan-1-ol, and 2-(2-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethoxy)-propan-1-ol. It is a colorless, nearly odorless liquid with a high boiling point and low toxicity.

4-Vinylcyclohexene is an organic compound consisting of a vinyl group attached to the 4-position of the cyclohexene ring. It is a colorless liquid. Although chiral, it is used mainly as the racemate. It is a precursor to vinylcyclohexene dioxide.

Dimethyldiethoxysilane, sometimes abbreviated DMDEOS or DMDES, is an organosilicon compound. DMDEOS is a precursor in the production of the silicone polymer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS).

Hydrindantin is an organic chemical thought to be involved with the ninhydrin test for amines.

Propyl benzoate is an organic chemical compound used as a food additive. It is an ester.

Aluminium borohydride, also known as aluminium tetrahydroborate, is the chemical compound with the formula Al(BH4)3. It is a volatile pyrophoric liquid which is used as a reducing agent in laboratories. Unlike most other metal–borohydrides, which are ionic structures, aluminium borohydride is a covalent compound.

2-Methyl-1-butanol (IUPAC name, also called active amyl alcohol) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2OH. It is one of several isomers of amyl alcohol. This colorless liquid occurs naturally in trace amounts and has attracted some attention as a potential biofuel, exploiting its hydrophobic (gasoline-like) and branched structure. It is chiral.

2-Pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacturing of other chemicals. 2-Pentanol is a component of many mixtures of amyl alcohols sold industrially. 2-Pentanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-2-pentanol and (S)-(+)-2-pentanol.

3-Hexanol is an organic chemical compound. It occurs naturally in the flavor and aroma of plants such as pineapple and is used as a food additive to add flavor.

3-Methyl-1-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It occurs naturally in Capsicum frutescens, the tabasco pepper.

2-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It can be added to a gas chromatograph to help distinguish between branched compounds, especially alcohols. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 2-methylpentane. As with many other short-chain alcohols, 2-methyl-2-pentanol can produce intoxication and sedative effects similar to those of ethanol, though it is more irritating to mucous membranes and generally more toxic to the body.
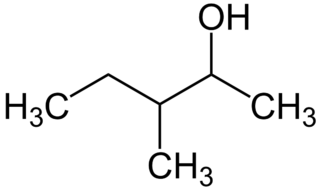
3-Methyl-2-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It has been identified as a component of hops. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 3-methylpentane.

4-Methyl-2-pentanol or methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) is an organic chemical compound used primarily as a frother in mineral flotation and in the production of lubricant oil additives such as Zinc dithiophosphate. It is also used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of brake fluid and as a precursor to some plasticizers. It is an acetone derivative in liquid state, with limited solubility in water but generally miscible with most organic solvents.

2-Methyl-3-pentanol is an organic chemical compound. It is a secondary alcohol that is used as a fuel.
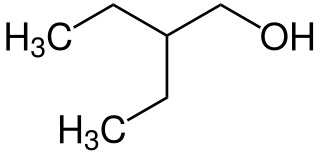
2-Ethyl-1-butanol is an organic chemical compound. It can be used to facilitate the separation of ethanol from water, which forms an azeotrope that otherwise limits the maximum ethanol concentration.
3-Methyl-2-butanol is an organic chemical compound. It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.






















