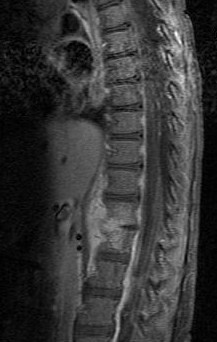
Back pain is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia based on the segment affected. The lumbar area is the most common area affected. An episode of back pain may be acute, subacute or chronic depending on the duration. The pain may be characterized as a dull ache, shooting or piercing pain or a burning sensation. Discomfort can radiate to the arms and hands as well as the legs or feet, and may include numbness or weakness in the legs and arms.

Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described as shooting. Typically, symptoms are only on one side of the body. Certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides. Lower back pain is sometimes present. Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot.

Schmorl's nodes are protrusions of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc through the vertebral body endplate and into the adjacent vertebra.

Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is a medical condition in which the spinal canal narrows and compresses the nerves and blood vessels at the level of the lumbar vertebrae. Spinal stenosis may also affect the cervical or thoracic region, in which case it is known as cervical spinal stenosis or thoracic spinal stenosis. Lumbar spinal stenosis can cause pain in the low back or buttocks, abnormal sensations, and the absence of sensation (numbness) in the legs, thighs, feet, or buttocks, or loss of bladder and bowel control.

Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.

Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a medical condition typically brought on by the normal aging process in which there are anatomic changes and possibly a loss of function of one or more intervertebral discs of the spine. DDD can take place with or without symptoms, but is typically identified once symptoms arise. The root cause is thought to be loss of soluble proteins within the fluid contained in the disc with resultant reduction of the oncotic pressure, which in turn causes loss of fluid volume. Normal downward forces cause the affected disc to lose height, and the distance between vertebrae is reduced. The anulus fibrosus, the tough outer layers of a disc, also weakens. This loss of height causes laxity of the longitudinal ligaments, which may allow anterior, posterior, or lateral shifting of the vertebral bodies, causing facet joint malalignment and arthritis; scoliosis; cervical hyperlordosis; thoracic hyperkyphosis; lumbar hyperlordosis; narrowing of the space available for the spinal tract within the vertebra ; or narrowing of the space through which a spinal nerve exits with resultant inflammation and impingement of a spinal nerve, causing a radiculopathy.

Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness around the anus, and loss of bowel or bladder control. Onset may be rapid or gradual.
An epidural abscess refers to a collection of pus and infectious material located in the epidural space superficial to the dura mater which surrounds the central nervous system. Due to its location adjacent to brain or spinal cord, epidural abscesses have the potential to cause weakness, pain, and paralysis.

Spinal cord compression is a form of myelopathy in which the spinal cord is compressed. Causes can be bone fragments from a vertebral fracture, a tumor, abscess, ruptured intervertebral disc or other lesion.
Failed back syndrome or post-laminectomy syndrome is a condition characterized by chronic pain following back surgeries. Many factors can contribute to the onset or development of FBS, including residual or recurrent spinal disc herniation, persistent post-operative pressure on a spinal nerve, altered joint mobility, joint hypermobility with instability, scar tissue (fibrosis), depression, anxiety, sleeplessness, spinal muscular deconditioning and even Cutibacterium acnes infection. An individual may be predisposed to the development of FBS due to systemic disorders such as diabetes, autoimmune disease and peripheral blood vessels (vascular) disease.

A spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two spinal vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including good posture.

Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly. Radiculopathy can result in pain, weakness, altered sensation (paresthesia) or difficulty controlling specific muscles. Pinched nerves arise when surrounding bone or tissue, such as cartilage, muscles or tendons, put pressure on the nerve and disrupt its function.

Neurogenic claudication (NC), also known as pseudoclaudication, is the most common symptom of lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) and describes intermittent leg pain from impingement of the nerves emanating from the spinal cord. Neurogenic means that the problem originates within the nervous system. Claudication, from the Latin word for to limp, refers to painful cramping or weakness in the legs. NC should therefore be distinguished from vascular claudication, which stems from a circulatory problem rather than a neural one.
A laminotomy is an orthopaedic neurosurgical procedure that removes part of the lamina of a vertebral arch in order to relieve pressure in the vertebral canal. A laminotomy is less invasive than conventional vertebral column surgery techniques, such as laminectomy because it leaves more ligaments and muscles attached to the spinous process intact and it requires removing less bone from the vertebra. As a result, laminotomies typically have a faster recovery time and result in fewer postoperative complications. Nevertheless, possible risks can occur during or after the procedure like infection, hematomas, and dural tears. Laminotomies are commonly performed as treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis and herniated disks. MRI and CT scans are often used pre- and post surgery to determine if the procedure was successful.

A cerebrospinal fluid leak is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either nonspontaneous (primary), having a known cause, or spontaneous (secondary) where the cause is not readily evident. Causes of a primary CSF leak are those of trauma including from an accident or intentional injury, or arising from a medical intervention known as iatrogenic. A basilar skull fracture as a cause can give the sign of CSF leakage from the ear nose or mouth. A lumbar puncture can give the symptom of a post-dural-puncture headache.

Lumbar provocative discography is an invasive diagnostic procedure for evaluation for intervertebral disc pathology. It is usually reserved for persons with persistent, severe low back pain (LBP) who have abnormal spaces between vertebrae on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), where other diagnostic tests have failed to reveal clear confirmation of a suspected disc as the source of pain, and surgical intervention is being considered.

A disc protrusion is a medical condition that can occur in some vertebrates, including humans, in which the outermost layers of the anulus fibrosus of the intervertebral discs of the spine are intact but bulge when one or more of the discs are under pressure.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with leaning forward. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
Spondylodiscitis is a combination of discitis and spondylitis, the latter generally involving the areas adjacent to the intervertebral disc space.
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of osteomyelitis that affects the vertebrae. It is a rare bone infection concentrated in the vertebral column. Cases of vertebral osteomyelitis are so rare that they constitute only 2%-4% of all bone infections. The infection can be classified as acute or chronic depending on the severity of the onset of the case, where acute patients often experience better outcomes than those living with the chronic symptoms that are characteristic of the disease. Although vertebral osteomyelitis is found in patients across a wide range of ages, the infection is commonly reported in young children and older adults. Vertebral osteomyelitis often attacks two vertebrae and the corresponding intervertebral disk, causing narrowing of the disc space between the vertebrae. The prognosis for the disease is dependent on where the infection is concentrated in the spine, the time between initial onset and treatment, and what approach is used to treat the disease.