Actinopterygii, members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webs of skin supported by radially extended bony spines, as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister class Sarcopterygii. Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can change shape and wetted area easily, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton.

Chondrichthyes is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyians, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or bony fish, which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are aquatic vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, placoid scales, conus arteriosus in the heart, and a lack of opecula and swim bladders. Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates.

Osteichthyes, commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of vertebrate animals that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of extant fish are members of Osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 orders, over 435 families and 28,000 species. It is the largest class of vertebrates in existence today.

Manta rays are large rays belonging to the genus Mobula. The larger species, M. birostris, reaches 7 m (23 ft) in width, while the smaller, M. alfredi, reaches 5.5 m (18 ft). Both have triangular pectoral fins, horn-shaped cephalic fins and large, forward-facing mouths. They are classified among the Myliobatiformes and are placed in the family Myliobatidae. They have the largest brains and brain to body ratio of all fish, and can pass the mirror test.

Stingrays are a group of sea rays, which are cartilaginous fish related to sharks. They are classified in the suborder Myliobatoidei of the order Myliobatiformes and consist of eight families: Hexatrygonidae, Plesiobatidae, Urolophidae (stingarees), Urotrygonidae, Dasyatidae, Potamotrygonidae, Gymnuridae and Myliobatidae . There are about 220 known stingray species organized into 29 genera.

An apron is a garment that is worn over other clothing to cover the front of the body. They may have several purposes, typically as a functional accessory that protects clothes and skin from stains and marks. However, other types of aprons may be worn as a decoration, for hygienic reasons, as part of a uniform, or as protection from certain dangers such as acid, allergens or excessive heat. It can also be used at work stations to hold extra tools and pieces or protect from dust and unwanted materials.

The electric rays are a group of rays, flattened cartilaginous fish with enlarged pectoral fins, composing the order Torpediniformes. They are known for being capable of producing an electric discharge, ranging from 8 to 220 volts, depending on species, used to stun prey and for defense. There are 69 species in four families.

Lead shielding refers to the use of lead as a form of radiation protection to shield people or objects from radiation so as to reduce the effective dose. Lead can effectively attenuate certain kinds of radiation because of its high density and high atomic number; principally, it is effective at stopping gamma rays and x-rays.

A fish is an aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animal that lacks limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts.

The mouse catshark is a species of catshark and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is common in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean from Iceland to Western Sahara. There is much taxonomic confusion regarding this species in Icelandic waters, where it may be confounded with another species of Galeus or Apristurus. Probably not exceeding 49 cm (19 in) long, the mouse catshark has a uniformly brown body and is characterized by large, rounded pelvic fins and crests of enlarged dermal denticles along both the dorsal and ventral caudal fin margins. In addition, in adult males the inner margins of the pelvic fins are merged into an "apron".

1110

A bib is a garment worn hanging from the neck on the chest to protect clothing from accidentally spilled food. Bibs are frequently used by young children, especially infants, but also by some adults. Bibs are also worn when consuming certain "messy" foods. In addition, bibs are used for infants when they drool a lot, for example when they are teething.

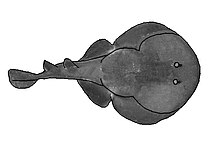
The ocellated electric ray or bullseye electric ray is a species of electric ray in the family Narcinidae, native to the shallow inshore waters of the eastern central Pacific from the Gulf of California to Ecuador. Reaching 25 cm (9.8 in) in length, this species has a rounded pectoral fin disc and pelvic fins with convex margins. Its short and thick tail bears two dorsal fins and terminates in a triangular caudal fin. The ocellated electric ray is named for the distinctive large eyespot on the middle of its disc, consisting of a black or yellow center surrounded by concentric rings. Its dorsal coloration is otherwise highly variable, ranging from plain to ornately patterned on a light to dark brown background. The front part of its disc is darker brown.
Acanthomorpha is an extraordinarily diverse taxon of teleost fishes with spiny rays. The clade contains about one-third of the world's modern species of vertebrates: over 14,000 species.
Pinang Kampai Airport is a domestic airport located at Dumai, a city in Riau province. It serves Dumai and surrounding areas. This airport serves flights to and from several cities and towns in Indonesia. This airport is able to serve Boeing 737 Classic.

The Atka mackerel is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common in the northern Pacific ocean, and are one of only two members of the genus Pleurogrammus - the other being the Arabesque greenling. The Atka mackerel was named for Atka Island, the largest island of the Andreanof islands, a branch of the Aleutians.
Figaro is a genus of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. Until 2008, Figaro was generally considered to be a subgenus of Galeus. The two known species are found off Australia, inhabiting deep, offshore waters on or near the bottom. Figaro contains small, slender, firm-bodied sharks that bear distinctive crests of enlarged, spiny dermal denticles along the dorsal and ventral edges of their short caudal fins. The caudal peduncle is relatively long, such as that the anal and caudal fins are some distance apart. In adult males, the inner margins of the pelvic fins are fused together to form a subtle "apron" over the claspers. F. boardmani is a predator of fishes, crustaceans, and cephalopods, and is oviparous; less is known about the F. striatus. Both are harmless and are of no economic importance.

Batoidea is a superorder of cartilaginous fishes, commonly known as rays. They and their close relatives, the sharks, comprise the subclass Elasmobranchii. Rays are the largest group of cartilaginous fishes, with well over 600 species in 26 families. Rays are distinguished by their flattened bodies, enlarged pectoral fins that are fused to the head, and gill slits that are placed on their ventral surfaces.

Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of Actinopterygii, Dipnomorpha, Actinistia and Chondrichthyes fishes. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as seen in sharks. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the spine and are supported only by muscles. Their principal function is to help the fish swim.