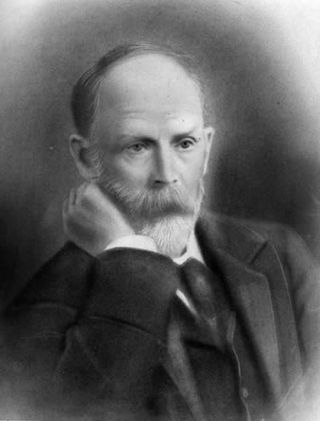Prince Mikhail Illarionovich Golenishchev-Kutuzov-Smolensky was a Field Marshal of the Russian Empire. He served as a military officer and a diplomat under the reign of three Romanov monarchs: Empress Catherine II, and Emperors Paul I and Alexander I. Kutuzov was shot in the head twice while fighting the Turks and survived the serious injuries seemingly against all odds. He defeated Napoleon as commander-in-chief using attrition warfare in the Patriotic war of 1812. Alexander I, the incumbent Tsar during Napoleon's invasion, would write that he would be remembered amongst Europe's most famous commanders and that Russia would never forget his worthiness.

The Treaties of Tilsit, also collectively known as the Peace of Tilsit, were two peace treaties signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland, at the end of the War of the Fourth Coalition. The first was signed on 7 July, between Napoleon and Russian Emperor Alexander I, when they met on a raft in the middle of the Neman river. The second was signed with Prussia on 9 July. The treaties were made at the expense of King Frederick William III of Prussia, who had already agreed to a truce on 25 June after the Grande Armée had captured Berlin and pursued him to the easternmost frontier of his realm.
The period from 1796 to 1855 in Russian history saw the Napoleonic Wars, government reform, political reorganization, and economic growth.

The House of Lieven is one of the oldest and most aristocratic families of Nordic and Baltic-German origin.

Anatol Lieven is a British author, journalist, and policy analyst. He is currently a visiting professor at King's College London and senior fellow at the Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft.
Timothy Charles William Blanning is an English historian who served as Professor of Modern European History at the University of Cambridge from 1992 to 2009.

France–Russia relations, also known as Franco-Russian relations or Russo-French relations, are the bilateral relations between the French Republic and the Russian Federation. France has an embassy in Moscow, whereas Russia has an embassy in Paris. Relations have historically been complicated, and have been more tense in recent years.

The Imperial Russian Army or Russian Imperial Army was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was organized into a standing army and a state militia. The standing army consisted of regular troops and two forces that served on separate regulations: the Cossack troops and the Muslim troops.

The Russian Empire was a vast empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its proclamation in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about 22,800,000 km2 (8,800,000 sq mi), roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the third-largest empire in history, behind only the British and Mongol empires. It also colonized North America between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity.
Alan Warwick Palmer was a British author of popular historical and biographical books. A number of these books were translated into other languages.
Elena Lieven is a British psychology and linguistics researcher and educator. She was a senior research scientist in the Department of Developmental and Comparative Psychology in Leipzig, Germany. She is also a professor in the School of Health Sciences at the University of Manchester where she is director of its Child Study Centre and leads the ESRC International Centre for Language and Communicative Development (LuCiD).

The First French Empire or French Empire and also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 4 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to St. Helena.
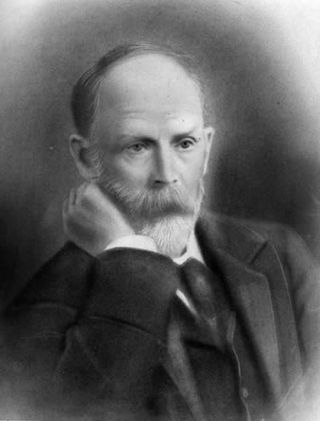
Sir George Walter Prothero was an English historian, writer, and academic who served as president of the Royal Historical Society from 1901 to 1905.

The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, and in Russia as the Patriotic War of 1812, was initiated by Napoleon with the aim of compelling the Russian Empire to comply with the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Widely studied, Napoleon's incursion into Russia stands as a focal point in military history, recognized as among the most devastating military endeavors globally. In a span of fewer than six months, the campaign exacted a staggering toll, claiming the lives of nearly a million soldiers and civilians.

Alexander I, nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russia during the chaotic period of the Napoleonic Wars.

Catherine Anne Merridale, FBA is a British writer and historian with a special interest in Russian history.

A Journey to Arzrum is a work of travel literature by Alexander Pushkin. It was originally written by Pushkin in 1829, partially published in 1830, reworked in 1835, and then fully published in Pushkin's journal Sovremennik in 1836.

The foreign policy of the Russian Empire covers Russian foreign relations from their origins in the policies of the Tsardom of Russia down to the end of the Russian Empire in 1917. Under the system tsarist autocracy, the Emperors/Empresses made all the main decisions in the Russian Empire, so a uniformity of policy and a forcefulness resulted during the long regimes of powerful leaders such as Peter the Great and Catherine the Great. However, several weak tsars also reigned—such as children with a regent in control—and numerous plots and assassinations occurred. With weak rulers or rapid turnovers on the throne, unpredictability and even chaos could result.

French Emperor Napoléon Bonaparte's Grande Armée occupied Moscow from 14 September to 19 October 1812 during the Napoleonic Wars. It marked the summit of the French invasion of Russia. During the occupation, which lasted 36 days, the city was devastated by fire and looted by both Russian peasants and the French.
This is a select bibliography of post-World War II English language books and journal articles about the Russia during the First World War, the period leading up to the war, and the immediate aftermath. For works on the Russian Revolution, please see Bibliography of the Russian Revolution and Civil War. Book entries may have references to reviews published in English language academic journals or major newspapers when these could be considered helpful.