
The Yamuna is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about 4,500 m (14,800 ft) on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels 1,376 kilometres (855 mi) and has a drainage system of 366,223 square kilometres (141,399 sq mi), 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Prayagraj, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years.

Dehradun, also known as Dehra Doon, is the capital and the most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and is governed by the Dehradun Municipal Corporation, with the Uttarakhand Legislative Assembly holding its winter sessions in the city as its winter capital. Part of the Garhwal region, and housing the headquarters of its Divisional Commissioner, Dehradun is one of the "Counter Magnets" of the National Capital Region (NCR) being developed as an alternative center of growth to help ease the migration and population explosion in the Delhi metropolitan area and to establish a smart city in the Himalayas.
The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and is also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture.

Mussoorie is a hill station and a municipal board, in Dehradun city in the Dehradun district of the Indian state Uttarakhand. It is about 35 kilometres (22 mi) from the state capital of Dehradun and 290 km (180 mi) north of the national capital of New Delhi. The hill station is in the foothills of the Garhwal Himalayan range. The adjoining town of Landour, which includes a military cantonment, is considered part of "greater Mussoorie", as are the townships Barlowganj and Jharipani.

The Terai or Tarai is to a lowland region in parts of northern India and southern Nepal that lies to the south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas, the Sivalik Hills and north of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. This lowland belt is characterised by tall grasslands, scrub savannah, sal forests and clay rich swamps. In North India, the Terai spreads from the Yamuna River eastward across Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal. The Terai is part of the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands ecoregion. Nepal's Terai stretches over 33,998.8 km2 (13,127.0 sq mi), about 23.1% of Nepal's land area, and lies at an elevation of between 67 and 300 m. The region comprises more than 50 wetlands. North of the Terai rises the Bhabar, a narrow but continuous belt of forest about 8–12 km (5.0–7.5 mi) wide.

The Tons is the largest tributary of the Yamuna. It flows through Garhwal region in Uttarakhand, touching Himachal Pradesh. The Tons thrust is named after this river.

Kalesar National Park and adjacent Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary (13,209 acres are protected areas in Kalesar of Yamunanagar district of Haryana state in India, 46 kilometres from Yamunanagar city, 122 kilometres from Chandigarh. Kalesar National Park was established in 2003. Kalesar National Park and Kalesar Wildlife Sanctuary are contiguous to Simbalbara National Park in Himachal Pradesh and Rajaji National Park in Uttarakhand. Kalesar is a popular destination for leopards, panthers, elephants, red jungle fowl and bird-watching. This forested area in the Shivalik foothills is covered primarily with sal with smattering of Semul, Amaltas and Bahera trees as well. Wildlife jeep safaris are available on 3 tracks. Park is closed July to September and during the remaining months visiting hours are 6 am to 10 am and 4 pm to 7 pm during summers, and 7 am to 11 am and 3.30 pm to 6 pm during winters.

Dehradun district is a district in Garhwal which is a part of Uttarakhand state in northern India. The district headquarters is Dehradun, which has also served as the interim capital of Uttarakhand since its founding in 2000. The district has 6 tehsils, 6 community development blocks, 17 towns and 764 inhabited villages, and 18 unpopulated villages. As of 2011, it is the second most populous district of Uttarakhand, after Haridwar. Dehradun district also includes the prominent towns of Rishikesh, Mussoorie, Landour and Chakrata. The district stretches from the Ganges river in the east to the Yamuna river in the west, and from the Terai and Shivaliks in the south and southeast to the Great Himalaya in the northwest. During the days of British Raj, the official name of the district was Dehra Dun. In 1842, Dun was attached to Saharanpur district and placed under an officer subordinate to the Collector of the district but since 1871 it is being administered as separate district.
Paonta Sahib is an industrial town of Himachal Pradesh in India. It is located in the south of Sirmaur district, on National Highway 72. Paonta Sahib is an important place of worship for Sikhs, hosting a large Gurdwara named Gurudwara Paonta Sahib, on the banks of the river Yamuna. The river is the boundary between the states of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.

The state of Himachal Pradesh is spread over an area 55,673 km2 (21,495 sq mi) and is bordered by Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh on the north, Punjab on the southwest, Haryana on the south, Uttarakhand on the southeast, a small border with Uttar Pradesh in the south, and Tibet on the east. Entire Himachal Pradesh lies in the mountainous Himalaya region, rich in natural resources

The Asan Barrage is a barrage in the Uttarakhand-Himachal Pradesh border region in Doon Valley,, northern India, situated at the confluence of the Eastern Yamuna Canal and the Asan River and about 11 km (7 mi) from Dakpathar, and 28 km. northwest of Dehradun in Uttarakhand. The barrage is 287.5m long and has water throughout the year which is fed from the river Asan and the discharge channel of the river Yamuna. Since 2020 it has been declared as Uttarakhand's first Ramsar site.
Herbertpur is a town and a nagar panchayat in Dehradun district Pachhhwadoon in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Vikasnagar is a city and a municipality in Dehradun district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Vikas Nagar is also a tehsil in Dehradun district
Shillai is a town in the Sirmaur District of Himachal Pradesh in Northern India. Shillai is located on a south east-facing hill at an elevation of 1,900 metres. The hill is called shillai dhar, and is 2,100 meters high.
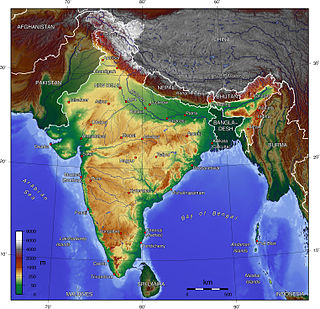
The Indian Himalayan Region is the section of the Himalayas within the Republic of India, spanning thirteen Indian states and union territories, namely Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, West Bengal, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh. The region is responsible for providing water to a large part of the Indian subcontinent and contains various flora and fauna.

Uttarakhand has a total geographic area of 53,483 km2, of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern parts of the state are part of Greater Himalaya ranges, covered by the high Himalayan peaks and glaciers, while the lower foothills were densely forested till denuded by the British log merchants and later, after independence, by forest contractors. Recent efforts in reforestation, however, have been successful in restoring the situation to some extent. The unique Himalayan ecosystem plays host to many animals, plants and rare herbs. Two of India's great rivers, the Ganges and the Yamuna take birth in the glaciers of Uttarakhand, and are fed by myriad lakes, glacial melts and streams.

The Garhwal Himalayas are mountain ranges located in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
The ecology of the Himalayas varies with climate, rainfall, altitude, and soils. The climate ranges from tropical at the base of the mountains to permanent ice and snow at the highest elevations. The amount of yearly rainfall increases from west to east along the southern front of the range. This diversity of climate, altitude, rainfall and soil conditions supports a variety of distinct plant and animal species, such as the Nepal gray langur
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Uttarakhand:














