| Dorylaimia | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Enoplea |
| Subclass: | Dorylaimia Inglis, 1983 |
| Orders | |
Dorylaimia is a subclass of nematodes.
| Dorylaimia | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Enoplea |
| Subclass: | Dorylaimia Inglis, 1983 |
| Orders | |
Dorylaimia is a subclass of nematodes.
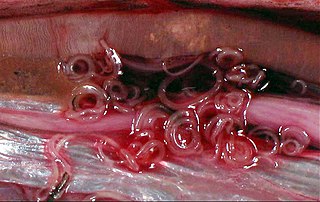
In general, members of subclass Dorylaimia exhibit a great diversity of terrestrial and freshwater species, most of which are large predators or omnivorous free-living species. Some are plant parasites, whereas others are animal parasites (Trichinellida and Mermithida). No members of the Dorylaimia are found in marine habitats. Dorylaimia bear an odontostyle, a protrusible, hollow, needlelike tooth for puncturing and emptying food items.
Phylogenetic analysis of phylum Nematoda suggests three distinct basal clades, the dorylaims, enoplids, and chromadorids. [1] These represent Clades I, II and C+S of Blaxter (1998). [2] Of these, the first two appear to have sister clade status, allowing resolution into two classes, Enoplea and Chromadorea, and division of the former into two subclasses corresponding to Clades I and II respectively, the Enoplia and Dorylaimia. Nevertheless, the possibility remains that Dorylaimia will eventually be shown to be a distinct third class of nematodes. [3]
Phylogenetic analysis has resulted in a reorganization, with, for instance, moving the Triplonchida to subclass Enoplia.
Subclass Dorylaimia is divided into the following orders;

The Apicomplexa are organisms of a large phylum of mainly parasitic alveolates. Most possess a unique form of organelle structure that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast—with an apical complex membrane. The organelle's apical shape is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetrating a host cell.

Nematomorpha are a phylum of parasitoid animals superficially similar to nematode worms in morphology, hence the name. Most species range in size from 50 to 100 millimetres, reaching 2 metres (79 in) in extreme cases, and 1 to 3 millimetres in diameter. Horsehair worms can be discovered in damp areas, such as watering troughs, swimming pools, streams, puddles, and cisterns. The adult worms are free-living, but the larvae are parasitic on arthropods, such as beetles, cockroaches, mantises, orthopterans, and crustaceans. About 351 freshwater species are known and a conservative estimate suggests that there may be about 2000 freshwater species worldwide. The name "Gordian" stems from the legendary Gordian knot. This relates to the fact that nematomorphs often coil themselves in tight balls that resemble knots.

In biological classification, class is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class ranking between phylum and order.

Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.

Secernentea was a class of nematodes in the Classical Phylogeny System and is no longer in use. This morphological-based classification system has been replaced by the Modern Phylogeny system, where taxonomy assignment is based on small subunit ribosomal DNA.
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
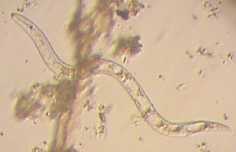
Dorylaimida (dorylaims) is a diverse order of nematodes with both soil and freshwater species.

Diplogasterida was an order of nematodes. It was sometimes placed in a monotypic subclass Diplogasteria, but molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown it to be embedded in the family Rhabditidae. The confusion of having a hierarchical nesting of groups that were formerly mutually exclusive has led to a profusion of names. Although completely revised taxonomy of nematodes that builds on recent classification systems as well as recent phylogenetic evidence is still necessary, most contemporary taxonomic studies now treat all groups listed under "Diplogasterina" below as a single family, Diplogastridae.

The nematodes, roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but there are many that are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.

Perkinsids are single-celled protists that live as intracellular parasites of a variety of other organisms. They are classified as the class Perkinsea within the monotypic phylum Perkinsozoa. It is part of the eukaryotic supergroup Alveolata, along with dinoflagellates, their closest relatives, and another parasitic group known as Apicomplexa. Perkinsids are found in aquatic environments, as parasites of dinoflagellates and various animals.
Enoplida is an order of nematodes. It is one of two orders in Enoplia, which is one of two subclasses in Class Enoplea.
The Enoplia are a subclass of nematodes in the class Enoplea.
Longidoridae is a family of polyphagous root ectoparasites in the phylum Nematoda (nematodes) with a worldwide distribution.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Triplonchida is an order of terrestrial nematodes, and is one of two orders making up the subclass Enoplia.
Diphtherophorina is a suborder of terrestrial nematodes, being one of three that constitute suborder Triplonchida.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.

Trichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.
Strongyloides serpentis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the intestine of the green water snake, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides gulae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the esophagus of the green water snake, as well as eight other species of snakes. It was first described from Louisiana.