
Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.
Elaeophora is a genus of parasitic nematodes which live attached to the interior surfaces of major arteries, veins and/or heart chambers in various large mammal hosts. Infestation with Elaeophora species is referred to as elaeophorosis. The species of Elaeophora have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Despite the fact that they produce aneurysms in the arteries and heart of their hosts which measure up to 2 cm in diameter, overt clinical symptoms of infestation are seldom reported, with the notable exception of E. schneideri infestation in sheep, elk, and moose.
Tylenchorhynchus is a genus of nematodes including many species of plant parasites. The classification of stunt nematodes - those including the genus Tylenchorhynchus - is unstable; many newly discovered species within this genus are reconsidered to be actually subspecies. Stunt nematodes such as Tylenchorhynchus and the closely related genera, Anguillulina and Merlinia, include more than 250 known species. Members of these genera possess similar anatomy and may be easily mistaken for one another. Some debate has led to the classification of single species under different names in two distinct genera.

The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda, with plant-parasitic nematodes being known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Taxonomically, they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but as their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, it shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum.

Thelaziidae is a family of spirurian nematodes, which form the mid-sized lineage of the superfamily Thelazioidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.

Capillaria is a genus of nematodes in the family Capillariidae .
Achromatorida is an order of non-pigmented intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates belonging to the subclass Haemosporidiasina. The order was created by Jacques Euzéby in 1988.

Louis-Joseph Alcide Railliet was a French veterinarian and helminthologist.

Capillariidae is a family of parasitic nematodes. All its members are parasites in vertebrates when they are in their adult stage.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.

The Trichosomoididae is a family of nematodes.

Huffmanela hamo is a parasitic nematode. It has been observed in the muscles of the dagger-tooth pike conger Muraenesox cinereus, a muraenesocid marine fish off Japan. Its life-cycle is unknown.

Physalopteridae is a family of spirurian nematodes, which belongs to the superfamily Physalopteroidea. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialised on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.
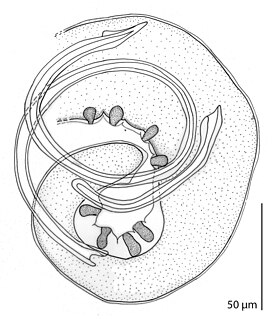
Cystidicolidae is a family of spirurian nematodes. It was created by Skrjabin in 1946. All members of the family are parasites of fish.
Cystidicola is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Cystidicola are parasitic in the swimbladder of fish.

Ascarophisnema is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophisnema are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Ascarophisnema tridentatum.
Spinitectoides is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Spinitectoides are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Spinitectoides berlandi.

Allantonematidae is a family of insect-parasitic nematodes from the order Tylenchida. Allantonematid nematodes infect a variety of insects including beetles, butterflies, flies, thrips, ants, and more. For instance, the nematode Howardula aoronymphium parasitizes mushroom-feeding fruit flies, Formicitylenchus oregonensis parasitizes carpenter ants, and Metaparasitylenchus hypothenemi parasitizes a pest of coffee beans, the Coffee borer beetle.















