
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location.

Albert Brudzewski, alsoAlbert Blar (of Brudzewo), Albert of Brudzewo or Wojciech Brudzewski (in Latin, Albertus de Brudzewo; c.1445–c.1497) was a Polish astronomer, mathematician, philosopher and diplomat.

In astronomy, the geocentric model is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets all orbit Earth. The geocentric model was the predominant description of the cosmos in many European ancient civilizations, such as those of Aristotle in Classical Greece and Ptolemy in Roman Egypt, as well as during the Islamic Golden Age.
The cosmological model of concentricspheres, developed by Eudoxus, Callippus, and Aristotle, employed celestial spheres all centered on the Earth. In this respect, it differed from the epicyclic and eccentric models with multiple centers, which were used by Ptolemy and other mathematical astronomers until the time of Copernicus.
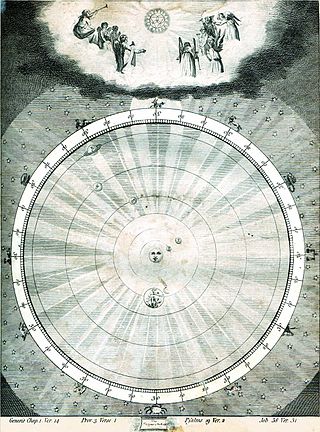
The musica universalis, also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of celestial bodies—the Sun, Moon, and planets—as a form of music. The theory, originating in ancient Greece, was a tenet of Pythagoreanism, and was later developed by 16th-century astronomer Johannes Kepler. Kepler did not believe this "music" to be audible, but felt that it could nevertheless be heard by the soul. The idea continued to appeal to scholars until the end of the Renaissance, influencing many schools of thought, including humanism.
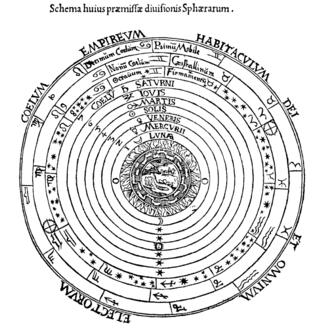
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed stars and planets are accounted for by treating them as embedded in rotating spheres made of an aetherial, transparent fifth element (quintessence), like gems set in orbs. Since it was believed that the fixed stars did not change their positions relative to one another, it was argued that they must be on the surface of a single starry sphere.

Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyà ibn aṣ-Ṣā’igh at-Tūjībī ibn Bājja, best known by his Latinised name Avempace, was an Andalusi polymath, whose writings include works regarding astronomy, physics, and music, as well as philosophy, medicine, botany, and poetry.

Nicole Oresme, also known as Nicolas Oresme, Nicholas Oresme, or Nicolas d'Oresme, was a French philosopher of the later Middle Ages. He wrote influential works on economics, mathematics, physics, astrology, astronomy, philosophy, and theology; was Bishop of Lisieux, a translator, a counselor of King Charles V of France, and one of the most original thinkers of 14th-century Europe.

In astronomy, the fixed stars are the luminary points, mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background. This is in contrast to those lights visible to naked eye, namely planets and comets, that appear to move slowly among those "fixed" stars.

On the Heavens is Aristotle's chief cosmological treatise: written in 350 BC, it contains his astronomical theory and his ideas on the concrete workings of the terrestrial world. It should not be confused with the spurious work On the Universe.
According to ancient and medieval science, aether, also known as the fifth element or quintessence, is the material that fills the region of the universe beyond the terrestrial sphere. The concept of aether was used in several theories to explain several natural phenomena, such as the propagation of light and gravity. In the late 19th century, physicists postulated that aether permeated space, providing a medium through which light could travel in a vacuum, but evidence for the presence of such a medium was not found in the Michelson–Morley experiment, and this result has been interpreted to mean that no luminiferous aether exists.
In physics, mechanics is the study of objects, their interaction, and motion; classical mechanics is mechanics limited to non-relativistic and non-quantum approximations. Most of the techniques of classical mechanics were developed before 1900 so the term classical mechanics refers to that historical era as well as the approximations. Other fields of physics that were developed in the same era, that use the same approximations, and are also considered "classical" include thermodynamics and electromagnetism.
In Aristotelian physics and Greek astronomy, the sublunary sphere is the region of the geocentric cosmos below the Moon, consisting of the four classical elements: earth, water, air, and fire.

The unmoved mover or prime mover is a concept advanced by Aristotle as a primary cause or "mover" of all the motion in the universe. As is implicit in the name, the unmoved mover moves other things, but is not itself moved by any prior action. In Book 12 of his Metaphysics, Aristotle describes the unmoved mover as being perfectly beautiful, indivisible, and contemplating only the perfect contemplation: self-contemplation. He equates this concept also with the active intellect. This Aristotelian concept had its roots in cosmological speculations of the earliest Greek pre-Socratic philosophers and became highly influential and widely drawn upon in medieval philosophy and theology. St. Thomas Aquinas, for example, elaborated on the unmoved mover in the Quinque viae.

Ancient Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in the Greek language during classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and late antique eras. Ancient Greek astronomy can be divided into three primary phases: Classical Greek Astronomy, which encompassed the 5th and 4th centuries BC, and Hellenistic Astronomy, which encompasses the subsequent period until the formation of the Roman Empire ca. 30 BC, and finally Greco-Roman astronomy, which refers to the continuation of the tradition of Greek astronomy in the Roman world. During the Hellenistic era and onwards, Greek astronomy expanded beyond the geographic region of Greece as the Greek language had become the language of scholarship throughout the Hellenistic world, in large part delimited by the boundaries of the Macedonian Empire established by Alexander the Great. The most prominent and influential practitioner of Greek astronomy was Ptolemy, whose treatise Almagest shaped astronomical thinking until the modern era. Most of the most prominent constellations known today are taken from Greek astronomy, albeit via the terminology they took on in Latin.

In classical, medieval, and Renaissance astronomy, the Primum Mobile was the outermost moving sphere in the geocentric model of the universe.
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural philosophy described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle. In his work Physics, Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, both living and inanimate, celestial and terrestrial – including all motion, quantitative change, qualitative change, and substantial change. To Aristotle, 'physics' was a broad field including subjects which would now be called the philosophy of mind, sensory experience, memory, anatomy and biology. It constitutes the foundation of the thought underlying many of his works.

The theory of impetus is an auxiliary or secondary theory of Aristotelian dynamics, put forth initially to explain projectile motion against gravity. It was introduced by John Philoponus in the 6th century, and elaborated by Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji at the end of the 12th century. The theory was modified by Avicenna in the 11th century and Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī in the 12th century, before it was later established in Western scientific thought by Jean Buridan in the 14th century. It is the intellectual precursor to the concepts of inertia, momentum and acceleration in classical mechanics.

Historical models of the Solar System first appeared during prehistoric periods and are being updated to this day. The models of the Solar System throughout history were first represented in the early form of cave markings and drawings, calendars and astronomical symbols. Then books and written records became the main source of information that expressed the way the people of the time thought of the Solar System.
The existence of extraterrestrial life is a scientific idea that has been debated for centuries. Initially, the question was purely speculative; in modern times a limited amount of scientific evidence provides some answers. The idea was first proposed in Ancient Greece, where it was supported by atomists and rejected by Aristotelians. The debate continued during the Middle Ages, when the discussion centered upon whether the notion of extraterrestrial life was compatible with the doctrines of Christianity. The Copernican Revolution radically altered mankind's image of the architecture of the cosmos by removing Earth from the center of the universe, which made the concept of extraterrestrial life more plausible. Today we have no conclusive evidence of extraterrestrial life, but experts in many different disciplines gather to study the idea under the scientific umbrella of astrobiology.














