Description
Leaves with blades about as long as the winged petioles and tapering into them, long tapered at the tip, with the upper pair of veins parallel to the midrib and leaving it at some distance from the base, 30 – 45 cm long. Blades longly oval, on both ends regularly narrowed, or lanceolate with 3 - 5 veins, without pellucid markings, 17 – 25 cm long x 2.5 – 5 cm wide.
Stem erect, along the whole length distinctly alate (3 - winged), 30 – 70 cm long. Inflorescence usually racemose, rarely branched in the lower whorl, having 6 - 13 whorls. Bracts longer than the pedicels with flowers, 1.5 – 2 cm long having 19 - 21 distinct ribs. Flowers sessile or subsessile on pedicels 2 – 4 mm long. Sepals about 5 mm long, with usually 18 ribs, corolla white. Aggregate fruit globular, 5 – 7 mm in diameter. Stamens usually 18, anthers 1.5 mm long, as long as the filaments. Achenes 2.5 – 3 mm long x 1 - 1.2mm wide, distinctly ribbed only in the lower part of the body, the upper third without ribs, lateral glands absent.

Pachypodium brevicaule is a species of plant that belongs to the family Apocynaceae.

Echinodorus cordifolius, the spade-leaf sword or creeping burhead, is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismatales. It is native to Mexico, the West Indies, Central America, South America and the southeastern United States.

Echinodorus horizontalis is a species of plant in the Alismataceae family. It is native to northern South America.
Echinodorus tunicatus is a species of aquatic plants in the family Alismataceae.

Echinodorus longiscapus is a perennial, aquatic plant of the Alismataceae, native to South America. It is cultivated as a pond or aquarium plant.

Echinodorus macrophyllus is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Brazil and Bolivia.

In Rataj's taxonomy Echinodorus ovalis is in Section Cordifolii, Subgenus Echinodorus. It is related to Echinodorus cordifolius and listed by some authorities and importers as a synonym of that species, e.g. E. cordifolius 'ovalis'.

Echinodorus subalatus is a species of aquatic plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Cuba, Mexico, Central America, Guyana, Venezuela, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. It is found naturally growing in mud by the side of streams.

Echinodorus uruguayensis or Echinodorus osiris is a plant species in the Alismataceae. It is native to South America.

Echinodorus berteroi is an aquatic plant species in the Alismataceae It is native to the southern and central parts of the United States, as well as Central America, the West Indies, and South America as far south as Argentina.

Echinodorus bracteatus is a species of plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia and Ecuador.

Echinodorus grandiflorus is a plant species in the Alismataceae. It is native to Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, Argentina, Venezuela and Florida.

Nepenthes andamana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Phang Nga Province, Thailand, where it grows near sea level in coastal savannah and grassland. It is thought to be most closely related to N. suratensis.
Albidella is a genus of plants in the Alismataceae. At the present time, four species is known. In 2014(when this page is first made),One is Albidella nymphaeifolia, formerly called Echinodorus nymphaeifolius. It is native to Cuba and the Yucatán Peninsula.
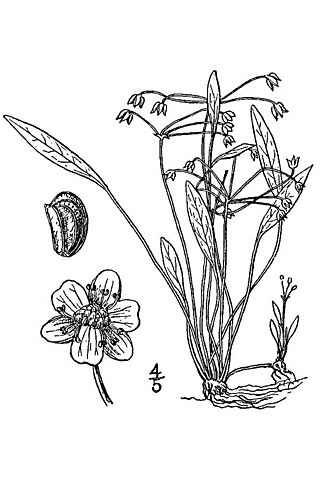
Helanthium tenellum, the pygmy chain sword, is a species of plants in the Alismataceae. It is native to the eastern United States, southern Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America

Mairia crenata is a perennial herbaceous plant of mostly 2–15 cm (1–6 in) high that is assigned to the family Asteraceae. It has a woody rootstock of up to 5 cm (2 in) long, from which brown, fleshy roots develop. The five to eighteen, hard and leathery, spoon-shaped leaves are in one to three rosettes, have a distinct main vein, blunt or pointy tip, often dark red or blackish margins with rounded teeth and a ½–2 cm (0.2–0.8 in) long stalk-like foot, often initially somewhat woolly hairy, on particularly the lower surface and the main vein, but this is easily rubbed off the shiny surfaces. Each rosette produces mostly one, sometimes up to four, mostly rusty or whitish woolly hairy, brown or dark red inflorescence stalks, usually 1½–15 cm long, each with two to eight, initially woolly, line-shaped to oval bracts, the lowest up to 3 cm (1.2 in), decreasing size further up, and carrying mostly one, rarely up to three flower heads. The flower heads have a bell-shaped involucre with about 40 bracts, sixteen to thirty three violet to white ray florets of about 1¼–1⅞ cm long, and many yellow disc florets. The species flowers anywhere between February and December but only after a fire has destroyed the overhead biomass or serious disturbance. It is an endemic species that is restricted to the Eastern Cape and Western Cape provinces of South Africa.
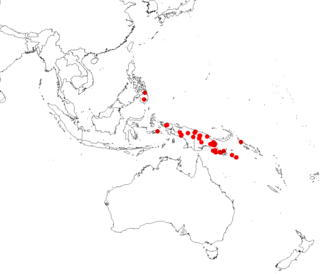
Parsonsia curvisepala is a woody vine of the family Apocynaceae, found in Malaysia, New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands, and Sulawesi. This species is second only to Parsonsia alboflavescens in its variability and wide geographic distribution.

Mairia coriacea is a perennial plant assigned to the family Asteraceae. It has broad, tough and leathery, evergreen leaves. These have a narrowed foot and an entire margin or a few shallow, irregular teeth. They grow in a rosette directly from the rootstock. The plant produces flower heads with one whorl of white to mauve ray florets around many yellow disc florets, with one or few on top of a dark reddish, woolly stalk. Flower heads appear after the overhead vegetation burnt down, often destroying the leaves in the process. It can be found in the southern mountains of South Africa's Western Cape province. It is called leather leaves in English.

Mairia petiolata is a tufted, variably hairy, perennial plant of up to 15 cm (6 in) assigned to the family Asteraceae. Its leaves are in a ground rosette, and have a stalk of mostly 2–5 cm long and an inverted egg-shaped to elliptic, 61⁄2–9 cm (2.6–4.6 in) long and 2–3 cm wide leaf blade, with a toothed margin. It mostly has two flower heads at the tip of the branches of each erect, dark reddish brown scape. The flower heads have a bell- to cup-shaped involucre that consists of 20–24, purplish, overlapping bracts in 3–4 whorls. These protect 12–16 pink, ray florets, surrounding many yellow disc florets. This species was only seen flowering once, in December. It is known from one location in the Langeberg, Western Cape province of South Africa.

Mairia hirsuta is a tufted perennial, herbaceous plant of up to 40 cm high, that is assigned to the family Asteraceae. Most of its narrow to broad elliptic or inverted egg-shaped leaves are part of the basal rosette, have margin that is rolled under, with rounded or pointy teeth or with some peg-like extensions, lightly woolly on the upper surface and densely woolly on the underside, but always the green remains visible. Flower heads have been found from July to November, mostly after a fire or when the soil has been disturbed. The species can be found in the southern mountains of the Western Cape province of South Africa.


















